Rejection reaction
introduction
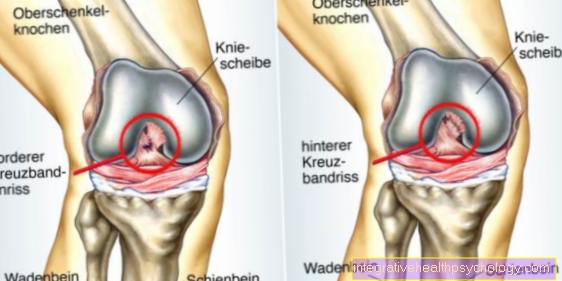
If our body's immune system detects foreign cells, it activates a wide variety of mechanisms to protect against the mostly unwanted intruders. Such a reaction is desired when it comes to pathogens such as bacteria, viruses or fungi. However, a rejection reaction is not desirable when it comes to an organ transplant. In the worst case, the exogenous cells are destroyed and the transplanted organ loses its function. However, the rejection can be prevented. For this purpose, drugs are used to suppress the natural reaction of the body's own defense system - this is known as immunosuppression. The corresponding drugs are called immunosuppressants.
A distinction is made between hyperacute, acute and chronic rejection reactions. A hyperacute reaction is already taking place a few minutes to hours after the surgery. The acute rejection reaction refers to the immune response in the first days and weeks after the transplant. Thanks to regular checks, this can usually be treated well. The chronic reaction on the other hand, it takes place more slowly and only leads to permanent damage to the organ over time. The acute reaction is often accompanied by typical symptoms, while chronic rejection can remain clinically normal for a long time.
diagnosis
In order to diagnose a possible rejection reaction in good time, it is important to be certain Values checked regularly at short intervals become. These include the Blood pressure, the temperature, the body weight, the fed Amount of liquid and the eliminated Urine volume. Furthermore, drug therapy should be reviewed. In this way one tries to recognize possible immune reactions in time or to prevent them.
If a rejection reaction is suspected, additional tests will be carried out. In addition to the physical, an examination of the Laboratory parameters and urine with urine stix, urine sediment and urine culture. In addition, apparatus-based examination methods are used. These include Ultrasonic of the transplanted organ and possibly a roentgen or one Magnetic resonance imaging. Furthermore, a biopsy, a tissue removal with a needle, carried out to histologically confirm the rejection reaction.
Read more about this topic here: biopsy
therapy
The therapy of the acute rejection reaction takes place with help immunosuppressive drugs and can be treated well if recognized early. Usually will high-dose cortisone for a period of three days. Furthermore, you increase the already existing immunosuppression and supplement it individually with another drug to suppress the immune system. If the rejection reaction proves resistant to cortisone, come special antibodies against T cells for use. This form of therapy should not be maintained for more than 3 to 10 days.
As part of a chronic rejection reaction plays the adequate dosage an important role. On the one hand, the immunosuppressive drug should be dosed so high that the cells of the transplanted organ are not destroyed, on the other hand, the body's own defenses must not be completely suppressed. A simple cold could have far-reaching consequences if the immune system is not functioning.
Immediately after the procedure is a higher dosage necessary to prevent subacute and acute rejection reactions. During this time, the immune system is particularly weak and susceptible to infection with bacteria, viruses or fungi. Strict hygiene measures should be observed here. In general, the immunosuppressive therapy has to last a lifetime.
forecast
The prognosis after organ transplantation promises a Higher life expectancy than leaving the original, more and more functionless organ.
About 60% of heart transplant patients live with the donor organ for more than ten years. Lung transplant recipients also benefit from a longer life expectancy of a few years. you experience often a significantly improved physical and mental quality of life. The prognosis after liver transplantation promises a function rate of the liver of 80% after 5 years and of 70% after 10 years. The function rate after one year with kidney transplantation is 85%. On average, the function of the transplanted kidney lasts 15 years. The prognosis after stem cell transplantation has been shown to prolong life in the context of certain types of cancer. This is especially true for forms of acute leukemia.
General it is true that the prognosis strongly depends on the following factors: Basic and concomitant diseases, General condition and Secondary diseases. A chronic rejection reaction cannot be completely prevented despite lifelong immunosuppressive therapy. The persistent, highly inflammatory processes can lead to a deterioration in organ function over time.
causes
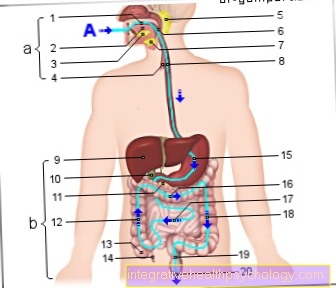
Our the body's immune system protects our body from foreign substances by destroying and killing invaders. The so-called play a special role in this context T cells. They belong to the group of white blood cells and have special surface proteins (Antigens). Antigens are receptors that Recognize characteristics of other cells and bind. The T cells are not only activated in this way, but also by other signals from the foreign substance. Shed the activated T cells certain messenger substances which in turn pass on the impulse to other cells of the immune system to fight the exogenous substance. So-called Cytokines contribute to Preservation and enhancement of the immune response at, during Chemokines a kind of Attractant represent for more inflammatory cells.
Immunosuppressive drugs intervene in this form of communication between the immune cells and prevent the natural answer on the exogenous cells.
Liver transplant rejection reaction
A Liver transplant can with some typical complications accompanied. In addition to the usual risks of a surgical procedure (wound infection, development of a thrombosis), the primary inoperability of the transplant liver after the procedure is one of the most critical early complications. In the worst case, this situation results in the emergency of a new transplant.
As part of a Rejection reaction occur certain Warning signals that should be taken seriously. These include clear exhaustion, physical Feeling weak, Loss of appetite and Increase in body temperature above 37.5 ° C for a few hours. Other typical symptoms are stomach pain, light brown stools and a dark colored urine. Often a Gthe color of the skin and the whites of the eyes (Jaundice) determine.
Rejection reaction after kidney transplantation
The acute rejection reaction after Kidney transplant is associated with typical symptoms that indicate a Deterioration in kidney function and indicate the activity of the body's immune system. Which includes exhaustion, Increase in body temperature to over 37.5 ° C for several hours, Loss of appetite, reduced urine output and Edema formation (Water retention in the tissue) and pain in the kidney area. A chronic rejection reaction, on the other hand, can remain clinically normal for a long time.
Regular checks of laboratory parameters as well Urine examinations play an important role because an increasing loss of function can be diagnosed more quickly in this way. First the Tissue extraction by biopsy then secures the suspected diagnosis a rejection reaction. Often it is an immunological damage to the kidney corpuscles, as a result of which more protein is excreted in the urine.
Lung transplant rejection reaction
Next to one increased risk of infection as a result of immunosuppression, patients learn Lung transplant some complications, most of which are well treatable. Most often, a constriction forms at the junction between the patient's airway and the donor lung (Stenosis). This usually happens within a period of between two and six months. The narrowing is widened with the help of a balloon or stent implantation.
Another complication is that acute rejection reaction after lung transplant. It typically shows the following Symptomswhich are to be interpreted as warning signs: Exhaustion, tiredness, a body temperature of more than 37.5 ° C over several hours and respiratory complaints. The latter includes persistent shortness of breath despite little or no physical exertion and persistent coughing.
Is the Suspicion close to a rejection reaction, immediately become one X-ray examination and a Bronchoscopy for the extraction of lung tissue by means of biopsy carried out. If the suspicion is confirmed, the rejection reaction can usually be treated without any problems.
Heart transplant rejection reaction
One to two weeks after the Heart transplant particularly strict hygiene rules must be observed as the patient Immunosuppressants received in high dosage. A few months after the procedure, the risk of rejection is greatest. The risk of a chronic rejection consists primarily in the increasing narrowing of the coronary arteries due to deposits and excessive cell growth.
Tiny ones Tissue sampling on the inside of the muscle, called biopsies, are taken at the beginning carried out closely. The first biopsy is done a few days after the procedure. About after a year are the coronary vessels in the Cardiac catheter examined. In addition to the specially carried out control measurements (weight, blood pressure, temperature, etc.), the family doctor regularly checks the heart function using ultrasound, blood tests and EKG.
The following Symptoms should be taken seriously: Feeling of exhaustion, quick fatigue, Increase in body temperature above 37.5 ° C for a few hours, Shortness of breath with little physical exertion, Edema formation (Water retention in the tissue) and as a result rapid weight gain as well Cardiac arrhythmias.
Rejection reaction after stem cell transplantation
Among the most common complications after Stem cell transplant counting Infections as a result of immunosuppressive drugs and so-called Graft-versus-host disease, in which the donor's immune cells turn against the recipient's cells. There is an increased risk especially in the first year, especially in the first six months after the procedure.
A Rejection reaction in the usual sense is against it rarely observed. It is associated with a lack of growth in the transplanted cells and a reduced number of cells in the blood. Continues to occur more frequently unspecific fever on.
Come in prophylactic and therapeutic use immunosuppressive drugs for use. If this treatment is not sufficient, a new transplant may be attempted.