Allergic reaction
definition
An allergic reaction is a reaction of the body to a certain non-infectious reagent - an allergen - which it recognizes as foreign and to which it reacts by releasing certain substances. These include substances that activate the immune system and inflammation mediators, which cause various symptoms in the affected person. Allergic reactions can be subdivided into different subtypes and can be mild to life-threatening.

causes
An allergic reaction is usually caused by a general predisposition to be overly sensitive to foreign, actually harmless substances.
Upon first contact with the allergen, the body then forms antibodies against this substance, since it classifies it as foreign and dangerous. This phase is also called sensitization and does not itself trigger any symptoms. However, if there is subsequent contact with the allergen, an allergic reaction with itching, wheals, reddening of the skin, a drop in blood pressure and life-threatening cardiovascular weakness can result. The extent of the allergic reaction depends on the extent of the release of inflammatory substances or the extent of the physical reaction at the cellular level. This basic tendency to develop allergies is also known in medicine as Atopy tendency. Other factors that could contribute to the development of allergies are controversial. The general disposition seems to play an important role, however.
Allergic reaction to an antibiotic
Antibiotics are medicines used to treat bacterial infections that are particularly common in causing allergic reactions. The penicillin allergy is particularly common. After taking the antibiotic, affected people usually develop a pronounced rash with excruciating itching and wheals. In the case of immediate reactions, these symptoms appear soon after taking the drug, usually within the first hour.
However, there are also delayed reactions in which the first symptoms only show up after a few hours or even days. The leading symptom is usually a so-called drug eruption - a pronounced rash that often only heals after a few days. This can also take on different degrees of expression, including life-threatening forms. If an allergic reaction to an antibiotic is found, it should not be given if possible. This is especially true if you have had severe allergic reactions. Affected people should tell any doctor treating them of the allergy so that they do not prescribe the wrong antibiotic.
Read more about this under Amoxicillin allergy.
Concomitant symptoms
The symptoms that accompany an allergic reaction are varied. Itching and reddening as well as wheals on the skin, watery and itchy, reddened eyes, a runny nose and frequent sneezing are particularly typical. Coughing can also occur. The mucous membranes swell when there are more severe allergic reactions. This can lead to shortness of breath and even suffocation. Very severe allergic reactions go hand in hand with fluid accumulation in all tissues and cause circulatory reactions with a drop in blood pressure and even circulatory failure. These symptoms are life threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Read more about this under Anaphylactic shock
Food allergies can also cause diarrhea and abdominal pain. General symptoms of an allergic reaction are also general fatigue and reduced performance.
Please also read:
- You can recognize histamine intolerance by these symptoms
- Food allergy
Wheals
Allergic reactions are often associated with the formation of wheals on the skin. Mast cells, which are located in the upper layers of the skin and react to substances with which the human body comes into contact, play an essential role in the development of these wheals. If these cells identify an allergen as foreign to the body, they release special substances - including histamine and leukotrienes. These substances cause fluid to escape from nearby blood vessels and accumulate under the skin. This tissue fluid is visible from the outside as a wheal. Wheals usually go away on their own after a short time without the need for treatment.
Read more about this under Wheals on the skin
itching
The itching that typically occurs in allergic reactions is also related to the activation of mast cells in the skin. Mast cells release histamine and other messenger substances that irritate the nerve fibers in the tissue and the surrounding cells. Itching is the result. In addition, the messenger substances released stimulate further mast cells to also release their histamine into the environment. This cascade leads to an exponential release of signal substances into the environment of the cell and causes the unpleasant symptoms. The itching continues until all mast cells in the affected area have released their messenger substances and these have been broken down again in the tissue.
Read more about this under Itchy skin - that's behind it
diagnosis
The diagnosis of an allergic reaction is usually easy to make. Often the person affected can already identify possible triggers - for example, with watery and itchy eyes after a long walk through blooming meadows and fields. The description of the typical symptoms such as itching, reddening and wheal formation through to shortness of breath and circulatory reactions usually leads to the correct diagnosis. It is then important to identify the exact trigger of the allergic reaction, which is not always easy. For example, an allergic reaction after a certain meal cannot simply be traced back to a certain food contained. A closer examination of the facts may then be necessary.
What to do?
Depending on the severity of an allergic reaction, it requires a different therapy.
Slight local reactions to an allergen that only cause reddening of the skin and itching usually do not require any therapy and disappear on their own within a short time if the trigger is avoided. Cooling and antiallergic gels can help alleviate symptoms.
However, if there are more severe symptoms that also include systemic reactions, such as shortness of breath, drop in blood pressure, rashes and itching all over the body or extensive swelling, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible. Clinical monitoring of the affected person must then be ensured in order to be able to react directly to dangerous symptoms such as shortness of breath and drop in blood pressure. Patients are then given anti-inflammatory drugs such as prednisolone, which are designed to curb the body's excessive immune response. In addition, fluids are administered to stabilize the circulation. When the symptoms have subsided and the patient has recovered, they can go home.
Read more about this under Therapy for an allergy
In this context, Vividrin® eye drops are used to treat allergic reactions. Vividrin® eye drops is a drug that is used to treat allergy-related symptoms in the eye. Read more on the subject below: Vividrin acute eye drops
Duration
The duration of an allergic reaction depends largely on its extent. Local reactions with reddening of the skin, itching and swelling, which are limited to a rather small part of the body, usually disappear on their own a few hours after contact with the allergen has ended.
However, if it was a severe allergic reaction that might even necessitate hospitalization, it can take a few days to weeks for the body to fully recover. The person's previous illnesses and age also influence how quickly they will recover from a severe allergic reaction. However, the classic, mild allergic reactions usually do not last long, so that complete freedom from symptoms can be expected after a few hours to days.
Differentiation according to location
On the skin
Allergic reactions on the skin are the most common manifestation of hypersensitivity. The most common contact allergies are caused by direct skin contact with a certain substance. The body recognizes this substance as foreign and initiates an immune reaction against it. This shows up on the skin as redness, wheals and itching. Blisters can also appear. If contact with the triggering substance is broken off, the local reaction usually disappears again within a few hours.
Read more about this under Rash from an allergy
Response to a mosquito / insect bite
Allergic reactions to mosquito or insect bites are among the most common allergic reactions, as insect venoms are among the most potent allergens. Up to a quarter of the population shows increased local reactions to insect bites that go beyond the small puncture site. The symptoms usually appear a short time after the bite and, like other allergic reactions, can range up to life-threatening shortness of breath and cardiovascular failure. Overall, these severe complications appear to be more common in insect bite allergies than in other allergies. In these cases a doctor should be consulted immediately.
The advantage of allergies to insect venom is that there is the possibility of so-called desensitization. To do this, the person affected is injected with the insect venom in a strong dilution under the skin. The dose is initially increased with each injection and given once a week. The patient is later given another injection once a month over a period of three to five years. In this way, very effective vaccination protection can be achieved, which, depending on the insect venom, offers a success rate of 80-95%. For people who have severe allergic reactions to insect venom, this is an optimal way to avoid them.
Read more about this under Inflamed insect bite - what to do and when is it dangerous?
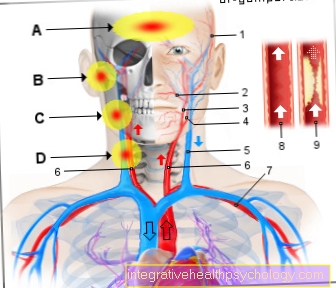
In the face
Allergic reactions can manifest themselves all over the body - including the face. The eye and nasal mucous membranes are particularly often affected by the reaction. The eyes are red and begin to water and itch. The nose is running or feels very dry. The skin on the face can also be affected. Redness, wheals, and itching can occur.
In the case of allergic reactions due to contact with a certain substance - for example a face cream - the symptoms often appear soon after the allergen is applied and do not improve as long as contact with the trigger persists. However, there are also late reactions to allergenic substances that only appear after a long time.
The risk of allergic reactions in the head and neck area is that the person's airways can swell. This is basically possible with any allergic reaction. Due to the spatial proximity, however, this danger is particularly present in the case of allergic reactions in the facial area. If eyes and lips swell and symptoms of shortness of breath occur, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
Read more about this under
- Rash On The Face - What Is The Cause?
- Swelling of the face
Reaction to a tattoo
Tattoos can cause allergic reactions. The colors used consist of mixtures of substances, among which the individual substances are potentially allergenic. Usually the symptoms of the allergic reaction are limited to the tattoo and its immediate surroundings, but if the reaction is pronounced, they can also occur over a large area or even trigger systemic symptoms such as shortness of breath and a drop in blood pressure. Much more common, however, is the local allergic reaction, which manifests itself as reddening, itching, and wheals or blisters on the affected areas of the skin. Should these symptoms persist, the tattoo should be removed. Other therapies are not promising, as the color that is introduced remains in the skin and continues to irritate the immune system. Laser therapy can remove a tattoo in several sessions.
Read about this too Tattoo Removal - The Best Methods For Tattoo Removal
Allergic reaction to alcohol
An allergic reaction to alcohol is very rare.If typical allergy symptoms occur after consuming alcoholic beverages, a certain ingredient in the drink is usually the cause of the symptoms, but not the alcohol itself. Wine, for example, contains histamine, which is also responsible for the development of typical symptoms in allergic reactions. If reddening of the skin, headache, diarrhea or the like occurs after drinking wine, it is usually a histamine intolerance - not an allergic reaction.
Read more on this topic at: Histamine intolerance
The most common allergenic ingredients in beer are malt and hops, wheat, barley and oats. Other alcoholic mixed drinks such as cocktails consist of various alcohols and juices, each of which can be potentially allergenic in itself. It is therefore important to pay attention to whether the consumption of these ingredients shows allergy symptoms in a context other than alcoholic beverages. In this way, the allergenic agent can be identified and avoided in the future. In principle it is possible that there is an allergic reaction to the alcohol itself; However, allergic reactions to other ingredients in the drinks are much more likely. If the same symptoms are found when consuming all types of alcohol, then alcohol itself could actually be the cause of the symptoms. An allergy test with a dermatologist may help identify the cause.









.jpg)