Allopurinol
definition
The drug known under the name Allopurinol belongs to the group of uricostatic agents and, as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor (inhibitor), is able to influence the breakdown of organic purine bases to form uric acid.
It is generally used to treat chronic gout and is one of the most effective drugs in this field, and due to its tremendous therapeutic success, it is hard to imagine the drug market without it.
Gout is an extremely painful joint disease (gout attack) triggered by increased uric acid concentration and the associated storage of crystallized salts and urate in the joints.
Areas of application
Allopurinol is used in everyday medical practice for the treatment of a wide variety of diseases and, due to its high therapeutic success, it is no longer possible to imagine the pharmaceutical market without it.
In patients with an increased Uric acid level in the blood (primary hyperuricemia > 8.5 mg / dl), allopurinol can help prevent Gout diseases are used.
Since gout is triggered by the increased uric acid concentration and the associated storage of crystallized salts and urate (uric acid) in the joints, gout can be avoided by lowering the uric acid concentration in the blood prevent.
Even with a secondary one, i.e. triggered by various previous illnesses and / or medical therapies Hyperuricemia, Allopurinol is used successfully in many cases.
In addition, patients with pre-existing urate nephropathy can be effectively helped by taking this medicine. At a Urate nephropathy it is a hereditary disease in which uric acid is stored in the kidney tissue and there too Uric acid stones (Shape of the kidney stone) is implemented.
The uric acid stones are mostly deposited in the urinary tract.
Also, allopurinol can be used to prevent Calcium oxalate stones (Form of Kidney stone) can be used.
For patients who have a Renal failure this drug must not be used. Likewise, during the pregnancy and the subsequent Lactation on an intake of Allopurinol be waived.
Mode of action
Allopurinol has an inhibiting effect on the breakdown of the organic purine base to uric acid. This inhibiting effect is mediated by a throttling of the enzyme Xanthine oxidase.
The drug takes care of this mechanism of action Allopurinol for a huge cut in Uric acid concentration in the bloodwhich in turn has the advantage that less uric acid has to be metabolized in the tissue.
The starting materials (precursors) of uric acid can easily be transferred to the kidney be eliminated.
Allopurinol will in most cases with an existing one Hyperuricemia (increased uric acid concentration in the blood) or after a Attack of gout used.
In addition, this medicinal product is extremely successful in the Therapy of gouty nephropathies or Uric acid stones.
Unwanted side effects
Among the most frequently recorded unwanted side effects from Allopurinol belong above all allergic skin reactionswhich are characterized by:
- Redness
- severe itching
and - Blistering
to make noticable.
In addition, some patients report in connection with a Allopurinol intake about the appearance of nausea and Vomit.
Education too some blood cells (leukopenia) can be negatively influenced by the active ingredient, it can im Trains deficiency symptoms occur during use.
Since kidney stones have developed in many patients, it is strongly recommended that they normal drinking amount to increase during the therapy phase because a lot Hydration greatly reduces the risk of kidney stones forming.
More unwanted side effects are:
- Damage to the liver
and - Diseases of the Kidneys
Allopurinol should therefore not be taken or only under strict medical supervision in the case of corresponding previous illnesses.
Interactions
The Medicinal Allopurinol can have the effect of countless others Medication strongly influence, for this reason it must be clarified with the attending physician before taking it, whether and how other necessary medication must be adjusted.
Allopurinol has a reinforcing effect on the effects of various medicines to prevent blood clotting (anticoagulants). Particular attention should therefore be paid to the necessary intake of so-called coumarins (warfarin, Marcumar).
In the course of an application of Allopurinol should be the daily dose of the Anticoagulants be reduced.
Also, the effect of Probenecid amplify. Probenecid is a drug which (just like allopurinol) is used to lower excessively high urea concentrations in the blood and therefore the Therapy for gout serves.
Particular caution is also required in patients with Chlorpropamide, one Sulfonylureawho to Diabetes therapy is used.
The effectiveness of this medicinal product is also increased by taking allopurinol at the same time.
Certain anti-epileptic drugs (especially Phenytoin), which serve to inhibit the excitability of nerve cells and in this way to treat Epilepsies can be used, must urgently be re-dosed when allopurinol is administered.
Stevens Johnson Syndrome
Although allopurinol has an important position in medicine and has achieved great success in the treatment of gout, undesirable drug effects (side effects) cannot be ruled out.
When prescribing this drug, the attending physician must always weigh up whether the clinical benefit outweighs the risk of side effects.
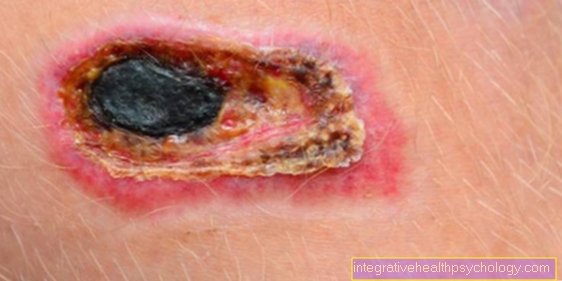
A possible complication in connection with the use of allopurinol is the occurrence of the so-called Stevens-Johnson syndrome. According to studies, allopurinol is the most common cause of this disease (Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a severe drug reaction that manifests itself primarily on the skin and is rare.
In the course of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the epidermis (top layer of skin) detaches on up to 10% of the body surface.
Read more about this: Stevens Johnson Syndrome








.jpg)