Signs of tuberculosis
What are the signs of tuberculosis?
The tuberculosis Infection with the pathogen goes unnoticed in the majority of cases, rarely there are uncharacteristic signs such as to cough or elevated temperature (fever). Even if the bacteria manage to establish themselves permanently in the body, this is only noticed in rare cases by the patient.
Only when the tuberculosis pathogens spread when the immune system is weakened, possibly years later, can a variety of signs appear. The type and severity of the tuberculosis signs depends on which organ is affected in this situation, also known as secondary infection. The most common are the lungs (60%,), the genitourinary system (urinary tract and genital organs, 30%) and joints (10%). Involvement of the meninges is particularly dangerous because this is particularly fatal (meningitis).
In some cases, especially if the immune system is poor and the course is severe, the disease can be called a B symptoms cause. These include signs of severe unintentional weight loss, increased temperature, fatigue and night sweats. These signs are an expression of a consuming disease and the body's immune response directed against it. Ultimately, the German name for tuberculosis, “consumption”, is based on this.
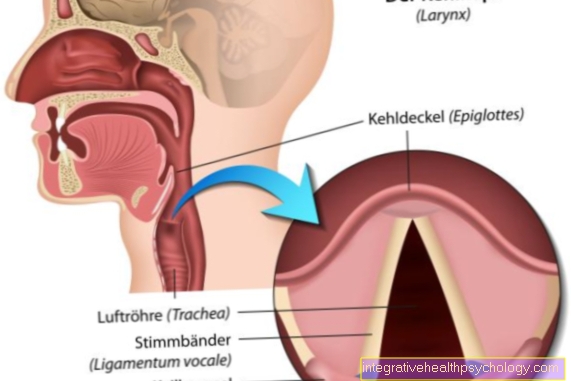
Other possible symptoms are prolonged coughing (chronic cough) (with or without sputum), difficulty breathing and coughing up blood. Ultimately, however, these signs are not very specific and therefore not very meaningful, as they can occur in almost all lung diseases.