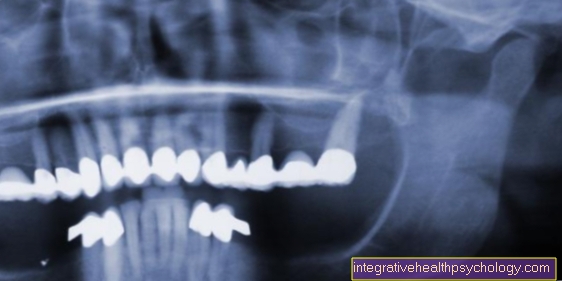
Arthroscopy of the wrist
introduction

The Arthroscopy is a great way to relieve pain and problems in the wrist chronic and acute type to get to the bottom.
Arthroscopy is an alternative to imaging such as roentgen, Computed Tomography (CT) and MRI of the hand (Magnetic resonance imaging).
The advantage of arthroscopy is that Lesions and problem points shown more precisely can be.
Disadvantages are that the arthroscopy in contrast to the imaging method invasive procedure represents. The patient must be in a surgical intervention in a sterile environment one anesthesia (Anesthesia) while the imaging only takes a brief moment with no major additional effort.
Arthroscopy is also a much more costly procedure. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that the procedure requires practice and professional experience on the part of the doctor, and on the other hand, several devices and instruments are needed in the operating room during the course of the procedure.
Another great advantage is that arthroscopy is not only used for diagnosis, but also for treatment can be used. So she has the imaging procedure a significant step ahead.
indication
Today is the Arthroscopy of the wrist only rarely used as a purely diagnostic measure. Rather, it usually takes place in the course of a Diagnostics with surgery instead of.
Arthroscopy is used for treatment acute wrist problems, for example after various trauma (broken wrist).
In the course of arthroscopy, a Reduction (Return) and fixation the fracture.
Arthroscopy can often show accompanying injuries in the fracture area that could not have been shown using imaging techniques.
Another place of use are chronic wrist discomfort (for example Wrist osteoarthritis).
Patients often come for arthroscopic treatment after a long period of time, because the conventional methods could not achieve a clear diagnosis or remedy the problem.
Preparation for arthroscopy
In the course of arthroscopy, one usually finds one axillary plexus anesthesia instead of. This means that the nerve cords that pull into the arm via the shoulder-armpit area are already there be anesthetized in the armpitso that the patient has no more sensation in the arm from the shoulder down.
If it is already clear in advance that this is a longer and more complex process, then an anesthetic can also be used for the patient intubated becomes.
One advantage of axillary anesthesia is that the Patient still able to communicate and can follow the arthroscopy if interested.
Furthermore, depending on the reason for the arthroscopy, the affected arm will either be bloodless or Tourniquet applied. In the case of tourniquet, the Prevents blood from flowing into the arm, for example by inflating a blood pressure cuff on the upper arm to a pressure that reduces the systolic blood pressure exceeds. The arm is thus in a state of anemia (Ischemia) offset. The reason for this is that it can prevent blood loss in the area of the surgical site. Another advantage is that the Operation area remains free of blood and so for the doctor more visible is. The tourniquet is i.a. used for chronic wrist diseases.
The blood evacuation is used when there is a fresh trauma that is to be treated by arthroscopy. During this process, a tourniquet is also created using a cuff on the upper arm. But before this cuff is fully inflated, the blood in the arm is squeezed out. This is done by unwinding the arm tightly. When this wrapping process is finished, the cuff is completely inflated and the arm remains in a bloodless state.
In addition to the anesthesia, there is also a special positioning of the patient instead of. The main concern here is that a pull is exerted on the joint to be arthroscoped. The pull is necessary so that the joint space is expanded. This is the only way for the surgeon to get an adequate view of the joint. This train is caught with the help of girl catchers. Extension sleeves generated. This is a braided tube that is closed at the top. With the open side, the pipe is pushed onto the finger and tightened. There is a hook on the closed tip that can be used to pull the extension sleeve. Such extension sleeves are attached to the index, middle and ring fingers, and then tightened in a vertical or horizontal position. Which position is chosen depends on the reason for the arthroscopy and the attending physician.
Appointment with a hand specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me at:
- Lumedis - orthopedics
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, appointments can only be made with private health insurers. I ask for understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Lumedis - Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
The arthroscope
Used for arthroscopy of the wrist different instruments needed.
The first thing the doctor needs is one Arthroscope. This is a very thin tube (1.9 - 2.7mm diameter) through which he can see into the joint. Which arthroscope thickness is chosen depends on which joint is to be examined. The smaller the joint, the smaller the diameter of the arthroscope.
There is a so-called trocar on the arthroscope. This allows the atroscope to be introduced into the selected location. The tip with which the puncture was made can then be pulled out, and the optics along with the remaining channel Light source and camera be introduced.
At the optics there is an entrance to a Salt solution To inject into the joint, for example to flush the area to be examined clear. There is a so that the saline solution can be removed from the joint Access for suction also on site. The same route can be used that was used for the rinsing solution by using a distributor tap (Three-way cock) is connected. This can be used to alternately rinse and vacuum.
As a further option, the joint can be punctured at a second point and suction can take place over it.
The doctor does not look directly into the joint through the arthroscope; instead, the image is displayed via a small camera recorded and transferred to a computer screen. The arthroscopy can be recorded, viewed repeatedly and given to the patient as a film to take home.
Since arthroscopy is only used in rare cases as a purely diagnostic measure further instruments for surgical measures needed.
An important one of them is that Shaver. It is a rod that can be inserted through the arthroscope, and at the end of which there is a movable knife that the surgeon can control by hand and use to remove selected areas in the joint. Other instruments used are tactile hooks, forceps for grasping, scissors and punches for biopsies in miniature format.
Arthroscopy procedure
The wrist will mostly over the back of the hand arthroscoped. At the beginning there are often different Muscle tendons and Bony prominences marked so that the doctor can find his way more easily and there are fewer complications from injuring other structures.
The next step is using a syringe liquid in the joint injected. After 3-5ml a resistance should be felt, which is due to the filling of the joint space with the irrigation fluid. However, if there are instabilities, a larger amount of liquid is often injected until resistance is felt. This is due to the fact that the various joint spaces of the wrist are connected to one another in the event of instabilities.
Next, the syringe is removed and inserted at the puncture site with a scalpel 2-3mm cut and spread it open with blunt scissors.
Now the arthroscope with the trocar can be inserted, and then the above-mentioned instruments and tools can be connected and inserted.
Places of use on the wrist
The arthroscope can be introduced at various joint points on the hand.
In addition to the actual wrist between the forearm and the Carpal bones (Articulatio radiocarpalis), can also be a Arthroscopy of the smaller joints on the hand, such as the joint between the two rows of carpal bones (Articulatio mediocarpalis), the articulated gap between ulna and radius (Radioulnar articulation) and the metatarsophalangeal joints of the fingers between the metacarpal bones and the finger bones (Articulationes metacarpophalangeales).
For the smaller joints is especially careful and controlled proceed as this increases the risk of injuries to structures running there (e.g. nerves).
Possible areas of application for arthroscopy
With the help of arthroscopy, the Cartilage surfaces, bone and Band structures of the individual parts of the wrist presented and examined become.
An important point is that Representation of the inner layer of the joint capsule (Synovial membrane - Synovial membrane) and the Synovial fluid. Here is a possible Inflammation of the synovial membrane discovered and validated by taking samples.
Arthroscopy can also be used Injuries to the articular cartilage represent. Unstable cartilage parts can be cut out, roughened cartilage areas ground down and parts of the cartilage and bone drilled around Stem cells the opportunity to give the cartilage superficially to rebuild.
In addition, injuries and ruptures of the ligaments of the wrists can be detected and treated. Damage to the ligaments connecting the carpal bones can lead to instability in the wrist. In the course of arthroscopy you can Ligaments repositioned (brought into the correct position) and over seams linked again become.
Another area of application is Removal of ganglia in the wrist. Ganglia (fuselage) often arise as a result of excessive strain on weak points in the joint capsule on the back of the hand.
Arthroscopy is also used successfully for Treatment of fractures at the radius (spoke) and the scaphoid (Scaphoid).





.jpg)