External meniscus
Synonyms in a broader sense
lateral meniscus
English: meniscus
definition
The outer meniscus is - together with the inner meniscus and the cruciate and collateral ligaments - part of the knee joint. It improves the fit of the joint surfaces and ensures optimal pressure distribution of forces. Because it - in contrast to the inner meniscus - is not fused with the collateral ligament, it is less tensioned when moving and is therefore very rarely affected in the event of injuries.
Anatomy and function of the menisci
The Menisci of the knee consist of Fiber cartilage. They are within the Knee joint, which comes from the articular knots (condyles) of Thigh bone (Femur) and Shin bone (Tibia) and the Kneecap (Patella) is formed. When viewed from the front, they lie like two wedges in the knee joint, with the base on the outside and narrowing towards the inside. Viewed from above, they have an approximate C shape.
Due to the relatively small contact area between the upper and lower leg bones, which do not fit together perfectly (so they are incongruent) the menisci are necessary to the articulation To optimize (the interaction) of these two surfaces and to optimally distribute the strong forces that act here. So they lie as a kind of "Socket“On the tibial condyles (articular knots of the tibia). At diffraction in the knee joint they slide backwards up to one centimeter to return to their starting position when extended. This strong tensile and compressive loads explains the susceptibility (at least of the medial meniscus) to injuries.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
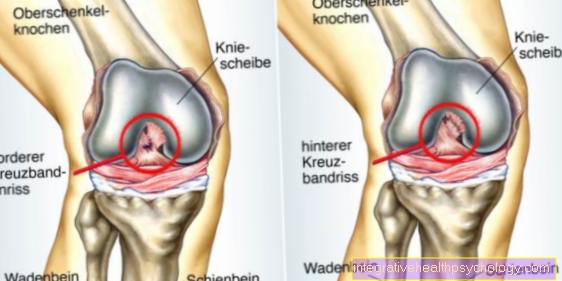
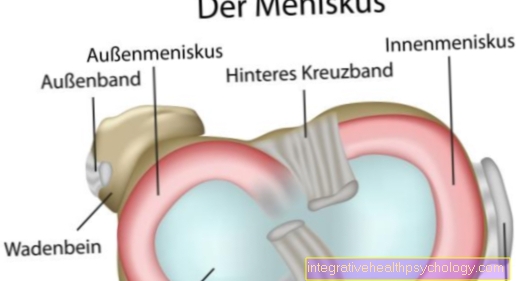
Illustration of the external meniscus
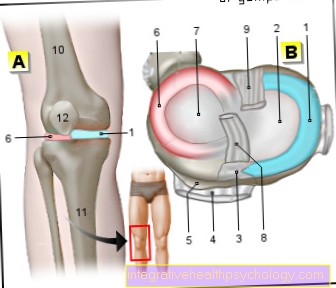
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Inner articular knot
(Shinb.) -
Medial condyle - Transverse ligament of the knee joint -
Lig. Transversum genus - Kneecap ligament -
Ligamentum patellae - Bursa - Bursa
- Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Outer joint nodules
(Shinb.) -
Lateral condyle - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Lig. Cruciatum anterius - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligamentum cruciatum posterius - Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Kneecap - patella
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Anatomy and function of the external meniscus
Of the External meniscus is stronger curved as the Medial meniscus, he has - except for an opening towards the inside - almost O shape. It lies on the outer half of the tibial plateau (tibial articular surface). There is that External meniscus on his Front horn and his Back horn in the Shin bone, more precisely in the area intercondylaris (i.e. the area between the articular cartilage).
In addition, the posterior horn of the external meniscus is covered by a ligament that Posterior meniscofmoral ligament (also Wrisberg ligament called), attached to the inner surface of the medial femoral condyle (inner articular cartilage of the thigh). So it pulls up diagonally and sits immediately behind the posterior cruciate ligament (Ligamentum cruciatus posterius) on.
The meniscus is fused with the joint capsule, but the outside is relatively thin. In addition, the outer meniscus - unlike the inner - is not connected to the collateral ligament (Ligamentum collaterale laterale) grown together. So it is much better movable. This also means that when it moves, it does not come under as much tension as the medial meniscus. So he's only in rarest Exceptional cases affected by injuries.
Blood supply to the external meniscus
Both Menisci are not at all in their central part and only sparsely permeated with blood vessels further outside. Therefore the outer - the area of the outer meniscus with the best blood supply also the name "red zone“.
The supply of the inner parts of the meniscus with nutrients happens mainly through the Joint capsule and the Synovial fluid (Synovia).
The poor blood supply causes that Lesions The menisci are slow to heal (damage). Ever further inside the damage lies, all the more worse the healing is taking place.
This is important in the care of Meniscal tears, because cracks in the outer zone due to the better blood supply basically means seam can be treated. This is less possible in the case of damage to the inner part of the meniscus; here it is more likely to be partial distance indicated by meniscus tissue.
Basically, meniscus tissue should only be removed if a suture is not possible, this is explained by the fact that Osteoarthritis risk of Knee joint the less meniscal tissue remains, the higher it is.
Clinical significance
Count Meniscus lesions among the most common injuries of the Knee joint, but this is almost always the Medial meniscus (often in combination with some of the ligaments of the knee joint). The external meniscus is injured only in the rarest of cases due to its anatomical conditions.
External meniscus torn

A minor injury in the external meniscus like a External meniscus tear is much rarer than for example one Medial meniscus tear.
The outer meniscus is sickle-shaped and can move more freely than the inner meniscus in the knee, which means that the outer meniscus can better avoid damage caused by an accident.
From a torn outer meniscus are special athlete (e.g. skiers, soccer players, handball players) because a quick turn of the knee is often enough to get a Meniscal injury sometimes also people with particularly knee-stressing jobs (e.g. tiler). But older people are also more susceptible to external meniscus injuries, as the cartilage substance becomes brittle and cracked over the course of life.
A torn outer meniscus causes drawing, stabbing pain in the knee area. Typically, the greatest pain is localized around the outer knee joint space, but often the exact pain area cannot be pinpointed.
The outer meniscus itself does not hurt because there are no nerve tracts in it. Occasionally there may be blockages in the knee because the torn outer meniscus often restricts mobility in the knee joint. There may also be problems with normal movements such as stretching the lower leg or squatting. The pain is often accompanied by knee swelling, which can occur within a few hours of the injury. The intensity and duration of the discomfort depends on the severity of the External meniscus tear from.
In older people and high-performance athletes, the external meniscus tear can also be degenerative (due to age / stress), which is often associated with no pain or discomfort.
Even small tears in the outer meniscus can lead to consequential damage, which is why appropriate therapy should be sought at an early stage.
The type of therapy chosen for a torn external meniscus depends on various factors such as age, physical activity and the extent of the symptoms.
Small tears in the outer meniscus can be caused by:
- Exercise therapy
- physiotherapy
- Electrotherapy
or - Medication
but in many cases it is one surgery necessary. A Knee joint endoscopy (arthoscopy) performed and the external meniscus either partially removed or sutured.
With an untreated external meniscus damage it can Joint mucosal inflammation or even one Osteoarthritis of the knee come.
To avoid tearing the outer meniscus, sports that are gentle on the joints (swim, Cycling) are preferred.
In sports that do Knee joint heavily strain, you should warm up well and wear suitable protectors that protect and stabilize the knee.