External meniscus tear
Definition of external meniscus tear
Under a Meniscal tear or a meniscus rupture is understood to be a tear in the meniscus of the Knee joint.
One External meniscus tear is found much less often than one Medial meniscus tear.
That's because the Medial meniscus on the one hand has a C-shape and on the other hand it is fixed to the Inner band of the knee is fused, which means that it has only very limited mobility, which leads to a higher risk of injury. Of the External meniscus however, is more in the form of a sickle and is not so strongly connected to its surroundings. This allows him to move more freely and thus better avoid damage caused by an accident.

Degree of severity and origin
Both at External meniscus tear as well as at Medial meniscus tear different degrees and different shapes of the crack can be distinguished.
- Grade 1 des External meniscus tear: central, punctiform tear,
- Grade 2 des External meniscus tear: horizontal tear that does not, however, reach the meniscus surface,
- Grade 3 des External meniscus tear: ribbon-shaped tear up to the surface of the meniscus,
- Grade 4 des External meniscus tear: multiple tears. The forms include the Basket handle tear (Tear along the length of the meniscus, with parts of the meniscus tearing off, sliding into the joint space and causing pain), the Transverse or radial crack and the Flap tear (a combination of transverse and longitudinal cracks).
Clinical examinations can be used to determine whether the Outside- or Medial meniscus is affected and what type of meniscus tear is present.
The most valuable imaging option for diagnostics is the MRI examination for a meniscus tear. In many cases, the MRI can show the location and severity of the injury and plan therapy based on the meniscus tear.
Read everything on the topic: MRI for a meniscus tear
There are a number of causes for a lateral meniscus tear, but the most common injury is the result of one long-term degenerative disease of Knee joint. Here, the knee is already damaged by permanent loads, which ultimately means that it doesn't take much until the meniscus ruptures.
The second most common cause of a lateral meniscus tear is on accident (Trauma), for example in sports such as Soccer or To ski. While the knee joint is relatively well armed against impact loads, it is prone to injuries as part of a Twisting trauma. The outer meniscus is at high risk of tearing when the knee joint is turned inward. It is not uncommon for there to be no direct reason for this injury.

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Diagnosis of an external meniscus tear
Diagnosing one External meniscus tear essentially takes place through two diagnostic measures:
- the examination by the doctor (ideally by a sports orthopedist)
- imaging tests (the best test for a meniscus tear is an MRI)
In the examination, the experienced doctor can use various Meniscus tests put pressure on the inner and outer meniscus. With a healthy one meniscus a meniscus test does not cause any symptoms.
If there is an external meniscus lesion, the meniscus test is usually positive. How well the external meniscus tear can be recognized by the doctor depends on his or her abilities and the age of the meniscus tear.
Especially with older meniscus tears the Meniscus test false negative.
In order to confirm or refute the result of the meniscus test, a MRI carried out on suspicion of a meniscus tear.
An MRI is a radiation-free form of examination in which the soft-tissue and cartilaginous structures of the knee joint can be shown particularly well.
Even the MRI does not offer 100% certainty about the diagnosis of a meniscus tear. Especially with small degenerative (age) tears, a meniscus tear can also be overlooked on an MRI.
Read more about these topics at:
- MRI for a meniscus tear
- Meniscus test
Figure meniscus tear
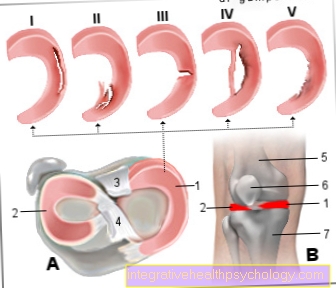
Meniscal tear
(= Meniscus rupture)
I - longitudinal tear
II - oblique view (rag tear)
III - radial crack (transverse crack)
IV - basket handle tear (special form)
V - degeneration (wear and tear)
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Lig. Cruciatum posterius - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Lig. Cruciatum anterius - Femur -
Femur - Kneecap - patella
- Shin - Tibia
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms and Therapy
Patient with a External meniscus tear mainly complain about usually stabbing or pulling pains. Typically, these are strongest in the area of the outer knee joint gap, but they can also occur diffusely in the knee, which is difficult to localize. In addition, some people have limited mobility in the knee joint. Especially the Elongation of the lower leg and that Crouch down are difficult. If there is a piece of the demolished meniscus trapped in the joint, the knee may even be completely blocked. For some, these complaints are accompanied by one swelling. In the case of a degenerative external meniscus tear, any symptoms can be completely absent over a longer period of time.
What kind of treatment Choosing for an external meniscus tear is dependent on many different factors (including Age, sportier activity, Extent of complaints, individual Needs or. To wish of the patient). However, some form of therapy must be done under all circumstances because cartilage is capable of a self-healing process only to a very limited extent and is at high risk for Consequential damage as a Osteoarthritis of the knee occurs when an external meniscus tear is left untreated for a long time.
If the damage is minor, you usually try one first conservative treatment. An adequate one physiotherapy can lead to complete healing for many. Serious damage, on the other hand, usually requires surgical treatment. Here the method of choice is the one Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy), in which different surgical techniques can be used.
With a timely therapy the prognosis of an external meniscus tear is very good. Complications as part of a surgery are rare in this procedure. The resilience of the knee joint must gradually take place under medical or physiotherapeutic supervision, but in most patients this is about depending on the severity of the injury, the choice of treatment and the individual condition 6 to 8 weeks given again completely.However, you should wait a little longer until you put more strain on the knee again, for example through certain sports.
Pain from a tear of the external meniscus
The knee joint is one of the most stressed joints in the body. Cracks in the outer meniscus often fall through stabbing or pulling pain on which often under pressure arise and are perceived as extremely unpleasant. Different types of pain can occur depending on the cause of the external meniscus tear and the extent of the injury. Generally you can choose between a acute and chronic damage to the cartilage can be distinguished. Pain associated with acute injuries to the Knee joint usually line up from a multitude of people Injuries to the cartilage and surrounding soft tissue together.
In contrast arise chronic Pain usually due to a wear of the cartilage tissue and develop insidiously.
Ideally, the Menisci of Knee joint and which are in Joint space located liquid a smooth and painless movement. If the outer meniscus has ruptured, this smooth movement can be restricted, which leads to the painful symptoms. Especially when Parts of the cartilage are torn off and are in the joint space, these ensure a friction and lead to Pain. In the event of a degenerative injury, in addition to increased friction and detached cartilage parts, the Inflammatory response the body plays a significant role in the development of pain. In addition, the bones involved in the knee joint due to detached cartilage parts rub and therefore pain can occur.
Pain that may occur when the external meniscus tears acute with the help of Pain medication be treated. At light Injuries can be a conservative Therapy help to improve the pain symptoms, whereas at extensive cartilage damage usually only one surgery is available as a treatment method for pain reduction.
Outer knee pain could also be a sign of a Outer ligament stretch or one Outer ligament tear and must be distinguished from meniscus damage.
OP
An external meniscus tear can occur especially if there is severe damage to the Cartilage is available using a operative treatment method are supplied. There are a number of different ways to treat the injury surgically. The operations are carried out as part of a Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy) done so after the operation hardly any scars stay.
With minor damage to the Cartilage comes that Sew up the tear used in cartilage. Through the use of modern sutures and techniques, the damaged cartilage can be restored to the bone connected and healing of the injured structure can be achieved. However, this surgical method is not possible with all forms of the external meniscus tear. This is especially the case localization of great importance and determines the feasibility of the operation.
Another option is to partially remove the External meniscus. Here, the torn off piece of cartilage is removed from the joint space awayso that this cannot impair normal joint mobility. The Partial removal of the outer meniscus can avoid consequential damage and minimize the symptoms of injury. However, partial removal is only possible if the damage to the cartilage does not exceed a certain level, otherwise a arthrosis of Joint can arise.
If the external meniscus is damaged more, a Cartilage transplant into consideration. With this form of treatment you have to choose between one artificial such as human cartilage replacement can be distinguished. Human cartilage replacement usually comes from deceased accident victims, whose meniscus is intact. Since the waiting times for a human implant are often very long, an artificial implant is usually sufficient in acute cases Polyurethane or Collagen for use.
The Duration of follow-up treatment differs from surgical method to surgical method and is also depending on the extent of the injury. Especially with one implantation of cartilage tissue is with one long post-treatment period to be expected, while a burden after Suturing or partial resection the injury more quickly is possible.
Duration of an external meniscus tear
The time it takes to heal a tear in the external meniscus varies considerably from person to person. Especially that extent and the localization the injury and the chosen treatment method determine how long it takes to heal an external meniscus tear. Since the External meniscus just poor circulation and is therefore only supplied with limited nutrients, the healing of the Cartilage last a very long time. Especially when central areas of the cartilage are concerned, this is unfavorable for a quick healing process.
In any case, one is important start of treatment as soon as possible, since otherwise consequential damage like a Osteoarthritis of the knee and permanent complaints can be expected. The duration of healing also depends on the success of the therapy. So is one conservative Therapy is not always successful even in the case of minor injuries and surgical therapy must follow. Positive results can be achieved with a conservative Therapy after a few Weeks to months to be expected.
Important with one operational Therapy is that consequent follow-up treatmentwhich can last different lengths depending on the surgical method. So after sewing up the tear or partial removal of the Cartilage beautiful after a few weeks a partial or full load of Knee joint take place while the Post-treatment of a cartilage transplant can take a long time.
Post-treatment duration
The duration of the healing and treatment of an external meniscus tear depends in principle on the individual extent of injury from. How long a sick leave exists in each individual case is also determined by the activity performed. So can a sick leave depending on the injury, treatment and activity usually between 3 weeks and 6 months last for.
Usually find Check-ups instead, who examine the course of treatment and the possibility of practicing a profession during the course. The consequent follow-up treatment and adequate protection of Knee joint is at the forefront of most treatment methods for an external meniscus tear. Early exposure to the Cartilage the healing process can be adversely affected and the development of possible consequential damage promoted. So especially people with technically demanding jobswho put a high strain on the knee joint, stay away from work longer than people with less occupational strain on the knee joint.
Conservative treatment for minor damage cartilage as well as some surgical treatments can already follow some weeks a Partial or full load of the cartilage. Severe damage or external meniscus tears unfavorable locations can one long post-treatment period and thus result in a long sick leave. How long an individual sick leave will last will be decided by the attending physician in the course of the follow-up treatment.











.jpg)