Ligament stretch in the knee
introduction
A Ligament stretch (Syn. Ligament strain) of the knee is caused by forceful movement of the Knee joint causes and can do both Inner band as well as that Outer band affect.
She is one of the most common sports injuries and can for example by a sudden rotational movement of the knee.

The transitions to one Torn ligament or one sprain are often fluid and therefore not always clearly distinguishable from one another. The Joint remains however, if the ligament is stretched stablewhile it is through a Rupture usually becomes unstable. To be one possible quick healing to achieve should the knee joint stabilized early on to protect the ligaments of the joint.
Causes of a ligament stretch in the knee
The causes of ligament stretching are manifold. In most cases they are extreme movements The cause of the ligament stretch in the knee. The strong movement becomes the natural Range of movement of the ligaments exceeded.
Since these situations often occur during exercise, ligament strains are the most common sports injuries. Ligament stretching occurs particularly frequently Sports with quick changes of direction or contact with opponents on.
These include in particular:
- Soccer
- basketball
- squash
- badminton
However, ligament stretching can also be caused by violent overstretching from the outside arise, for example, if the opponent hits the knee joint from one side while exercising.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Symptoms of a ligament stretch in the knee
The most common symptoms of ligament stretch are Pain and Swelling. The pain especially persists Movements of the affected joint. In contrast to a torn ligament, the swellings are often rather minor.
Because the affected ligament of the knee joint not torn is, the joint remains despite the pain stable and resilient. So are Walking and standing still possible, but not always painless. In addition, ligament stretching occurs in the knee usually no bruise (Hematoma) since there is no Injury to blood vessels comes. As a result, the hematoma is another criterion that distinguishes it from a torn ligament.
Swelling from a ligament stretch in the knee
Pain is that Main symptoms a ligament stretch in the knee. In addition, a Kneesswelling occur. But both symptoms fall less strong than, for example, a torn ligament.
The swelling is low, sometimes even completely absent. This is because, when stretching, no or only little surrounding tissue damaged and there is no rupture of blood vessels, as would be the case with a torn ligament. Bruising (Hematomas) are therefore also missing in ligament expansion.
If there is swelling, it usually goes back quicklywhen the knee chilled and spared becomes.
Diagnosis of a ligament stretch in the knee
The diagnosis usually results from the
- Description of the course of the accident
- the symptoms and
- the clinical examination
First, the doctor checks whether that is Joint stable is and a External pressure pain consists. In addition, the doctor determines whether a bruise has arisen; this would be an indication of a torn ligament. There is only one Swelling of the joint, is this Stable knee joint and no bruise has developed, these are clear indications of a ligament stretch.
To clinically test the stability of the knee joint, the Drawer test be performed. This makes it possible to determine whether the Cruciate ligaments of the knee joint are intact. Through the Unfolding test can be determined whether the Inner or outer ligaments of the knee joint are injured. Here is the Knee joint against a pressure outwards and inwards emotional. Intact ligaments severely restrict this movement; if the ligament is torn, the knee joint can move outwards or inwards moved beyond normal range of motion become.
These clinical examinations can give the doctor an indication of the extent of the injury. However, the exact diagnosis can be difficult because the injury causes the Muscles tense more reflexively and therefore the examination of the ligaments cannot always be carried out conclusively.
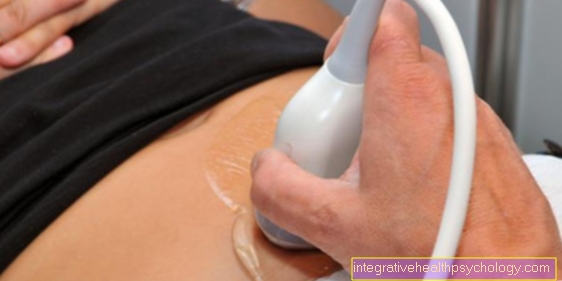
A ligament stretch at the knee can only be imaged by one Ultrasonic or MRI of the knee being represented. If the examiner is sure that the ligament is stretched, an ultrasound or MRI of the knee can be dispensed with. Since the transition to a partial ligament tear or even a ligament tear is fluid, an imaging procedure can often be useful.
Treatment of a ligament stretch in the knee
Immediately after the accident, the PECH rule to be started. The individual letters in "PECH" stand for the first letters of the four most important Initial measures after a ligament stretch:
- Pause
- E.is
- C.compression
- Hochlager
In any case, the sporting activity interrupted immediately be to a further damage to avoid the ligaments. Through the Cooling of the knee joint on the one hand the Relieved pain and prevent swelling of the joint. Through a Printing compound (Compression) will also be one increased swelling prevented. Since it becomes a increased reflex blood flow of the fabric comes this would without compression leads to increased swelling to lead. Elevate also serves to counteract severe swelling of the knee joint.
Basically, ligament stretches should follow not solely by immobilization of the joint and ligaments are treated. Usually it is important to have the ligaments to stabilize functionally. This relieves the strain on the stretched ligaments, but the joint can moved further within a limited framework become.
To treat ligament strains of the knee, be Stretch rails applied. Bandages or a Plaster sleeve ("Tutor") be used. This ranges from Thigh until Ankle joint and holds the knee in one Stretching position. So excessive movements of the knee joint are not possible and the damaged ligaments become spared and relieved, while the movements of the rest of the ligaments and muscles are not severely restricted.
Since the ligaments are intact and therefore stable after a ligament stretch, the knee joint can still burdened become. It should, however no pain occur. If the ligaments are stretched very much, a Exercise break from 6 to 8 weeks become necessary.
If there is no more pain afterwards, the load can slowly be increased again. Since the tapes were intact the whole time, the Exercise again without restrictions after healing become.
The treatment of the torn ligament on the knee is individually tailored to the respective case.
Taping for a ligament stretch in the knee

In addition to Support bandages there are so-called tapes. Tapes are elastic, self-adhesive rubber bandsthat can only be stretched lengthways. she stabilize thus the knee and the stretched ligaments.
Tapes become directly on the skin glued. This can be either a Physiotherapist or Orthopedist take over, or you can glue the tapes on yourself. Depending on Injury Pattern exist different types stick on the tape.
If you tape a stretch of the ligament on the knee itself, it should be noted that the tape around the Kneecap is applied and not over them runs. Is started above the kneecap with the knee joint flexed. Then the band is pulled down past the knee, slightly taut, and glued below the kneecap. Do the same for the other side of the kneecap. For even more stability you can put the ends of the adhesive tape on top of each other or alternatively a small one Cross band attach.
Tapes stabilize and in some cases also alleviate the pain of a ligament stretch in the knee, but they are no substitute for a full therapy. So before you use tapes, you should have a doctor examine whether it is really just a ligament stretch in the knee and not a torn ligament or something similar.
You still have it despite the tapes PainThat begs the question of whether or not you can keep your leg off for a while save should to allow the ligament stretch to heal completely.
Read more on this topic at: Tap your knees
Course of a ligament stretch in the knee
Usually one is simple ligament stretching harmless and only with temporary impairments connected. Usually the ligament stretch heals without any complications off when in pain affected knee joint spared becomes. If the sports activities interrupted for a few days and there is no longer any pain, the knee joint can then fully loaded again become.
However, there will be a ligament stretch of the knee joint not sufficiently spared, instabilities of the knee joint can result further injuries to the ligamentous apparatus consequences. This will make the Function of the knee joint impaired and the uneven loading of the joint surfaces creates a premature wear and tear of the cartilage surfaces. A early osteoarthritis with permanent pain in the knee joint is the result.
In addition, a damaged ligament can be much faster damaged again as a previously healthy ligamentous apparatus. This can cause strains or even repeatedly Tears of the knee ligaments arise. The chances of recovery are getting worse and worse if not treated to a permanent instability of the knee ligament apparatus.
Duration of a ligament stretch in the knee
A Stretching of the ligaments in the Knee joint is a painful affair. Depending on the severity the injury it takes different lengths of timeuntil the joint is fully resilient again.
The Pain in the course of a ligament stretching often leave after a few days to. cooling and reduced stress of the knee help to speed up this process, so that the pain after 1-2 days are no longer noticeable.
To complete healing the injury should be the knee though 1-2 weeks Give time. During these weeks one should also try the leg to burden as little as possible. cooling, compression and Elevate of the leg according to the PECH rule accelerate the healing process here too.
In case of a severe ligament stretch the recovery process can also happen in the knee more time take advantage of.
You should only put weight on the knee again when the The swelling has completely subsided and the Pain disappeared are.
With sporting activities you can start as soon as you can completely painless for about a week and the pain does not recur even during exercise. You also have the option to support stability in the knee Support bandages months after the injury to wear. These reduce the risk of instability in the knee joint and prevent the development of osteoarthritis.
Sick leave for a ligament stretch in the knee
Ligament stretching in the knee do not necessarily require one Sick leave. People who work during their work mainly sitting, if at all only for some days on sick leave.
At work that constantly or in Stand The duration of the sick leave depends on the duration of the sick leave according to the severity of the ligament stretch in the knee, or after the course of the injury.
To 1-2 weeks Most patients are able to go about their work again without restriction, since the pain has disappeared.
Professional athlete become common longer on sick leave. The risk of getting injured again if you return to sport prematurely is too great. Consequential injuries are usually more serious and last longer than the first injury. In addition, there is also the risk that Instabilities develop that one Joint wear favor and thus that Arthritis risk increase.
Summary
A ligament stretch of the knee joint is one of the most common sports injuries. It mainly arises in sports quick changes of direction and contact with opponents. Ligament stretching is usually harmless.
A distinction to a torn ligament is that
- moderate swelling
- the absence of a bruise and
- the existing stability of the knee joint
By a temporary Protection of the affected ligaments through bandages or a Stretching bar, the pain usually goes away quickly. If the ligament is severely stretched, a Sports break of up to 8 weeks become necessary. If there is no longer any pain, the affected knee joint may slowly burdened again become.
A full load and resumption of physical activity is required Freedom from pain possible without the risk of further injury. Only if the strain is continued while in pain is there a risk of one further injury of the ligaments resulting in a torn ligament. In this case it is Stability of the knee joint restricted and can have long-term consequences.


.jpg)



.jpg)