Treatment of a Baker's cyst
therapy
Basically, the Treatment of Baker's Cyst the conservative and operational measures to disposal.
As already mentioned, the Form of treatment for Baker's cyst according to the cause of the Baker's cyst. Lots Baker's cysts cause only moderate discomfort. These can certainly be treated conservatively. It should be noted, however, that conservative measures do not treat the cause.
The alternative treatment of Baker's cyst
The alternative treatment is directed Not primarily against the cause of Baker's cyst, than the wear processes in Knee joint.
Only if the knee joint function improves, a permanent improvement of the complaints in the hollow of the knee can be expected.
Please also read: Baker's cyst in the knee
Conservative treatment of Baker's cyst
1. Drug treatment of Baker's cyst: There are anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) Drugs from the group of non-steroidal (without cortisone) anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and diclofenac are used. Recently, COX 2 (cyclooxygenase) inhibitors have also been used as therapeutic agents. Cyclooxygenase is a key enzyme in the production of pain-producing substances (pain mediators), with the advantage of having fewer side effects on the gastric mucosa in particular. However, the effectiveness of this group seems to be inferior to the classic drugs. The use of cortisone-containing preparations in a Baker's cyst is not safe because of the numerous side effects, but it is very effective Syringe can be administered directly into the knee to stop the inflammatory process locally. In order not to let the risk of cortisone become too great, cortisone should not be administered more than three times a year. Hyaluronic acid therapy has developed particularly effective in the treatment of Baker's cyst in recent years. These are the body's own substances that can improve the quality of the remaining cartilage. In this way, the "water formation" can be reduced and ideally the Baker's cyst regresses. The hyaluronic acid treatment is not carried out directly on the Baker's cyst but on the knee joint, where the water for the Baker's cyst is produced.
2. Puncture the cyst: The contents of the cyst can also be sucked out with a syringe. However, a recurrence of the cyst must be expected, since, to describe it figuratively, “the lake is pumped empty, but the supplying river continues”.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Illustration of a Baker's cyst
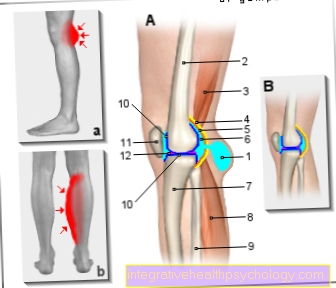
- Baker's cyst
(Popliteal cyst) - Femur -
Femur - Semi-membranous muscle -
Semimembranosus muscle - Joint capsule, fiber layer
(yellow) -
Capsula articularis,
Membrana fibrosa - Joint capsule, soft layer
(orange) -
Capsula articularis,
Synovial membrane - Joint cavity
(filled with synovial fluid) -
Articular cavity, synovia - Shin - Tibia
- Internal calf muscle -
M. gastrocnemius, caput mediale - Fibula - Fibula
- Articular cartilage (dark blue) -
Cartilago articularis - Kneecap - patella
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis
A - Knee joint effusion with Baker's cyst
B - Healthy knee joint
a - swelling in the hollow of the knee
b - swelling in the calf muscles
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Medication
The Treatment of a Baker's cyst can also be different through the gift of Medication respectively. In principle come above all anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) Medication for use. Due to the fact that active ingredients from the group of so-called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (short: NSAIDs, so drugs without cortisone) have both analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, they are particularly suitable for treating Baker's cyst. Typical drugs of this group of active ingredients are Ibuprofen and Diclofenac. With these drugs, however, it must be noted that the long-term use significant damage to the gastrointestinal tract can lead. For this reason, the duration of the application should be kept as short as possible.
In addition, the simultaneous use of Proton pump inhibitors help to prevent stomach problems that may arise. For some time now also find special inhibitors of the Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX 2 inhibitors) Used in the treatment of Baker's cyst. Cyclooxygenase is the key enzyme in the synthesis of various pain mediators. The advantage of the selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 is that the side effects in relation to the Gastric mucosa can be reduced significantly. In terms of effectiveness in the treatment of Baker's cyst, however, the selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2 appear to be inferior to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Medications containing cortisone are usually not administered orally (in tablet form) in the presence of a Baker's cyst. The reason for this is the fact that the numerous side effects of drugs containing cortisone should not be underestimated. However, cortisone-containing drugs can often be used in patients with Baker's cyst local be applied. In order to prevent the inflammatory processes from spreading, these drugs are administered with a syringe applied directly to the affected knee. However, even with this method there is a risk of serious side effects. For this reason, the topical application of the cortisone-containing drugs should a maximum of three times a year respectively.
It is also suitable Hyaluronic acid especially good for treating Baker's cyst. Under the term "Hyaluronic acid“One understands a substance which the quality of Cartilage tissue can improve. Regular use of these drugs can reduce water retention in the Baker's cyst area. In addition, the application of hyaluronic acid can even lead to the Baker's cyst forms completely back.
homeopathy
The sole use of homeopathy can with a Baker's cyst no treatment success cause. Usually such a cyst must be medicinally and / or surgically be treated. In addition to conventional medical treatment, however, the use of homeopathy can help support the healing process and alleviate the symptoms felt by the affected patient.
One of the most important medicines in the field of homeopathy Arnica 30C. Arnica is made from arnica flowers, which contain essential oils, flavenoids and sesquiterpene lactones. The effect of drugs containing arnica is mainly based on the anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties this substance. In addition, other active ingredients have been found in arnica flowers that have a stimulating effect on the immune system impact. In general, arnica is one of the most widely used active ingredients in homeopathy. Although globulis containing arnica are considered to be particularly gentle in the treatment of Baker's cyst, various can be used in their use Side effects occur. For external use, for example allergic reaction be evoked. In many patients, these allergic reactions take the form of Rashes, itching and education smaller Vesicles.
physical therapy
The regular implementation of physical therapy can be used in treating a Baker's cyst help to delay an operative intervention. In most cases, physiotherapy alone is not enough to treat the Baker's cyst. Before physiotherapy is prescribed, it is essential to determine the underlying physiotherapy for the respective patient The cause of the Baker's cyst to be clarified. This is especially important because of the stress on the affected person Knee joint can be counterproductive for some underlying diseases. Many of the patients affected by a Baker's cyst showed the condition of a Kinesio tape lymph system as particularly helpful. In addition, one can be performed during physiotherapy moderate leg axis training help to alleviate the symptoms caused by the Baker's cyst.
At overweight patient who suffer from a Baker's cyst can also have special things Water training to be ordered. This form of treatment is considered to be particularly gentle on the joints and can lead to the irritation in the affected knee being alleviated.
In general, physiotherapy in the treatment of Baker's cyst should take care that the knee is through targeted muscle building stabilized and thus long-term relief becomes.
surgery
If there is a Baker's cyst, all options for conservative therapy are usually exhausted before surgical treatment (OP) is applied. Patients in whom no significant improvement in symptoms can be achieved even after six months should consider an operation. As a rule, no treatment success can be guaranteed after such a long therapy period without surgery.
Also in the surgical treatment (OP) the rehabilitation of the underlying disease responsible for the development of the Baker's cyst is in the foreground. In this context, damage to the menisci and knee arthrosis play a decisive role.
The disease responsible for the Baker's cyst can be operated on with the help of an open or closed procedure. In cases where the knee joint disease is caused by a Arthroscopy can be treated, a regression of the Baker's cyst can usually be observed. For this reason, direct removal of the Baker's cyst is only necessary in the rarest of cases.
Patients suffering from one of the various rheumatic diseases are an exception in this context. Since in these cases there is mostly inflammatory tissue in the Baker's cyst, it must be completely removed.
The operation of the Baker's cyst is usually performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the attending physician must ensure that the cyst is always removed as a whole. This means that the style that connects the Baker's cyst with the joint capsule must also be interrupted. Otherwise, the affected patient may develop another Baker's cyst despite treatment. After the surgical removal (OP) of the cyst, a sample of the capsular tissue should be examined in the tissue. In this way, malignancy of the cyst tissue can be excluded.
Read more on this topic at: OP of a Baker's cyst
Treatment of a ruptured Baker's cyst
A Baker's cyst usually causes severe pain in affected patients. These pain symptoms become when the Knee joint significantly reinforced. For this reason, both the mobility and the functionality of the knee joint are often severely restricted in patients suffering from Baker's cyst.
A Baker's cyst bursts usually rather seldom. In patients who have ruptured this form of knee joint cyst, however, one often shows up Increase in perceived pain. A baker's cyst that has ruptured can cause Knee fluid (Synovial fluid) enters the surrounding tissue. This causes the symptoms to shift in the affected patient.
The pain caused by the Baker's cyst can be in such cases radiate into the calf. In addition, a Baker's cyst that has burst often occurs significant swelling in the areas surrounding the knee joint. Many patients who have burst a Baker's cyst also report having the feeling of cold water running down their lower leg. In the area of the epidermis one can in many cases Redness detect.
The Symptoms a baker's cyst that has burst are similar to the signs of a Blood clot in the leg veins. In addition, there may be a sudden increase in actually limited range of motion be an indication that the cyst may have burst. Patients who suffer from a Baker's cyst and suddenly discover redness and swelling in the calf area urgently consult a specialist immediately. Appropriate treatment should be initiated immediately if a Baker's cyst has burst. Failure to visit a doctor promptly can lead to serious complications.










.jpg)