Bump on the gum
Definition- what is a bump on the gum line?
A bump on the gum may have developed unnoticed over a long period of time and may only be noticed late by the patient, or it may appear acutely after an injury or previous dental treatment.
Inflammatory processes can also cause the gums to swell, and bumps or nodules can form on the gums. A distinction is made between bumps filled with fluid (e.g. pus) and unfilled hard or soft bumps on the gums.

causes
Inflammation is often responsible for a bump on the tooth rock. Especially after a root canal treatment or a tip resection.
With root canal treatment, the inflamed tooth nerve is removed and the nerve canals cleaned and then filled with root filling material. It is not uncommon for bacteria to remain at the root tips and infect the surrounding bone and the periodontal membrane. The infection cannot escape for the time being and the gums swell in this area and a bump filled with pus forms. This bump can cause severe pressure pain.
Even after a root tip resection, in which the inflamed root tips are removed in a minor surgical procedure, bacteria already in the surrounding bone can trigger an inflammation with a subsequent boil.
Another cause of a bump on the gum is an external injury, for example from excessive and pressure-intensive tooth brushing. Inflammatory bumps on the gums resulting from mechanical stimuli also include epulides. They can be soft and red, or pale red and hard to the touch. They also arise from wearing dentures and at the same time can trigger pain or simply arise unnoticed on the gums. Only when they get bigger do the patient notice them. Such epulides can occur especially during pregnancy due to the change in the hormonal balance.
Gum pockets and purely periodontal diseases can also cause inflammation and this can lead to a bulge on the gums.
Read more on the topic:
- Inflammation of the gums
- Inflammation after apicectomy
Bump in the upper jaw
A bump on the gums in the upper jaw may at first be completely painless and unnoticed.
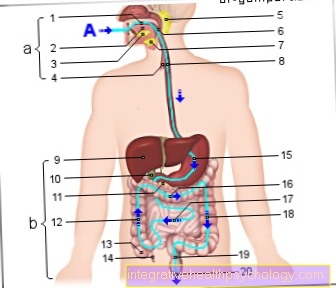
The tooth roots in the upper jaw border the maxillary sinuses. If an inflamed tooth is the trigger, the pus usually escapes into the nearby maxillary sinus first. There is a cavity there that is filled with pus, only when the pus has to escape again and the inflammation spreads further, there is typically severe pressure pain, which can then reach the eye.
During this time, a bump usually forms on the gum in close proximity to the affected tooth. An inflamed maxillary sinus without a diseased tooth can also trigger a swelling or bulge on the upper jaw. Usually, however, there is a rather large swelling that could also be visible from the outside.
You may also be interested in this topic:
- Root inflammation
- Inflammation under a denture
Bump in the lower jaw
Especially in the lower jaw, wearing a denture can cause a bulge on the gums. The dental prosthesis in the lower jaw usually has a much worse hold and fit than in the upper jaw and often slips over the alveolar ridge. This creates unnatural stimuli and pressure points for the gums. This mechanical load then leads to an epulis, a tissue swelling on the gums.
An epulis can look round or mushroom-shaped, and a distinction is made between an inflammatory form, which usually appears red and soft, or a non-inflamed form, which usually appears light pink and hard. Both should be examined by a dentist in any case to rule out other diseases of the jaw. Inflamed gum pockets are more common in the lower jaw, and these can also be noticeable as a bump. In particular, wisdom teeth in the lower jaw that are in the breakthrough trigger such inflammations.Inflamed gum pockets and the resulting boils are called a periodontal pocket abscess in this case.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the wisdom tooth
Concomitant symptoms
An acutely inflamed bump on the gums can often lead to severe pain and a feeling of pressure in this area.
If the inflammation continues, the bump can become significantly larger and it can also lead to a fever. An unpleasant smell or bad taste in the mouth is not uncommon and there may be more bleeding gums when brushing your teeth. The bump may restrict chewing or swallowing.
Pain
Pain due to a bump on the gums often indicates a tooth root inflammation or results from previous root canal treatment.
Periodontal diseases such as gingival pockets and receding gums can also trigger a painful bump. At the beginning, the patients notice a feeling of tension, which becomes steadily stronger until a dull pain develops. The pain can become very severe and then feel pressing and knocking. Warmth or lying flat can make the pain worse.
Also read: Periodontal pockets - recognize and treat
Boil
A boil is caused by inflammation in the bone and tooth. A so-called abscess develops.
The abscess is a focus of inflammation that has become isolated from the surrounding tissue. The formation of pus is a defense reaction of the body against pathogens. The surrounding bone can be seriously affected and there can be increased bone loss in this area. With a boil on the gums, a diseased tooth is usually the cause.
Read more on the topic: Abscess on the tooth
Bump on the gum without pain
At the beginning of the formation of a bump on the gums, no pain has to be felt.
Usually a bump develops unnoticed if it is not inflammable or if the inflammation has already found a way to drain. Fistula can develop through which the inflammatory secretions and pus can drain. Especially in the early stages, a gum fistula does not cause any symptoms.
Often the appropriate treatment is started too late and the symptoms can intensify and then become painful.
Another possibility for an initially painless bump on the gums can be an inflammation in the upper jaw. Due to the proximity to the maxillary sinuses, the inflammatory secretion initially escapes into the maxillary sinus and initially remains unnoticed or is misinterpreted. This condition also worsens quickly without treatment and later causes severe pain.
Epulides can also occur on the gums. As a rule, epulides always develop painlessly and are noticed by the patient quite late. They are caused by a previous injury, by hormonal changes or by pressure points caused by wearing dentures. They feel hard or soft and are not filled with pus or other secretions.
You might also be interested in this topic: Fistula on the tooth
diagnosis
A bump on the gum can be very painful, so a visit to the dentist is advisable.
A dentist can assess and diagnose diseases of the teeth and jaw using an X-ray image. Often a simple X-ray is sufficient, but if the bump is in the upper jaw and the maxillary sinuses could be involved, a three-dimensional image (CT, DVT) would be much more accurate and helpful in making a diagnosis. The first examination also includes looking into the mouth and examining the individual teeth, for example checking vitality.
Similar topics that might interest you: Swollen gums
Dent on tooth after root canal treatment
A nervous tooth can cause inflammation in the jaw again and again.
After a root canal treatment, residual bacteria can still be at the tip of the root and infect the periodontal membrane again, a bulge on the gums can then occur and the tooth must be treated again. Usually an apicectomy is then performed or an antibiotic is administered first.
Read more on the topic: Root canal treatment
treatment
A dent on the gum will be diagnosed by the dentist, and an X-ray can also be helpful.
A boil is an inflammatory process caused by bacteria and is often treated initially with an antibiotic (e.g. Amoxicillin® or Clindamycin®). The inflammation in this area creates an acidic environment and the anesthesia cannot work. A painless treatment of the tooth would then only be possible to a limited extent. In the further course the cause should be eliminated here.
If the bump originates from a tooth with inflammation of the root, a root canal treatment should be started. The bump on the gum then quickly recedes, as the inflammatory secretion and pus can drain over the tooth. In the case of a tooth that has already been treated with a root canal, the cause is not so easy to fix; one possibility would be an apicectomy. A relief of the symptoms can be the opening of the boil and a subsequent disinfecting rinse (e.g. Chlorhexidin®).
In the case of an inflamed gingival pocket, the pocket should first be thoroughly cleaned and then a local medicinal insert with an analgesic and anti-inflammatory ointment (e.g. Dontisolon®). In addition, pain reliever tablets such as Ibuprofen® are recommended. If the bump on the gum is an epulis, surgical removal is possible; an additional pathological laboratory examination should be carried out to rule out other jaw diseases.
These home remedies can help
In the case of a boil, rinsing with chamomile tea or over-the-counter mouthwashes from the pharmacy (e.g. CHX®) can help and alleviate the symptoms a little. Clove oil is also said to have a pain-relieving effect; to do this, absorb the oil with a cotton swab and dab it on the affected area. This can be repeated several times a day.
Garlic and onions are said to have a similar effect. In the case of a purulent inflammation in the jaw, one should not lie down flat, as the blood circulation in the lying position causes the tissue to be supplied with even more blood and this can lead to warming and the resulting greater pain.
Heat increases the pain, so cooling pads from the refrigerator can help. Never place the cooling pads directly on the skin to avoid hypothermia. It is better to wrap the cooling pads in a thin tea towel or a kitchen towel. Unfortunately, home remedies can only alleviate the symptoms and make the pain a little more bearable, they do not lead to a cure and a visit to the dentist is advisable.
Duration
The length of treatment depends on the severity and spread of the inflammation that is causing the bump on the gums.
An exact time cannot be given here. If an antibiotic is used for the initial treatment, it usually takes 2-3 days to take effect. Usually the symptoms are much better after the first treatment at the dentist and the lump disappears. If the bump on the gum has another cause and it is an epulis, it can grow unnoticed for several weeks. After surgical removal, these areas are usually symptom-free immediately after healing.