connective tissue
introduction
The term connective tissue includes various types of tissue. The connective tissue is not only part of the skin but also an essential part of the body's interior or organs.
The connective tissue thus makes a decisive contribution to the functionality of the human body and, in the event of defects, can lead to loss of function or even diseases.

Structure of the connective tissue
Connective tissue comprises many different tissues in the human body. Connective tissue runs through the entire body. All in all, it covers about 20 kg for a normal weight person. The connective tissue consists of cells and a lot of cell-free substance, the so-called matrix. Connective tissue cells are fibrocytes (cells that form connective tissue), cartilage cells (Chondrocytes), Bone cells (Osteocytes), Fat cells, pigment cells (Melanocytes), as well as all human defense cells, i.e. the white blood cells, of which a great many are not only found in the blood system, but also in the connective tissue. The cell-free substance consists of water, proteins and fibers; there are collagen fibers and elastic fibers.
A sufficient vitamin C level is important for the development of collagen fibers. There are four different types of collagen, which occur in different proportions depending on the organ and are essential for the stability of the connective tissue. In addition to collagen fibers, there are also elastic fibers, which, like rubber, are important for the elasticity of some human ligaments.They occur increasingly in the yellow spinal ligaments and thus enable the back to bend and stretch.
The connective tissue is divided into different tissue types. What all tissue types have in common is that they develop from a common system of the embryo.
Bone and cartilage tissue are considered to be supporting tissue. The fat tissue with the fat cells (Adipocytes) counts as a separate tissue type. It is not only found in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, but also surrounds all internal organs and fills the bone marrow.
Loose connective tissue is found under the skin and as a filling substance in many internal organs. Tight connective tissue forms the cornea of the eye, the meninges and all organ capsules.
The tendons, ligaments and intervertebral discs of the spine consist of fibrous, parallel connective tissue. Lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow have reticulated connective tissue. Gelatinous connective tissue is found in the umbilical cord and in the teeth below the hard substance. A particularly cell-rich connective tissue builds up the ovaries of women. Strictly speaking, even muscles and blood vessels with blood cells count as connective tissue.
Illustration of the connective tissue
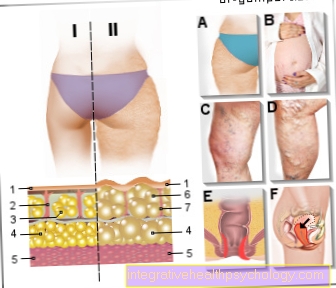
connective tissue
I - skin with strong
connective tissue
(Firm skin surface)
II - skin with
Connective tissue weakness
(Dents on the
Skin surface)
- Skin - Cutis
- Strengthened fabric fibers
- Normal fat cells -
Adipocytes - Deep layers of fat
(Fat reserve) - muscle
- Enlarged fat cells
- Weak tissue fibers
Signs of weak connective tissue:
A - cellulite (orange peel) -
dented skin structure
B - pregnancy or
Stretch marks
C - spider veins
(a type of mini convulsive vein)
D - varicose veins
(Varices)
E - hemorrhoids
(Rectal varicose veins)
F - uterine subsidence
(Lowering the uterus in
your holding apparatus)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
What role does vitamin C play in connective tissue?
In connective tissue there are, on the one hand, many different cells and, on the other hand, a great deal of cell-free substance. This is called the matrix and consists of water, proteins, elastic fibers and collagen fibers. Vitamin C is essential for building such collagen fibers. It is an essential coenzyme for the preparation of the storage of the amino acids lysine and proline in the strand of collagen fibers.
It also binds individual fibers to form connective tissue. If there is a lack of vitamin C, very weak connective tissue develops in the skin, muscles, bones and blood vessels. The insufficient synthesis of connective tissue due to the vitamin C deficiency can lead to bleeding gums, fragility of the vessels, slow wound healing. Furthermore, without the presence of vitamin C, the tissue becomes more permeable to pathogens.
What role does collagen play in connective tissue?
Collagen is the basic structure of connective tissue and is essential for its mechanical stability. In contrast to elastic fibers, collagen fibers are not very stretchable, but can withstand high loads.
Depending on the type of tissue or location, one can differentiate between four types of collagen. The tensile strength of tendons and ligaments in the body, the pressure resistance of articular cartilage or the flexibility of bones are due to the presence of collagen in connective tissue.
What is the function of connective tissue?
Due to its structure, the connective tissue has a variety of functions. On the one hand, it has a defense function through the defense and inflammatory cells contained in the connective tissue. Bone and cartilage tissues are firm connective tissues with a support function.
The connective tissue surrounds the internal organs and leads blood and lymph vessels as well as nerves to them. On the one hand, it has a framework function, and on the other hand, it is important for the supply of the organs: Due to the high water content, it serves as a water reservoir and enables the connective tissue to migrate nutrients and oxygen to the organs and muscles, as well as carbon dioxide and waste products from the Organs in the draining blood vessels. Last but not least, the fat tissue has an energy storage function, for which the fat tissue is primarily responsible.
How can you strengthen the connective tissue?
Connective tissue is a problematic topic for many people - whether from a cosmetic or medical point of view. Therefore, there is often a desire to strengthen the connective tissue, but how?
Connective tissue is found everywhere in the body, whether around organs or muscles; However, only the skin and possibly veins that appear as varicose veins or spider veins are evident. There are different approaches to strengthen the connective tissue in these areas. In homeopathy, remedies such as Silicea, Acidum hydrofluoricum and Calcium fluoratum are said to strengthen the connective tissue from within. Schüssler salts such as Cuprum arsenicosum also have such an effect. All of these agents have a beneficial effect on the connective tissue and have a supportive effect in terms of strengthening the connective tissue. However, from a conventional medical point of view, strengthening through this alone is rather unlikely. Therefore, at best, they should be used in combination with other approaches.
Furthermore, a healthy and balanced diet can have a positive effect - not only on body weight, but also on the weakness of the connective tissue. Because if you pay attention to your weight in a healthy manner, the connective tissue is also relieved by reducing the tensile forces acting on it. In this way, possible stretch marks, which often occur with weak connective tissue (even in slim people), can be prevented.
Learn more about: Stretch marks on the buttocks
Massages with certain oils also have a beneficial effect on strengthening the connective tissue. The tissue is supplied with more blood, which promotes its build-up and breakdown and the supply of important nutrients is improved, and cell renewal is stimulated. This effect can be increased with certain massage balls or gloves that have a raised surface. The massage oil makes the connective tissue more elastic and flexible.
Physical activity is one of the most important ways to strengthen connective tissue. This reduces superfluous fat deposits that stretch the connective tissue. By building muscle in the affected areas, the connective tissue is simultaneously strengthened and tightened. Particularly in the case of varicose veins, strengthening the muscle wall of the vessels and the surrounding tissue can prevent further bulging. This happens, among other things, through increased blood flow to the tissue through training. It is up to you which sport you choose, all of which have a positive effect.
It makes sense to target the areas of weak connective tissue with fitness exercises. The best known are stomach-legs-butt exercises. But first and foremost, it should be fun so that regularity can be achieved. Because the quality of the connective tissue is given and inherited individually to a certain extent in each individual, one can definitely achieve a visible improvement in the connective tissue structure with the means mentioned here. However, a change cannot be expected from the outset; all of the above measures require both perseverance and patience.
Read more on this topic at: Strengthen connective tissue
Can you strengthen connective tissue through nutrition?
In addition to health aspects, your own diet can also have an impact on the quality of the connective tissue. So that the body can continue to produce collagen and thus the stabilizing framework of the connective tissue undisturbed, the necessary substances must be absorbed through food. These include vitamin C. This is essential for collagen synthesis and should be consumed in sufficient quantities daily through fruits and vegetables. The recommended daily requirement for vitamin C is 100mg.
Furthermore, the amino acid lysine is essential for a stable connective tissue structure. Lysine occurs naturally only in already existing proteins and has to be supplied through food. Lysine is mainly found in dairy products, meat, walnuts, peas and rice. An average amount of 30-60 mg lysine per kg body weight is recommended.
Adequate daily fluid intake is also essential to achieve stable connective tissue. On average, an adult should ingest about 35 ml of fluid per kg of body weight.
Read more on the topic: Strengthen connective tissue through nutrition
How can you tighten the connective tissue?
The connective tissue is very heavily used in the course of life.
This can be noticeable through wrinkles and sagging areas of the skin. The reasons for this are different.
On the one hand, there are strong fluctuations in weight, which can be caused not only by changing eating habits, but also by pregnancy.
Put simply, the existing connective tissue structure is "worn out", which is only reversed to a certain extent. Exercise, which is beneficial for tight connective tissue, can also be a cause. Finally, the natural aging process, in which the quality of tissue renewal decreases, also plays a major role.
There are different approaches to tightening connective tissue, something that is discussed again and again in society and the media. The easiest and most sensible method for the prevention and treatment of slack connective tissue is definitely sport in connection with a healthy lifestyle. Since the connective tissue has a certain potential for regression, you can achieve a lot with this. The shape of the connective tissue can be defined by building up muscles in certain areas of the body such as the buttocks, thighs, arms and stomach. If you do regular and targeted sport, a visible effect can be expected after a certain time. In addition, firming creams and body oils can be used, all of which are available in the drugstore or pharmacy. These should be applied in circular movements and possibly with massage gloves or the like so that blood flow and cell renewal are stimulated. However, you shouldn't set your expectations too high here - too much is often promised by product advertising. The sole use of such products is definitely beneficial and has a preventive effect, especially when the connective tissue is still tight. The tightening of connective tissue through this has its limits, however. Nevertheless, it is worth the effort, especially if you also do sports in combination.
The most effective method of tightening connective tissue is cosmetic surgery. In principle, everything is possible here - from eyelid to tummy tuck.
This should definitely be done professionally and well thought out.
Because even if you are in otherwise healthy condition and undergo such an operation, it is still an operation under general anesthesia, which carries certain risks and side effects.
In addition, the results depend on the surgeon and cannot always change the appearance to the satisfaction of those affected. Nevertheless, in some cases cosmetic surgery can do a lot more than just tighten connective tissue, as many of those affected suffer greatly from the problem areas. From a medical point of view, some interventions make perfect sense. It is best to always weigh this together with the surgeon.
Read more on this topic at: Tighten connective tissue
What role does connective tissue play in cellulite?
Cellulite is a non-inflammatory change in connective tissue that occurs only in women. It manifests itself as dents-rich skin reminiscent of the surface of an orange.
The reason that it mainly affects women is a difference in the structure of the connective tissue between men and women. The connective tissue of women is more loosely networked than that of men. The connective tissue fibers run perpendicular to the surface. As a result, fat cells can bind together more easily than accumulation of cells from the inside press against the surface of the skin and cause dents in the skin. As a result, fat cells can move more easily.
Genetic predisposition also plays a decisive role in the development of cellulite. The hormone estrogen, which men have only very little in contrast to women, ensures a breakdown of the collagen that stabilizes the connective tissue. For this reason, fat cells can spread more easily and promote the development of cellulite.
What can you do if the connective tissue is torn?
Fine cracks in the skin or in the connective tissue are also known as stretch marks. The development of the cracks in the connective tissue is highly dependent on the own connective tissue. The cracks are not dangerous to health, but are often perceived as annoying by those affected. You cannot completely remove the cracks. However, there are ways to improve the appearance of the small cracks in the skin.
Some sufferers claim to have achieved an improvement through the application or massaging of oils. These special oils are available in every drug store.
There is also the possibility of laser therapy. Here you can get advice in specialized practices.
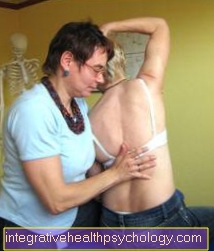
What is connective tissue massage?
A connective tissue massage is one of the so-called reflex zone massages, which in turn are based on the theory of segment therapy. This describes the treatment of a particular area of skin that can be assigned to a specific spinal cord segment. The function of internal organs that are connected to a skin area via nerve tracts can also be influenced depending on the associated skin area.
In a connective tissue massage, this is mechanically stimulated mainly with the fingertips. As a rule, this triggers an uncomfortable feeling to a painful feeling.
In addition, small bruises may appear on the treated areas in the first few days after treatment. The connective tissue massage is intended to increase the blood flow and prevent or even dissolve the connective tissue and muscle fascia from sticking together. Connective tissue massage should not be used in pregnancy, heart disease or acute inflammation.
Read more on the topic: Connective tissue massage
Inflammation in the connective tissue
Inflammation is a body reaction that is supposed to enable the immune system to act more actively and increasingly in certain areas of the body. Inflammation always occurs in the connective tissue and in the vascular system.
They express themselves through typical symptoms. These include redness, pain, swelling, and warming. Another symptom is often restricted mobility.
The connective tissue is poorly supplied with oxygen at the inflamed area. The reason lies in the fact that the swelling makes it difficult to transport oxygen to the cells. The cells themselves begin to produce energy without oxygen. A by-product of this energy gain is lactic acid, which makes the tissue acidic. Basically, in order to treat inflammation, the cause of the inflammation must be identified.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of connective tissue
Connective Tissue Pain - What Not To Be?
The body's own restructuring processes of the connective tissue can be responsible for pain of various kinds. The connective tissue can also contract and cramp like muscles.
If the connective tissue is significantly changed or dense, the muscle below is restricted in its ability to move and pain occurs as a result.
For changes in the connective tissue, which are often associated with pain, very long periods of time in a relieving posture, operations, stress, overstretching, trauma or, in general, a severe lack of movement. Depending on the cause, the fasciae stick together with the connective tissue and harden continuously. Remodeling processes start in the connective tissue, in which the elastic components are replaced by non-stretchable collagen fibers. The basic tension in the tissue increases significantly and pain can arise.
Hardened connective tissue in the neck or back area can also be the reason for pain in these areas. A healthy amount of exercise is therefore essential to prevent the pain in the connective tissue.
Read more on the topic: Pain in connective tissue
Glued connective tissue
Connective tissue Structures can stick together and thereby Big pain cause. Affected connective tissue can be found anywhere in the body. The most common places are Joints, between muscle layers or between organs affected. Causes are mostly inflammatory processescaused by influences from the outside, such as. increased stress through sport or from within, like bleeding or after surgery can arise. All of the above causes lead to some kind stress in the body and especially at the affected connective tissue site. This stress leads to Release of messenger substances from cells and blood vessels that make up one increased production of precursors of connective tissue which cause a increased liability affect surrounding tissue. The inflammation causes connective tissue to stick together. At Move arises a increased train on the bond, since the layers can no longer slide freely past one another as before. This hurts very strong. Through the Relieving posture, which is taken in a row, the affected come into one Vicious circle, as they cramp even more muscularly or no longer move the joints sufficiently. This creates even more pain and an even stronger posture is adopted.
The best way to break this vicious circle of glued connective tissue is through early and targeted exercise therapy, like physiotherapy, or through special massages the affected area. This should be further Prevent sticking and the loosen up existing ones. The inflammatory process should be through early as well anti-inflammatory drugs or cooling of the affected area. In the worst case, it is advisable to consult a doctor in order to weigh up a possible surgical procedure.
Connective tissue diseases
The connective tissue has numerous components whose change can lead to various diseases. These can be genetic, triggered by autoimmune processes or caused by deficiencies such as vitamin C, among other things.
Connective tissue hardening - what is the underlying cause?
A hardening of the connective tissue, referred to as scleroderma in medical terminology. This is an autoimmune disease in which the connective tissue becomes increasingly solid.
The exact causes of connective tissue hardening have not yet been adequately clarified. However, there are a number of factors that can influence the causes of the hardening of the connective tissue. On the one hand, genetic predisposition plays a major role. On the other hand, it is believed that there is a connection between cancer and hardening of the connective tissue. Furthermore, environmental factors such as the handling of chemicals at work play a decisive role.
Furthermore, antibodies against certain receptors, i.e. docking points of growth factors, i.e. specialized proteins, are associated with the disease of hardening of connective tissue.
scurvy
Vitamin C deficiency leads to scurvy. Wounds do not heal well and bleeding from the mouth and gums and teeth fall out. This disease often affected the pirates, who were unable to eat fresh fruit on their long sea voyages.
Marfan's Syndrome
This hereditary syndrome shows how important the correct structure of collagen fibers is. There is a genetic disorder of the smallest connective tissue fibers, the connective tissue in the entire body is unstable. The patients are very tall, have long, hyperextensible fingers, often bulging of the main artery and visual disturbances due to slipping of the eye lens, which is poorly anchored here. You can find out more about this here.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type III is also one of the diseases of the connective tissue in which collagen fibers are affected.
Connective tissue cancer
Cancer in connective tissue falls under the term soft tissue tumors. This term encompasses tumors of different tissues, such as connective tissue or muscles.
The majority of these soft tissue tumors are benign. The very rare malignant form is known as soft tissue sarcoma. The causes of the formation are still unclear in medicine. However, one suspects certain risk factors such as asbestos or previous radiation exposure. Genetic predisposition can also play a significant role. In most cases, however, no causes for the development of the soft tissue tumor can be found.
The most common and most important symptom of soft tissue sarcoma is a persistent, i.e. persistent, rapidly growing and painful swelling, which is usually larger than 5 cm. If these criteria apply, it is advisable to consult a doctor for advice. However, it is very important to note that the occurrence of soft tissue sarcomas in connective tissue is very low in Germany.
Rheumatism in connective tissue - does it exist?
Rheumatism is not an independent disease, but describes a variety of different diseases. These are inflammation, pain in ligaments, tendons, joints, bones or in the connective tissue and complaints of the locomotor or holding apparatus.
Rheumatism, which takes place in the connective tissue, is classified as a collagenosis, a type of connective tissue disease. Collagenous connective tissue can be found in the body in muscles, tendons, skin, bones or cartilage and gives the connective tissue its stability and structure. Collagenoses are autoimmune diseases in which the defense is directed against the body's own cells of the connective tissue. The connective tissue is not the direct place of origin of the rheumatism, but plays a decisive role in this collective term for various diseases.











.jpg)