Bisoprolol
Synonyms
Bisohexal, Rivacor, Bilol, Bisacardiol, beta blockers
General

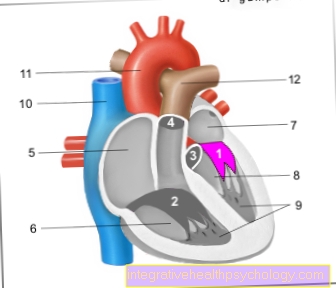
Bisoprolol belongs to the group of beta-blockers.
Beta receptors, also known as beta adrenergic receptors, are found in different places in the body and are activated by the hormone adrenaline, which is released by the body when it is exerted, excited and tense. In particular, many of the beta receptors are located in the heart, which beats faster and stronger when adrenaline is released, so that the body can meet the demands that are placed on it. The cardiac output must be increased, i.e. the amount of blood that the heart pumps out per minute.
Blood pressure is also increased because muscle cells are also found in the blood vessels (arteries and veins) of the body. Blood pressure increases or decreases depending on how tense or relaxed you are.
However, blood pressure also depends on other factors, such as arteriosclerosis or how sporty you are. Other beta receptors are located in the lungs and muscles.
Beta blockers like bisoprolol make use of this mechanism and attack the beta receptors directly and block the receptor so that adrenaline can no longer bind to the receptor. The result is that the heart beats slower and is better supplied with oxygen. In addition, the muscle cells in the vessels relax and thus the blood pressure is lowered.
Read more on the topic: Effect of beta blockers
Typical areas of application of beta blockers such as bisoprolol are high blood pressure, heart failure (heart failure) and circulatory disorders of the coronary arteries (angina pectoris).
to form
The active substance Bisoprolol fumarate is under different trade names expelled: Bisohexal, Rivacor, Bilol, Bisacardiol and numerous others. There is also bisoprolol in combination with Hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic, for increased blood pressure control (e.g. Bilol comp., Concor plus).
Bisoprolol is usually prescribed in tablet form in strengths of 1.25mg, 2.5mg, 3.75mg, 5mg, 7.5mg and 10mg.
dosage
The Dosage of bisoprolol depends on Type of illness. Unless otherwise prescribed, the tablets are sober in the morning to be taken with some liquid.
Beta blockers we should basically use bisoprolol dosed gradually be meaning that about a Period of about two weeks the dosage slowly continuously increased becomes. The application is not limited in time and dose changes should be determined by the doctor.
Bisoprolol should under no circumstances without prior medical consultation should be discontinued as it is used in patients with circulatory disorders of the coronary arteries (coronary artery disease, angina pectoris) Deterioration of condition can come. Again, the dosage of bisoprolol should be slowly reduced over a period of 7-10 days.
Unless otherwise prescribed, the dosage is:
- at high blood pressure 5mg once a day, with mild high blood pressure may also be sufficient 2.5mg. A dose increase if the effect is insufficient up to 10mg per day.
- in the coronary heart disease (CHD, angina pectoris) 5mg once a day with a possible dose increase up to 10mg.
- in the stable chronic heart failure 1.25mg-10mg. The dosage is increased gradually. In addition, in the standard therapy of chronic heart failure in addition ACE inhibitors, Diuretics and maybe Cardiac glycosides given.
When should Bisohexal® not be used?
Absolute contraindications
- chronic Heart failure, acute or decompensating
- strong slowed pulse (so-called bradycardia; Heart rate before the start of treatment below 50 beats / min)
- Conduction disorders between the pacemakers of the heart (sinus atrial Block; AV block II. And III. Degree)
- morbid Sinus Node Syndrome (Sick sinus syndrome)
- low blood pressure (so-called hypotension; systolic blood pressure or upper value <90mmHg)
Relative contraindication
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease how COPD (severe chronic obstructive pulmonary dysfunction) or bronchial asthma
- deafness and pain in the hands and / or feet caused by vascular cramps (Raynaud's syndrome)
- Diabetes mellitus
- psoriasis (Psoriasis)
- untreated Tumors of the adrenal medulla (pheochromocytoma)
Of the Anesthetist should be in front of a general anesthetic Be informed about taking bisoprolol, as there may be interactions between bisoprolol and the anesthetics.
Special patient groups
- Elderly patients: In the case of very poor kidney and liver function, the dose should be adjusted and kept as low as possible if possible.
- Pregnant women: Only after consultation with the doctor and careful risk-benefit assessment, as the drug is in the blood circulation of the unborn child and thus disrupt its development. Likewise, one It is not recommended to use during breastfeeding, as insufficient results are available as to whether bisoprolol can pass into breast milk.
- Children: As there is no therapeutic experience, children should not be treated with bisoprolol.
- Athlete: Taking bisoprolol can lead to a positive result in the doping test.
Since bisoprolol is tolerated differently, it cannot be ruled out that the Reactivity when using machines or the Ability to drive can be affected; However, it is no direct effect known. This should be taken into account especially at the start of treatment, when adjusting the dose or changing the preparation.
Bisoprolol and alcohol
Simultaneously Alcohol consumption may increase the effects of bisoprolol.
Interactions
Concomitant use of other drugs should discussed with the doctor or pharmacist this applies in particular to centrally acting antihypertensive drugs such as clonidine or the combination with other antihypertensive drugs such as Diuretics, Calcium channel blockers of the verapamil and dilitacem types, Antiarrhythmics (Medicines to treat irregular heartbeat), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), blood sugar-lowering drugs or insulin, Cardiac glycosides (digitalis), drugs against depressions and the anti-malarial drug mefloquine.
Bisoprolol and the pill
There are no interactions known.
Side effects
It can be special too Start treatment to dizziness and a headache (Improvement usually after 1-2 weeks), nausea, Vomit and others Gastrointestinal complaints, Fatigue, circulatory disorders and a drop in blood pressure.
Also were sleep disorders, dry eyes, Confusion, mood swings, stronger sweat, erectile dysfunction, Hypersensitivity reactions and cramping of the Respiratory muscles the bronchi observed.


.jpg)