Bladder Rectum Disorder - What Is It?
What is bladder rectal disorder?
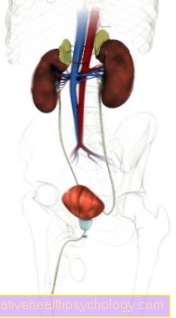
Bladder and rectum disorder is a malfunction in urination and bowel movements. This often includes various symptoms.
If the bladder malfunctions, urine will pass involuntarily. The urine output can no longer be arbitrarily controlled. Often there is also the feeling that the bladder cannot be completely emptied (residual urine). This is associated with difficult urination.
In addition, the function of the rectum is disturbed. The patients have sensory disorders in the anal area and suffer from fecal incontinence. This complex of symptoms is summarized under the term bladder-rectal disorder.
Read more about the symptoms of bladder rectal disorder:
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary retention

Concomitant symptoms
Depending on the cause of the bladder rectal disorder, there are various accompanying symptoms.
For example, if a herniated disc causes the symptoms, this is usually accompanied by massive back pain. These can also radiate into the legs or feet.
Other nerves can also be damaged by the bulging intervertebral disc, which then leads to paralysis and sensitivity disorders. Most bladder and rectal disorders are accompanied by numbness (loss of sensitivity) in the genitals, in the anal area and on the inner thighs. The nerves that control bladder and bowel function supply these areas sensitively. Often this also causes sexual dysfunction. Immediate surgical intervention is necessary to prevent permanent damage and incontinence. The protruding disc tissue must be surgically removed.
Treatment of bladder rectal disorder
As mentioned earlier, there are several causes of bladder and rectal disorder. The treatment options are as varied as the causes of the disease.
If the bladder and rectum disorder occurs as part of a herniated disc, an immediate surgical procedure is necessary.
If this disorder occurs in patients with multiple sclerosis, the patient would first be treated with high-dose cortisone therapy.
If the cause of the bladder and rectal disorder cannot be eliminated (for example, due to paraplegia), it is important to treat the symptoms. In terms of the bladder, this means preventing the urine from backing up in the kidneys and preventing the bladder from emptying regularly; this can be done with sterile disposable catheters. Even with intestinal dysfunction, the goal is regular, predictable and time-limited emptying of the bowel. There are also various aids here.
Get more information about the respective therapies:
- Urinary catheter - what is it good for?
- Treatment of a herniated disc
- Therapy of multiple sclerosis
When will I be healthy again?
How long the bladder rectal disorder lasts depends on the cause. Depending on the cause, the patient can better control his excretions over the course of the process. In multiple sclerosis, symptoms can regress after cortisone therapy. If surgical intervention is performed in good time in the event of a herniated disc, the nerve tissue damaged by pressure can usually recover. The symptoms recede. Paraplegia is usually a permanent severing of the nerve fibers. The bladder and rectum disorder is usually permanent.
Prognosis of bladder rectal disorder
The prognosis for bladder rectal disorder depends on its cause. If it occurs as part of complete paraplegia, the prognosis is poor. A cure is not possible according to the current state of science.
Whether a bladder and rectum disorder can be cured after a herniated disc depends on how quickly the surgical procedure takes place. If the operation succeeds in relieving the pressure on the nerve cells while there are still living nerve cells, the prognosis for the patient is usually good. The symptoms can regress.
This also applies to bladder and rectum disorders in multiple sclerosis; with appropriate drug therapy there is a chance of healing.
Learn more about the Cure for paraplegia.
Causes of bladder rectal disorder
The causes of bladder and rectal disorder are diverse. Usually diseases of the nervous system are the cause.
On the one hand, this can affect the processing of impulses in the brain. In this case, strokes, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and brain tumors would be possible causes of the bladder rectal disorder.
On the other hand, the transmission of stimuli can also be interrupted directly. This is the case, for example, with a herniated disc. Here the slipped parts of the intervertebral disc press on the emerging nerves and damage them. Even with paraplegia, the connections from the central nervous system to the bladder and rectum are interrupted; in this case already at the spinal cord level.
disc prolapse
A common cause of bladder and rectal disorder is a herniated disc.Here the bulging intervertebral disc presses on the sensitive nerve tissue. This pressure causes the nerve cells to slowly die off. This leads to massive pain and paralysis. Bladder and rectum disorders can also occur if the corresponding nerve cells are damaged. This is an absolute emergency. Most of the time, immediate surgery is needed to relieve pressure on the nerve fibers. This can often prevent a permanent loss of function of the bladder and bowel. In this way, permanent incontinence can usually be avoided through early surgical intervention.
Do you think you have a herniated disc? Find out here what the typical Symptoms of a herniated disc are.
Diagnosis of bladder rectal disorder
The causes of bladder and rectal disorders can be very diverse. In order to be able to make the diagnosis, a specific anamnesis is important. You have to ask the patient carefully whether only thin stool or also formed stool involuntarily comes off. The same goes for bladder dysfunction. Does the patient feel that the bladder cannot be completely emptied? Is it difficult to urinate? If both bladder and rectal function are equally impaired, it is usually a neurological disease. Accordingly, further neurological symptoms should be asked in the medical history. Specific questions should also be asked about back pain or previous problems with the intervertebral disc.
This is followed by a physical exam. Depending on the suspected diagnosis, various apparatus examinations follow; usually an imaging representation of the brain and spinal cord / spine using CT and / or MRI.
MRI of the lumbar spine
If, based on the medical history and physical examination, you suspect that a herniated disc is the cause of the bladder and rectum disorder, you should have an MRI scan of the lumbar spine (lumbar spine) performed. Here you can see which spinal segments are affected by the herniated disc. Sometimes this can be multiple segments. The advantage of the MRI examination is that in addition to the vertebral bodies, the intervertebral discs and also the nerve tissue can be displayed well. One would see whether intervertebral disc tissue presses on nerve cells in the spinal cord or the spinal nerves. In most cases, the MRI scan is even performed without a contrast medium.
Read more about the Diagnosing a herniated disc.










.jpg)