Bladder cancer therapy
How can bladder cancer be treated?

The therapy of the Bladder tumor depends on the individual stages. Tumors that do not grow invasively by the muscle are resected transurethrally. The urethra of the tumor resected with the help of an electrical loop and removed from the bladder flushed.
The resection must be carried out deep into the bladder layers in order to completely remove the tumor base. The individual tumor remnants and wall components are sent separately to the histology department so that the exact spread of the tumor can be assessed. It can also be used to confirm that the tumor has been completely removed from the bladder. If this is not the case, a subsequent resection must be carried out.
If the tumor grows invasively or recurrently, the bladder must be completely removed. A distinction is made between continent and incontinent surgical procedures. In incontinent urinary drainage surgery, the two ureters are inserted into the Small intestine and from this a drain is formed. This is a method that can be carried out more quickly and with fewer complications and is used accordingly in patients for whom no longer-lasting operation would be reasonable. With the continent surgical procedures, three more possibilities can be distinguished.
- For one, part of the Ileum formed into a new bubble and then on again kidney and urethra connected. Complications can be infections, incontinence, scarring and urinary disorders.
- Another option is urinary diversion through the navel. An ileocecal pouch is attached to the navel. The urine is drained by regular catheterization. This is done by the patient himself and is usually not painful. Of course, it takes some getting used to.
- In the past there was also the variant of directing urine into the intestines. However, this not only brings with it the problem of an associated very thin stool. There is also a significantly increased risk of Colon cancerwhich is why an annual Colonoscopy (Colonoscopy) is necessary. If the bladder carcinoma has metastasized to other organs, the tumor becomes with it chemotherapy treated. Radiation is often performed for soft tissue or bone metastases. This has a palliative-analgesic effect and is no longer used for healing.

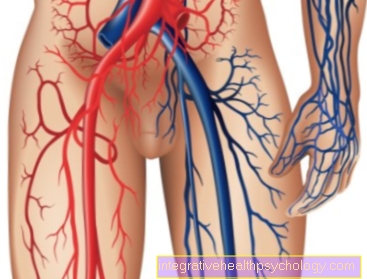
- Ureter - Ureter
- Transitional epithelium - Urothelium
- Shift layer of the
Mucous membrane - Lamina propria - Inner longitudinal layer -
Stratum longitudinal internum - Outer longitudinal layer -
Stratum longitudinal externum - Middle ring layer -
Circular stratum - Connective tissue covering with
Blood vessels - Tunica adventitia - Aortic fork - Aortic bifurcation
- Rectum - Rectum
- Urinary bladder - Vesica urinaria
- Adrenal gland -
Glandula suprarenalis - Right kidney - Ren dexter
- Renal pelvis - Pelvis renalis
- Lower vena cava - Inferior vena cava
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations