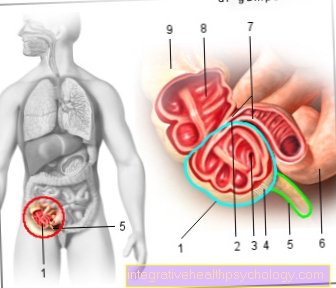
Bruise in the knee
introduction
A bruise in the knee is also known as "hemarthrosis". The common word "Hematoma“Is synonymous with bruises on all parts of the body. A bruise can be thought of as the filling of tissue with blood as a result of an injury or an accident.
Read on here: How do you treat a bruise?

General
Almost all tissues in the human body are supplied with blood, which contains oxygen and nutrients. If the affected tissue, in this case the structures of the knee, is injured, the blood vessels can also be damaged. The blood then exits the vessel and accumulates in the tissue and in body cavities. The blood can no longer be transported away from there via the veins and the damage in the vessel causes the affected area to fill with blood and thicken.
We very often observe the formation and course of bruises when we get a so-called "bruise". The area of the bruise becomes thicker, warmer, and can also be painful to touch. After a few days the color changes to a more yellowish spot before the spot disappears completely.
A bruise in the knee, on the other hand, is a common side effect of sports injuries. Due to the high daily stress, the knee joint is very prone to injuries to the ligamentous apparatus, cartilage or bones. Common causes of bruising are meniscus tears, collateral ligament tears, cruciate ligament tears, or broken bones. Joint effusions in the knee are not infrequently extremely painful, the knee swells and is visibly blue-green in color from the outside.
Some home remedies can be used as immediate measures, such as rapid cooling of the knee, which reduces the bleeding. A doctor should then be consulted as soon as possible, as not only does the causal injury require treatment, but the bruise itself can permanently damage the knee.
Under certain circumstances, joint effusions can form after knee operations, for example on the meniscus or cruciate ligament. If the bruise does not resolve itself after a while, medication can encourage faster healing. In some cases it becomes necessary to puncture the joint by using a needle to aspirate the fluid directly from the cavities in the joint.
Another treatment for bruises in the knee are so-called "Hematoma tapesThese are stuck tightly on the outside of the joint and can both alleviate the pain and accelerate the regression of the hematoma.
What you might also be interested in: Knee puncture
causes
Bruising in the knee joint can result from a range of different causes. In most cases they are the result of an injury to structures in the knee. Such injuries can occur in everyday movements for no apparent cause, as a long-term consequence of permanent improper stress and wear and tear or in connection with sports accidents.
High-risk sports for knee joint injuries are primarily skiing and football, as well as all sports that require particular strength and stress on the legs. The knee joint is particularly susceptible to so-called "rotational trauma". If the lower leg is twisted too much in relation to the thigh due to a vigorous, incorrect movement, the cruciate ligaments, the collateral ligaments and the two menisci in particular can be injured. The extent of the injuries ranges from overstretching to complete rupture of the ligaments. All tears in the ligaments in the knee urgently require treatment by an orthopedic surgeon. With jerky injuries, it often happens that vascular structures that run through the knee are also injured. The blood that is transported through them then pours into the surrounding tissue and the cavities of the knee joint.
Any injuries to the knee, especially those involving the bones, for example the kneecap, can result from strong external influences, for example in the event of a severe fall. Both slight bruises and broken bones can result in hematomas. These bruises are expressed as a so-called horse kiss.
It is not uncommon for knee bruises to occur after knee operations. The body perceives the operation as a kind of injury. Some medications can also cause bruising in different parts of the body. A doctor should clarify which drug is responsible for this and whether the drug therapy must be stopped.
In rare cases, a bruise in the knee can occur for no apparent cause and without a previous accident. If something like this occurs more frequently, also in other parts of the body, it can sometimes indicate more serious illnesses. A doctor should be consulted in order to rule out internal diseases that involve a tendency to bleed.
Read more on the topic:
- Knees twisted
- Cruciate ligament overstretched
Bruising of the knee after knee surgery
Bleeding occurs during and after operations. If a major injury in the knee joint is treated surgically, it can develop inside the joint cavities minor or major bleeding come. For major operations after which bleeding is likely, the surgeon will often do one Drainage placed in the surgical woundthrough which the accumulating blood can drain. If the bleeding seems to decrease or stop, this drain can be removed. It can still happen that a Bruising occurs. Because the swelling also through for example bacterial pus can be caused, the effusion must be observed. If the effusion does not improve within a few days to weeks, a doctor must decide whether that is Dotted knee must be or even one operative treatment necessary is.
Appearance of bruises in the knee after arthroscopy
A bruise in the knee can also after an arthroscopy, so one Jointoscopy, arise.
The introduction of the medical instruments into the knee joint irritates the joint cavity and leads to swelling in the knee.
Does the procedure have a therapeutic goal - e.g. the operation of a torn ligament in the knee or the suturing of a damaged cartilage - are fine or also larger blood vesselswhich can be found in almost every tissue, damaged. It is not a big one, it is rather diffuse bleedingwhich, however, weighs heavily in a narrow space like the knee joint and one significant swelling with pain can evoke.
However, a bruise in the knee after an arthroscopy is one frequent accompanimentthat is in the vast majority of cases regresses by itself after a while and shouldn't cause concern. For example, an infection can only occur in exceptional cases, which then has to be treated further.

Symptoms
With small hematomas, there is often only one slight swelling and a Tenderness in front. Additionally is the affected area is visibly discolored from the outside, first red, then blue, later yellow. Larger bruises on the knee can cause greater, more permanent pain. This is also known as Tension paincaused by the spread and swelling of the effusion. In addition, the swelling is Freedom of movement restricted.
In the case of large bruises in the knee joint, the so-called "dancing patella". Here, even with light pressure on the kneecap, you notice that the kneecap seems to float through the accumulated fluid in the knee. The phenomenon only occurs with joint effusions of around 50ml.
treatment
In most cases, hematomas are not dangerous and will resolve on their own in a few days. The blood that has passed from the vessel into the tissue, initially coagulates and then will awayby the body it degraded by enzymes. The various breakdown products that arise in the process also explain the development of the colors of the “blue spot” from red, through blue and green, to yellow.
Immediately after the injury and the onset of swelling on the knee, the knee needs to be cooled. The cool temperature causes the blood vessels to contract and bleeding to decrease or stop. As a result, the hematoma does not spread as far in the tissue and the swelling is also less.
A doctor should decide how to proceed with treatment. The bruise itself is common not in need of treatmentwhen the cause of the effusion has been resolved. In other cases, the orthopedic surgeon can also provide a so-called "Hematoma tape“Stick on the knee, which accelerates the healing process and makes it easier by simultaneously relieving pain.
In rare cases, the joint effusion may not heal on its own and a Puncture of the knee becomes necessary. The blood is sucked out of a cavity in the knee joint with a needle.
Treatment with tape
A bruise in the knee can also be treated with so-called "taping". They are also called "Kinesio tape"Or"Meditape" designated. Not all kinesio tapes are for use at Knee joint effusions suitable. Special tapes for the treatment of bruises are also called "Hematoma tapes“.
You can buy the tapes in pharmacies and medical supply stores and apply and stick them yourself. This requires some practice at the beginning, which is why it is advisable to consult an orthopedic surgeon first.
The tapes must be attached very tightly to the skin and should completely cover the hematoma. For this you need particularly wide tapes that are elastic in all directions, which is why not all kinesio tapes are suitable.
The hematoma tape should be the reduce pain and the Accelerate the healing process. If that does not happen and the bruise is still there after weeks, the doctor should be discussed about how to proceed. In such cases it may be necessary to repair the bruise with an operation or puncture.
Should you cool or warm bruises on your knee?
Basically, bruises should be chilled become; through the cold the blood vessels constrict, it flows less blood in the affected tissuewhich improves the swelling and reduces the effusion more quickly. Against that Pain Cooling is a tried and tested means (alongside pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen). Ideally, one will be stored in the refrigerator Cool pack Wrapped in a towel and placed on the affected area so that the skin does not freeze.
Puncture to treat bruises
If the bruise in the joint does not resolve itself, the knee should be punctured and as much blood as possible removed. In the long run, the blood in the joint cavities can damage the cartilage and cause inflammation.
In these cases, the doctor may puncture the knee and the patient should immediately see improvement in the bruise and pain. The doctor pierces the knee joint with a thin needle and tries to suck out as much of the blood as possible.
However, there are also risks associated with the puncture. If the puncture is performed incorrectly, structures in the knee joint can be injured by the needle. The puncture can also cause new bleeding. If the puncture is performed unsanitary, the knee can become inflamed and lead to further pain and joint effusions.
Care should also be taken to ensure that the original injury that caused the bruise is repaired. Otherwise, the puncture will not be successful because the joint cavity can quickly fill up with blood again.
Read more about this at: Knee puncture
Home remedies for a bruise
In addition to the tried and tested conventional medical treatment methods and the application of a cool pack, you can also various home remedies help treat a bruise in the knee.
One with acetic acid Clay (from the pharmacy) soaked cloth that is wrapped around the knee can be used as well as a bath Arnica essence be helpful. However, neither should be used on open wounds (e.g. after an operation). A proven remedy are also Quark wrap: For this, about 250g of cold quark from the refrigerator is evenly distributed on a towel and wrapped around the knee.
However, once the bruise is present, in most cases it only helps to wait and see. If the bruise changes color to yellow after a day, it is a good sign that the hematoma is healing by itself.
Healing time from a bruise in the knee
Smaller hematomas can be easily observed in their course using the colors they take on. It takes about two weeks from the moment the swelling appears until the swelling has completely subsided. Larger bruises, especially after operations, can last for weeks. A doctor should be consulted who will decide on treatment. Some hematomas do not resolve on their own. These are also known as organized hematomas. In this case, the doctor should perform a puncture, place a drainage or surgically remove the effusion. With such large bruises, it can take weeks to months to completely heal, depending on the course.
Read more about this under Duration of a bruise












.jpg)