Blood sponge in the baby
definition
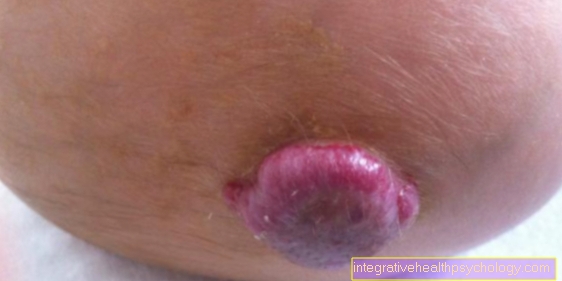
A blood sponge is a benign tumor that is caused by the growth of small blood vessels on the skin. Blood sponges are not prone to malignant degeneration. Since they consist of the smallest blood vessels, they have a reddish or bluish shimmer and are slightly raised. Blood sponges, technically known as hemangiomas, are present in around one third from birth. The remaining blood sponges appear around the third to fourth week of life. About one to three percent of all babies are affected by a blood sponge. Blood sponges are around five times more likely to occur in girls than in boys.
The cavernous hemangioma is also an important special form of hemangioma. To learn more about it, read: Cavernous Hemangioma - How Dangerous Is It?
causes
Why blood sponges develop has not yet been really clarified. It is believed that in many cases there is a hereditary component. There are no measures to prevent a blood sponge in a newborn. One theory that explains the cause of a blood sponge is that Blood sponges due to a dysregulation of vascularization in early pregnancy arise.
diagnosis
Most often the diagnosis can be blood sponge as Eye diagnosis be asked. This means that the appearance of a blood sponge is usually relatively characteristic, so that the doctor can do this without consulting any further diagnostics Make a diagnosis by appearance can. Sometimes, however, another closes Ultrasound examination and in very rare cases one Computed Tomography in order to be able to assess the inward expansion of the blood sponge. Additionally should measured the hemangioma so that the size can be compared during further controls. In the best case, the doctor will also take a photo documentation so that the blood sponge can best be compared during further checks.
Concomitant symptoms
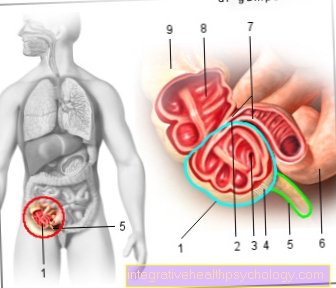
Usually blood sponges are used not accompanied by other symptoms. They do not itch and are not painful. Sometimes they can a little pressure sensitive be. Blood sponges are benign tumors that are basically harmless. In addition to the blood sponges visible from the outside, there are also internal blood sponges that do not grow on the skin and are therefore not visible from the outside. This Internal hemangiomas can grow and affect internal organsby compressing structures. For example, internal blood sponges, depending on their location, can lead to breathing difficulties, problems with eating or jaundice. Internal blood sponges can also affect hearing and vision. If a child has several external blood sponges, a doctor should also use ultrasound to look for internal blood sponges.
treatment
As a rule, a blood sponge does not have to be treated. Often it even shrinks over time until it does eventually disappears entirely. However, this process takes several years. Since it is a benign lump, a benign tumor, it usually becomes a hemangioma removed only for cosmetic reasons, for example when it is prominently on the face. The face and neck are by far the most common locations of a blood sponge, which is sometimes perceived as disfiguring by those affected, so they decide to remove it. Since more than half of the blood sponges regress in the course of the child's first year of life, should be refrained from removing in childhood, because even a removal can sometimes leave disfiguring scars.
If a blood sponge is to be removed, this is usually the case with the help of cold therapy (cryotherapy) or Laser therapy carried out in several sessions. Both icing and the use of lasers cause a growth stop and lead to a slow fading the tumor until it has completely disappeared at some point. The icing is often poorly tolerated by children because it is painful. In the past, radiation was also used for removal, but since the side effects were too great, this treatment method was abandoned.
Partly becomes a blood sponge also surgically removed. This is particularly useful when a blood sponge grows close to important structures such as the eye or ear. In some cases, a blood sponge will also with cortisone supplements tried to treat this method but has been increasingly through the use of Propanolol, a beta blocker, replaced.
Beta blockers for blood sponges in babies
In addition to the traditional methods of removing a blood sponge, freezing and lasers, also have Beta blockers an effect on blood sponges. Beta blockers are coming usually used to treat irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, or heart failure for use. It was found out by chance that they also act on blood sponges in newborns. Beta blockers can be used in hemangioma due to various effects: On the one hand, they lead to one Narrowing of blood vessels, inhibit vascular proliferation (vascular growth) and can cause programmed cell death. All of these three effects promote the regression of a blood sponge. Beta blockers can be used in the treatment of blood sponge used from the fifth week will and will in the form of a drink solution administered. Usually this is the beta blocker Propranolol used. Since 2014 beta blockers have also been officially approved for the treatment of blood sponges, so that they no longer have to be used as so-called off-labe use.
What to do when it grows
Straight An increase in the size of the blood sponge is not unusual in the first few months of life, but should be observed by a doctor. If a hemangioma grows at a later point in time, this should also be shown to a doctor in any case. However, the growth of a blood sponge is usually not an indication for therapyunless requested by the patient or their parents. Since blood sponges are most commonly found on the face, growth near the eyes, ears, mouth, or nose is not uncommon.
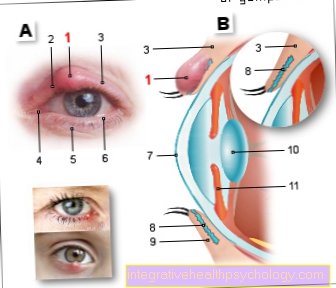
If a blood sponge is on the eye, its growth can exert pressure on the eyeball, which can lead to ametropia or squint. Food intake can also be affected by a hemangioma in the mouth. A hemangioma on the nose can make breathing difficult. Therefore, children with blood sponges in critical position should receive regular medical care. If there is a blood sponge on the eye, ear, nose or mouth, you usually decide early on to remove it.
What to do if it is bleeding
Are bleeding from blood sponges very rare, but are in principle possible, since a blood sponge is a tumor made up of small blood vessels. If a blood sponge is bleeding, it is usually only about a small amount of bleeding that can be stopped by pressureso that usually no additional measures are required.
forecast
The prognosis of a blood sponge is basically good, as it is a benign tumor. In the initial phase, in the first months of life, the blood sponge often increases in size, which is not a cause for concern. Nevertheless, controls at the pediatrician do no harm. In most cases, blood sponges shrink over time until they have completely disappeared at some point. As a rule, blood sponges go through a growth phase, a standstill phase and a regression phase. If a blood sponge is still present after the age of ten, regression is less likely.
In addition to these harmless blood sponges, there are also blood sponges that grow inward and can block organs. Here the prognosis can look different.
Please also read: Hemangioma
Blood sponge on the baby's head
About 60 percent of all blood sponges occur on the head or neck. These localizations are often perceived as disfiguring, which is why they are removed. Blood sponges on the face should be checked regularly so that they do not affect the eyes, mouth or the like.
Blood sponge on the baby's finger
A blood sponge usually occurs on the face or neck, but in principle a hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, including the finger. If the blood sponge is on the fingertip, the factual sense can be impaired.












.jpg)