Burning in the head
What is a burning sensation in the head?
Headaches can come in different forms. Burning is one of them. This sensation is due to nerve irritation (Neuralgia), for example due to inflammation or entrapment. The brain matter itself does not contain nerves. They are located on the meninges, blood vessels, cranial and spinal nerves and the skin. However, the pain can also arise in another location and radiate to the head or only be perceived there. A lightning-like shooting in alternating with pain-free phases is typical.
There are many possible causes. In addition to harmless triggers, it can also be a sign of serious illness. If the symptoms persist or further symptoms occur, it is advisable to look for the cause. As with headache in general, however, this cannot always be found.

causes
Burning sensation can occur with any type of headache. For common tension headaches, migraines and rarer forms such as cluster headache and trigeminal neuralgia.
In cluster headache (Binge Horton Syndrome) there is severe unilateral pain in the area of the eyes. Accompanies reddening of the eyes, tearing, runny nose and sweating. The attacks usually occur at night and last between 15 and 180 minutes.
Read more about the topic here: Cluster headache
Trigeminal neuralgia is a disease of a cranial nerve that runs across the face. Lightning-like, extremely strong pain attacks occur, mostly one-sided. With a duration of a few seconds, up to 100 attacks per day are possible.
Read more about the topic here: Trigeminal neuralgia
Other causes can be: Stress, depression, nerve entrapment near the spine, tension, shingles (herpes zoster) on the face, high blood pressure, poor diet (insufficient fluid intake, large amounts of alcohol) and, rarely, but significant: an inflammation of the optic nerve (Optic neuritis) with mostly one-sided burning sensation in the eye area, accompanied by visual disturbances.
Burning in the head with mental illness
Pain is a sensory perception that is subject to complex processing by the nervous system. This happens through the interaction of nerve cells via so-called neurotransmitters. Their release can be influenced by stress or mental illness and thus change the perception of pain.
Otherwise unnoticed or barely perceived physical stimuli can suddenly be perceived as painful, in this case burning.
Burning in the head with multiple sclerosis
About a third of all multiple sclerosis patients, especially young women, have an inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis) at the onset of the disease. This usually only occurs in one eye. Those affected complain of reduced visual acuity, failures, especially in the central field of vision, color vision disorders and movement-dependent pain behind the eye. This optic nerve inflammation usually precedes other symptoms of multiple sclerosis and is therefore an important indicator for early diagnosis.
Read more on the subject at: Optic nerve inflammation in MS
Burning head in depression
Depression can be accompanied by physical complaints or even underlie them (larvae / somatized depression). In the case of severe depression, in addition to decreased drive and depressed mood, physical symptoms often occur. Pain with no apparent physical cause is possible. There is a good chance that the physical symptoms will go away after appropriate treatment with psychotherapy and possibly antidepressants.
With a masked depression, the pain is not an accompanying symptom, but rather an expression of the mental illness. However, this is not perceived by the patient, it is "hidden", so to speak. In any case, the cause of depression must be taken seriously and treated.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of depression
treatment
Symptoms can often be improved with a healthy lifestyle. These include avoiding excessive amounts of caffeine and alcohol, abstaining from nicotine, getting enough sleep and exercise, and maintaining the correct blood pressure.
In general, a holistic view of the complaints is an advantage. The respective needs of the patient should be taken into account. The following can be used: occupational and physiotherapy (e.g. massages, physiotherapy), physical applications (e.g. cold and heat applications), psychotherapy (e.g. behavioral therapy, biofeedback methods), naturopathic methods or acupuncture.
The measures mentioned can be useful for every patient. Especially since a cause of the headache cannot always be found. If, however, burning headaches occur over a longer period of time, keeping a headache diary can be very helpful in looking for the cause and planning therapy.
Find out more at: Headache diary
If an underlying disease is known, it should be treated appropriately. Various drugs for short-term and long-term pain treatment come into question here.
Simple pain relievers (e.g. ibuprofen) help with severe tension headaches. It should be noted that if the drug is taken too frequently, the headache may be exacerbated (painkiller-induced headache). Restraint is required here.
Psychotherapy and antidepressants help with depression. If there is multiple sclerosis, a variety of drugs (e.g. cortisone) can be considered. The aim is to regulate the immune system, which attacks the body's own nerves. Care by neurologists is necessary here.
At this point we recommend that you also deal with the home remedies for headaches. Medicines can relieve pain for a certain period of time, but in the long run they have numerous side effects. You should therefore also read the following article under: Home remedies for headaches
Duration
The duration of burning varies depending on the cause. Since this is not always found, the symptoms can persist in the long term. Here, above all, individually tailored, holistic treatment is important in order to prevent progression and provide relief. However, if the cause of the burning sensation is clear, rapid and targeted therapy is necessary. Often, however, the symptoms are relapsing or persistent. However, the appropriate treatments are effective.
Concomitant symptoms
The burning sensation in the head can be accompanied by numerous other symptoms: headaches of another kind (stinging, tingling, boring, throbbing, etc.), feeling of pressure, visual disturbances, dizziness, nausea, sensitivity to light, sweating, red eyes, tearing, insomnia, tiredness, fatigue, ringing in the ears, Failures of facial muscles, double vision, taste or smell disorders, loss of appetite and depressive moods.
Pressure in the head
A feeling of pressure can occur especially with high blood pressure, stress or poor nutrition. A pain diary can be helpful in determining the cause. Pay attention to the following points: In which situations do the complaints occur? Are there any triggers? Is the pressure sustained or is it relapsing? Is the intensity constant or fluctuating over the course of the day? Where exactly is the feeling of pressure: all over the head or limited to one region?
All of this information can help the person affected and their doctor to find causes and treat them or at least provide relief by avoiding triggers.
a headache
Burning as a form of headache can of course also be accompanied by headaches of all kinds: drilling, pulsing, stabbing, pressing, pulling. Here, too, it is important to pay attention to the characteristics of the complaints. Does the burning sensation and the rest of the headache occur simultaneously or independently?
If the burning sensation is part of a common tension headache, pain relievers like aspirin or ibuprofen can help. If the burning sensation is an independent symptom, in addition to the headache, a doctor should be consulted for further clarification.
Read more on the subject at: Tension headache
Tension
Muscular tension is common in the population. In the context of sports injuries or in everyday life due to incorrect posture and stress. This tension can cause massive pain and radiate far from where it originated.
The back and the spine should always be considered as possible causes. Are you already known to have joint or spinal problems? Are there professional (heavy lifting at work) or private (overweight, lack of exercise) risks? Diseases of the intervertebral discs should be emphasized here. It is an extremely common symptom of wear and tear in middle age, which should be addressed early with exercise, physiotherapy and painkillers.
nausea
This symptom often accompanies other complaints. Another cause can be a disease of the balance organ in the inner ear. In addition to nausea, this also leads to dizziness, vomiting and possibly hearing disorders. However, it can also be an indication of increased intracranial pressure, triggered for example by brain tumors or bleeding. The latter are serious but rather rare causes.
Read more on the subject at: Headache with nausea
diagnosis
If the burning sensation persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is advisable to consult a doctor. Given the multitude of possible causes, a precise description of the symptoms is important. A pain diary can help here.
If there is a suspicion of neuralgia in a single nerve, this can be switched off with a local anesthetic and identified as a possible trigger. If serious illness is suspected, imaging of the head (CT or MRI) may be indicated. In this way, diseases such as multiple sclerosis or vascular changes can be detected. However, this is rarely necessary.
Usually the doctor can make a diagnosis by describing the symptoms. Duration, accompanying symptoms, triggers and other information often provide useful information.
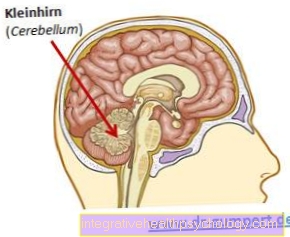
MRI of the head
The high-resolution MRI allows the brain structure and the supplying blood vessels to be displayed precisely. The advantages over the CT are the higher resolution and the lack of radiation exposure. However, imaging is not always necessary. This should be done in consultation with the attending physician and after a thorough physical examination.
MRI is of particular importance in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Foci of damage in the brain caused by the disease can be visualized using MRI.
Read more on the subject below: MRI of the head









.jpg)