Butterfly on the cable pull
introduction
In order to do justice to the principle of varying the training load, the chest muscle training can and should be designed variably. Training on the cable pulley can be used in addition to normal training and is primarily used to define the chest muscles. However, since both arms work symmetrically and a firm stance is required, this training requires a certain amount of movement coordination.
Trained muscles
- pectoralis major (M. pecotralis mayor)
- Triceps (M. triceps brachii)
Figure chest muscles
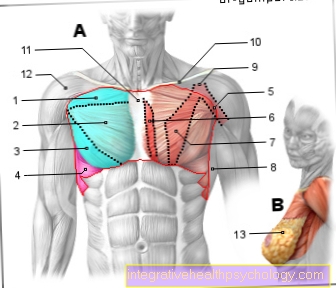
Chest muscles
- Pectoralis major
(Collarbone - proportion) -
Muscle pectoralis major,
Pars clavicularis - Pectoralis major
(Sternum - ribs - area) -
Muscle pectoralis major,
Pars sternocostalis - Pectoralis major
(Abdominal area) -
Muscle pectoralis major,
Pars abdominalis - Anterior saw muscle -
Muscle serratus anterior - Raven beak
Upper arm muscle
(second layer) -
Muscle coracobrachialis - Sternum muscle (often absent) -
Sternalis muscle - Small pectoral muscle
(second layer) -
Muscle pectoralis minor - Broad back muscle -
Latissimus dorsi muscle - Raven beak process -
Coracoid process - Collarbone -
Clavicle - Sternum - sternum
- Deltoid -
Muscle deltoideus - Fat and connective tissue,
as well as glandular lobes -
Glandula mammaria
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
description
The athlete stands in a step position, the upper body is leaning forward. The head is an extension of the spine, facing forward. The hands hold the handles of the cable pulley firmly at chest height. In the starting position, the shoulder blades are close together and the chest muscles are stretched to the maximum. The arms are led diagonally forwards and downwards towards each other, the chest muscles are contracted and the shoulder blades move away from each other. The upper body moves as little as possible.
Modifications
The exercise can be performed with the help of an expander.
The expander is attached at chest height. The flexibility depends on the performance level of the trainee.