Swollen lymph nodes during pregnancy
definition
Lymph nodes are small filter stations throughout the body that play a central role in activating the immune system.Swelling due to an increase in volume occurs as part of lymph node activation and usually occurs in the case of inflammatory processes or a malignant disease, such as Cancer, on. Inflammation would be referred to as a benign disease, so to speak.
Regardless of the underlying cause of a lymph node swelling, it is, in combination with other warning symptoms and depending on the location, worth investigating in order to protect the mother and the unborn child.

The possible causes
The increase in volume of a lymph node is based on the fact that the phagocytes of the immune system are located in this filter station and eliminate harmful pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, as well as other particles (degenerate, potentially malignant cells and toxic substances).
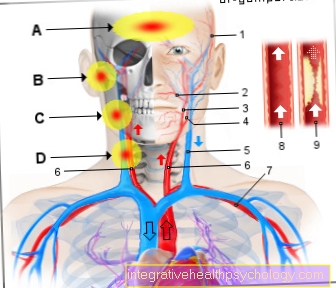
The lymph nodes, which are also palpable from the outside, are regional lymph nodes, which are responsible for an assigned area of the body. In the event of a local or systemic inflammatory reaction, the immune cells migrate to their lymph node stations and begin their defense there. There is an enlargement and possibly a tenderness to pressure. This is due to the fact that the number of white blood cells (leukocytosis) increases during pregnancy. This is intended to intercept infections by the immune system and protect the child or mother. Overall, the immune system can be viewed as sensitive during pregnancy. Lymph node activation and swelling are more noticeable than in a non-pregnant woman.
As mentioned earlier, lymph node swelling can result from either a malignant or benign disease. Infections are a common cause, in rare cases autoimmune diseases and storage diseases. The infections can be, for example, more harmless illnesses such as colds, gastrointestinal or urinary tract infections, but also more serious illnesses can lead to lymph node swelling.
Read more on the topic: Respiratory infection in pregnancy
Particular caution is required with the disease complex, which is also abbreviated as "STORCH", and which is explained at the beginning of every pregnancy. These are the diseases syphilis, toxoplasmosis, O (indicative of “Others”), rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex. Mothers who have neither had these diseases nor vaccinated against them are at risk of developing the disease during pregnancy. It can cause permanent damage to the child. In the case of an enlargement of the lymph nodes that cannot be explained by other infections, these STORCH diseases should be taken into consideration.
The enlargement from autoimmune or storage diseases is less common. In the case of a non-movable and painless, rather coarse enlarged lymph node, the possibility of a malignant origin should be clarified. It can be, for example, a lymphoma (lymph node cancer) or a spread of cancer from another organ.
Find out more about the topic here: Infections in pregnancy
The different localization
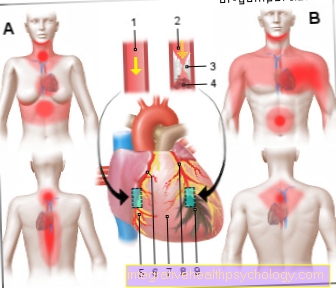
The localization in the armpit
In addition to a swollen lymph node, swelling in the armpit during pregnancy can also be a dislocated mammary gland, which grows under the influence of hormones during pregnancy and can look like a lymph node.
In the context of an infection that affects the entire body or originates, for example, from a wound in the chest area, an axillary lymph node can also swell. What should be worrying, however, is the fact that swollen lymph nodes in the armpit in women can also be metastases from breast cancer.
Find out more about the topic here: Lymph node swelling in the armpit - how dangerous is it?
The localization on the neck
Enlarged lymph nodes of the neck are generally the most common, as infections of the upper respiratory tract are common. This is due to the fact that many germs are absorbed through the mouth and nose and this is where the first defense stations are located. Even after the infection has subsided, the regression of the lymph nodes can take some time and should not cause concern.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, a doctor should be consulted. More rarely, cells from oropharynx cancer can settle in a cervical lymph node, which is called metastasis.
You can find more on this topic here:
- Lymph node swelling in the neck- How dangerous is it?
- Common cold during pregnancy
Localization in the groin
The lymph nodes of the groin represent the immune defense station from the genital area. They can be swollen due to an infection or a reaction after sexual intercourse.
In principle, the same applies as for other localizations of swollen lymph nodes: If the symptoms are “painless, hard and immovable”, an immediate diagnosis applies, as is the case for other signs of inflammation such as fever, fatigue and foul-smelling discharge (which can indicate sexually transmitted diseases).
Find out more about the topic here: How dangerous are swollen lymph nodes in the groin?
Swollen lymph nodes behind the ear
The lymph nodes behind the ear are filter stations for a small, circumscribed area of the head.
For example, inflammation of the parotid gland from salivary stones can cause lymph nodes to swell and increase in size.
The pathogen causing toxoplasmosis can be responsible for this more rarely. Since the swelling is often painful, a quick visit to the doctor is advisable.
More information on the topic: Swollen lymph nodes behind the ear
Concomitant symptoms
Two large groups of concomitant symptoms can occur with swollen lymph nodes, depending on how they originated (benign or malignant).
In the benign, where we assume an infection, fever, fatigue, exhaustion and a drop in performance can occur. Depending on the localization and origin of the disease, more specific complaints can occur (for example, discharge and swollen lymph nodes in the groin in the case of sexually transmitted diseases or runny nose and sore throat with swollen cervical lymph nodes in the case of a cold).
The other complex of complaints related to malignant diseases is also called B symptoms. These are fever, weight loss, and night sweats.
Querying and differentiating these two large groups can already point the way for further investigations.
diagnosis
First of all, it is important to clarify since when the enlargement was noticed in order to be able to classify whether it is an acute or chronic process.
The enlarged lymph node should be palpated and examined for mobility and tenderness. If a malignant process is suspected, any general practitioner can usually provide further information with an ultrasound. Further imaging measures could e.g. be an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or a scintigraphy with contrast agent.
A biopsy, i.e. taking a sample from the lymph node, can be useful for clarifying the type of cell present. A blood sample can also be taken to check for increased inflammation values.
The treatment
If lymph nodes are swollen as part of an infection, they should be viewed more as a symptom and not as the center of the disease itself.
In this case, the relevant infection should be cured and the focus should not be placed on the swelling of the lymph nodes. Depending on the infection, there is then a corresponding therapy. In the case of mild bacterial and viral infections, no measures should be taken. In the case of severe bacterial infections, high-dose antibiotics should be given.
If a malignant background for a lymph node swelling has actually been proven, the therapy revolves around the treatment of the cancer. Such treatment can be a surgical procedure or it can be treated with radiation or chemotherapy. However, this cannot be precisely stated across the board and falls into a special field (oncology).
Also read our topic: Antibiotics in Pregnancy
Duration
Lymph node swelling lasts as long as the immune system fights off a pathogen. The duration of a palpable swelling of the lymph nodes depends on the severity of the clinical picture and the condition of the immune system.
Swollen lymph nodes that have existed for more than 1-2 weeks are more likely to indicate a stubborn or chronic case and should be examined by a doctor. All the more so if the lymph nodes cannot be moved, are coarse and painless.
Read more about the topic here: Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes
Do lymph nodes swell during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is neither a disease nor an inflammatory process in the sense that a defense reaction of the body would be required.
It can happen that the increased sensitivity of the immune system causes the lymph nodes to swell faster or more prominently than in non-pregnant women.
You can find more information about the changes in the body during pregnancy on our page: Everything about pregnancy








.jpg)