Dosage of Clexane
introduction
The respective dosage of Clexane® is selected according to the respective area of application.
Important: The dosages given are only guidelines and must always be selected and adjusted by a doctor according to the respective illness.

dosage
The Dose of Clexane® is determined depending on body weight or the disease risk or disease.
- Thrombosis prophylaxis: At low risk, 20mg / 0.2ml Clexane® is prescribed, at high risk, however, 40mg / 0.4ml.
- Thrombotherapy: If there is a thrombosis, 1 mg Clexane® per kilogram of body weight is administered twice a day.
- Unstable angina / non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI): Every 12 hours, 1 mg per kilogram of body weight is given.
- ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI): First, a bolus of 30mg is given, followed by a dose of 1mg per kilogram of body weight.
Except for intravenous bolus administration, Clexane® is injected under the skin into the subcutaneous fat tissue (administration = see c. = Subcutaneous injection; so-called "abdominal injection"). If the kidney function is severely impaired (creatinine clearance <30 ml / min), the Clexane® dose is reduced.
1mg Clexane® corresponds to an anti-Xa dose of 100 IU (international units). This means that 1mg Clexane® 100 IU inhibits factor Xa.
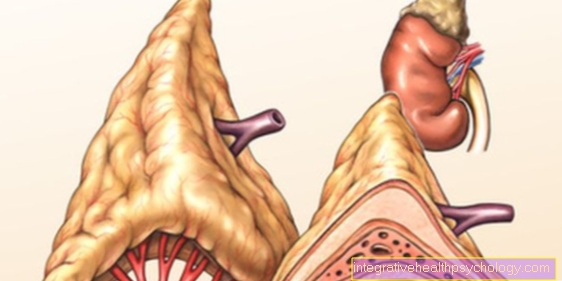
Clexane for renal insufficiency
The elimination of Clexane® is impaired in patients with impaired renal function. How much depends on the degree of renal insufficiency. If the excretion is reduced, the Clexane® concentration in the body is increased and, as Clexane® is a blood thinner, the risk of bleeding increases. Therefore, depending on the severity of the renal insufficiency, the Clexane® dose must be adjusted. In patients receiving Clexane® for thrombosis prophylaxis, the dose should be from one glomerular filtration rate (GFR) can be reduced from 15-30 ml / min to 20 mg subcutaneously once a day. Otherwise the dose for healthy kidneys is 40 mg. If the GFR is below 15 ml / min, Clexane® should no longer be used. In addition to thrombosis prophylaxis, Clexane® is also used to treat thromboses and embolisms that have occurred. A higher dose is necessary here than for thrombosis prophylaxis. No dose adjustment is necessary up to a GFR of 30 ml / min. If the GFR is between 15-30 ml / min, a dose of 1 mg / kg is still recommended, but the dosing interval should be increased from 12 to 24 hours. Instead of being administered twice a day, Clexane should only be used once a day.
Clexane for overweight
Clexane® is usually dosed according to the formula 1 mg / kg, i.e. weight-adapted. This means, for example, that a patient who weighs 70 kg receives 70 mg of Clexane (Clexane 0.7) while a patient who weighs 100 kg receives 100 mg of Clexane (Clexane 1.0). There is therefore no need to adjust the dose upwards or downwards in the case of overweight or obesity.
Therapeutic dosage
Clexane® is administered in therapeutic doses for diseases such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation or myocardial infarction. The therapeutic dosage depends on the weight and is calculated according to the formula 1 mg / kg. A woman with a body weight of 60 kg therefore receives Clexane 60 mg (Clexane 0.6). When Clexane is given in therapeutic doses, it is given twice a day. It is applied subcutaneously, i.e. under the skin, in the area of the abdomen or thighs.
Clexane® for atrial fibrillation
Clexane® can be used to thin the blood in patients with atrial fibrillation. Patients with atrial fibrillation have a significantly increased risk of stroke, so blood thinning is necessary. As a rule, atrial fibrillation is not treated permanently with Clexane® as this would mean that the patient would have to apply an injection twice a day for a lifetime.However, Clexane® is used especially at the beginning, i.e. with the initial diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. The therapeutic dosage, i.e. 1 mg / kg twice a day, applies. As a rule, patients are switched to an oral blood thinner during the course. Either on Marcumar (Phenprocoumon) or one of the direct oral anticoagulants. These include, for example, Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) or Eliquis (Apixaban).
Clexane® for deep vein thrombosis
Clexane® is approved for the blood-thinning treatment of deep vein thrombosis. The blood needs to be thinned to prevent more clots from forming. Clexane® must be administered in a therapeutic dose, i.e. twice a day at a dose of 1 mg / kg. The duration of use depends on the cause of the thrombosis and whether it is a first-time event or a recurrent thrombosis.
Clexane® for pulmonary embolism
Clexane is also used to treat pulmonary embolism twice a day at a dose of 1 mg / kg. Here, too, the duration of therapy is different and depends on several individual factors
Can I take Clexane® longer?
Patients receiving Clexane® therapeutically should usually receive blood-thinning therapy over a longer period of time. It is therefore the rule that these patients do not receive injections for the entire period but are switched to tablet therapy. Here, blood thinners are either relatively new drugs from the group of so-called direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) or the older drug Marcumar (Phenprocoumon). Marcumar is hired on the basis of a blood test, the INR. For most diseases to be treated, the INR should be in a range of 2-3 during therapy. In patients who are not taking any blood-thinning medication, it is around 1. In the first few days that Marcumar is given, the INR increases slowly, but is not yet in the target range. This means that the patient does not yet have sufficiently thin blood and is therefore not protected. Therefore, during this time, Clexane is given in an overlapping manner in order to bridge the time until the Marcumar level is high enough to make the blood as thin as desired. Clexane is given in therapeutic doses until the desired value is reached. Usually an INR of 1.8 or 2 is the limit value from which Clexane no longer has to be given overlapping.
Overdose
The greatest dangers of overdosing on Clexane® are Bleeding complications. These express themselves, for example, as Epistaxis (Epistaxis), bloody urine (Hematuria), bruises (Hematomas) of the skin, small bleeding in the skin (Petechiae) or bloody tarry stool (Melena). Signs of hidden, invisible bleeding include a drop in blood pressure or certain laboratory changes (Hemoglobin drop, hemoglobin = red blood pigment).
Actions to be taken when such complications occur are first Discontinue administration of Clexane® and at Severe bleeding during the course of an antidote injection: Protamine. This neutralizing agent is dosed in the first 8 hours after administration of Clexane® like Clexane® itself. If this time is exceeded, a lower protamine dosage is sufficient; if it is longer than 12 hours, it is no longer indicated to give protamine.
However, the bleeding can only be partially stopped by protamine, as this substance mainly attacks the anti-factor IIa activity. The anti-factor Xa activity, on the other hand, which makes up the main part of the effectiveness of Clexane®, can only be influenced with high doses and a maximum of 60%.