Egg cell
synonym
Oocyte, ovum
General
The egg cell is the female germ cell in humans.
It's haploid. This means that it only contains one set of chromosomes. In women, egg cells arise from the primordial germ cells and are used to multiply and pass on the genetic characteristics of the mother to her child.
Emergence
Egg cells are produced in the ovary (Ovary) in a process known as oogenesis.
In oogenesis, two maturities take place:
- the first division corresponds to a meiosis,
- the second of a mitosis.
The second meiosis only takes place when the egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell. At the end of oogenesis there are consequently four cells, of which only two are really developed into fully-fledged egg cells, the others are released as so-called polar bodies.
In contrast to their precursor cells, the resulting cells are no longer diploid, but haploid, i.e. they only contain one set of chromosomes. When an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell (sperm), which is also haploid, and these two cells fuse together, a diploid cell with a complete set of chromosomes is created again, from which a zygote capable of dividing and finally the embryo can develop.
While the male germ cell only supplies DNA to the zygote, the egg cell contributes not only its DNA but also cell water (cytoplasm) and other cell organelles, especially the mitochondria, which also contain DNA, but which can only be passed on from the mother's side.
Illustration of an egg cell
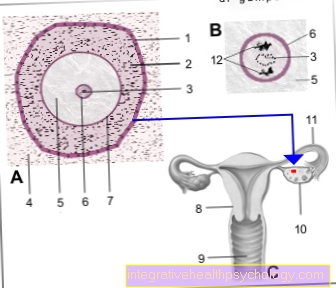
- Basin -
Membrana basalis folliculi - Granular layer
(seed-rich layer
of follicle cells) -
Epithelium stratificatum
cuboideum - Granules -
Nucleolus - Basic tissue of the ovary -
Stroma ovarii - Egg cell - Ovocytus
- Cell nucleus - Nucleus
- Glass skin - Zona pellucida
- Uterus - uterus
- Sheath - vagina
- Ovary - Ovary
- Fallopian tubes - Tuba uterina
- Polar bodies
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Structure of the egg cell
ova are the biggest Cells that occur in nature. For this reason, even the human egg cell, which is one of the smaller among all vertebrates, is still included naked eye visible.
The egg cells of mammals are not as big as those of, for example, birds or reptiles, as the Embryos of mammals over the Plaster cake (placenta) and therefore no yolk or egg white is required as additional food within the egg cell. A human egg cell has one on average diameter from 0.11 to 0.14 millimeters.
There is one on the very outside of the egg cell Shell layer called Zona pellucida, the outer Egg shell. This layer plays an important role in fertilization, because certain proteins that are contained in this shell bind the Sperm cell can be done to the egg cell. Once this has taken place, the zona pellucida dissolves.
The so-called Perivitellin space on. This holds true in this area sperm for a short time when it has succeeded in penetrating the zona pellucida. There are also the Polar bodiesshowing the excess DNA that the full-fledged egg cells no longer need.
On the other side of this fluid-filled space lies the inner egg shellthat cover the cell membrane of the egg cell (Oolemm) represents. This is inside the egg cell Ooplasm, in which the cell nucleus with the haploid DNA is located. In addition, there are some vesicles in the ooplasm that contain fat and albumin, among other things. These are used in the first phase of the Embryonic development of the nutrition the cell.
Number of egg cells ?!
Until recently, it was believed that women with a certain number are born from egg cells that can no longer change in the course of life. According to this belief, it was thought that after the last egg cell ovulated, a infertility result.
However, current research shows that this is not true:
Even in adulthood there are Ovaries well Ice stem cellswhich are still capable of division. In principle, the production of new egg cells is apparently still possible in adult women, but more detailed studies have yet to be carried out.
ovulation
Of the many ovathat are in Ovary approximately all develops four Weeks (according to the female cycle) only one egg cell is ready to a stage in which it is finally released from the ovary and from Fallopian tubes is recorded.
This phenomenon is known as ovulation or ovulation.
Like the entire cycle, this process is also controlled by Hormones. In the fallopian tube, the egg cell is now either from a sperm fertilized, whereupon they settle in the mucous membrane of the uterus can nest and a pregnancy begins.
If this does not happen, the egg cell reaches the uterus unfertilized, which means that the mucous membrane, which is thick at this point in time, is not needed there and is rejected by the body. This then leaves the female body through the vagina together with the egg cell and it comes to Menstrual period (Menstruation).
Read our article on this: ovulation
Fertilization of the egg
Fertilization, also called fertilization, is the fusion of the female egg cell with the male sperm. In humans, this can happen naturally through insemination during sexual intercourse and is possible around the time of ovulation. However, the development of modern medicine allows fertilization to take place artificially, mostly outside the body.
Several methods are available for this; The basis for all of them is the extraction of sperm, which takes place through masturbation or surgically from the testicles.
In vitro fertilization takes place in a test tube. Eggs must be removed from the woman. The egg cell and the sperm can now either be brought together in a test tube and find each other on their own, so that the actual fertilization takes place without external help. After in vitro fertilization, the fertilized egg cell, usually two at a time, has to be placed in the uterine lining. The chances that the egg will implant and become pregnant are around 40% and depend on some biological parameters such as the woman's age.
However, it is also possible to carry out an intracytoplasmic sperm injection; this is mainly carried out with less mobile sperm. A sperm is injected directly into the egg using a pipette.
There is also intrauterine insemination. In this method, the collected sperm are placed in the woman's uterus during the ovulation period so that fertilization takes place in the woman's body.
More on this topic under: Fertilization of the egg cell
Egg donation
With egg donation, several egg cells are removed from a woman at the same time after ovulation. This is done either with the help of a drug that causes several eggs to ovulate, after which the eggs can be removed vaginally. If this is not possible, the egg cells are surgically removed from the ovary, also known as the ovary. This usually requires an operation with general anesthesia.
Read more about this on the main page: Egg donation
Egg donation is used when a woman no longer has any eggs of her own and still wants to get pregnant. Egg donation is also used by so-called surrogate mothers, i.e. women who have a strange child because the actual mother is not able to do so.
Egg donation is prohibited in Germany and some other EU countries. This is the reason why some couples who want to have children decide to have this procedure carried out in another country. Countries in the EU that have made egg donation legal include the Netherlands, France and a few others. It is reported that egg donors in the United States who study at an elite university and have appropriate appearances are getting five-digit amounts for their eggs.
The complications of egg donation should not be underestimated. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome can occur after drug stimulation of the ovary; this is accompanied by pain and nausea. Furthermore, fluid can accumulate in the abdominal cavity (ascites), which has to be suctioned off. In the worst case, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome can lead to death.
Freeze eggs
Around Freezing eggs they have to be won first. To the medicinal stimulation and vaginal removal can these frozen and turned into one artificially fertilized later become.
Originally Egg freezing was used to young women before egg-damaging treatmentlike one chemotherapy at Cancersto remove healthy egg cells, so as to their Realize the desire to have children at a later date to be able to.
Meanwhile the technology is also from healthy women used, for example for professional reasons having a child late but would prefer to use biologically younger egg cells. With increasing age mother the risk of hereditary malformations increases as the Trisomy 21.