Diseases of the elbow
We cannot do without moving our hands and (forearms) arms, both in free quotation and when working. The elbow is centrally involved in these movements and can become ill in different ways. Sports injuries, inflammation or signs of wear and tear in old age are noticeable on the elbow and sometimes have a very restrictive effect in everyday life.
Here you will find an overview of the most common diseases of the elbow.
Classification
In the following you will find the most common diseases and injuries to the elbow broken down according to:
- Inflammation of the elbow
- Illnesses as a result of overuse or wear and tear
- Injuries to the elbow
- Specific diseases of the elbow
Inflammation of the elbow
Bursitis
Bursitis on the elbow (also Olecranon bursitis called) is a painful inflammatory condition of the joint that results from improper loading. The main symptom is often a painful swelling, which is usually very tender to the touch. The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of clinical symptoms; the chances of recovery are very good with adequate therapy.
Read more on this topic at: Bursitis on the elbow
Inflammation of the biceps tendon
The long biceps tendon is usually affected by the inflammation. The inflammation leads to the deposition of calcium salts, which limits the movement of the biceps tendon. Certain physical activities can lead to inflammation of the biceps tendon. It often affects professional athletes or people who do intensive sports. The diagnosis is made by the doctor and therapy can be conservative or surgical.
Read more about this under: Inflammation of the biceps tendon
Appointment with an elbow expert?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a former performance-oriented tennis player, I specialized early on in the conservative treatment of the elbow.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
arthritis
Arthritis describes the inflammation in the elbow joint. This can be infection-related or non-infection-related. In arthritis caused by infection, bacteria get into the elbow. Non-infectious arthritis, also known as rheumatoid arthritis, is a disease that belongs to the rheumatic group.
Read more on this topic at: arthritis
Illnesses as a result of overuse or wear and tear
Osteoarthritis in the elbow
The term osteoarthritis covers the group of chronic degenerative diseases. These are characterized by the fact that the articular cartilage is worn out, which can happen on the one hand as part of natural wear and tear during the aging process and on the other hand due to certain traumas. The therapy can be conservative or surgical.
Read more on this topic at: Elbow osteoarthritis
Tennis elbow
Tennis elbow is a pain syndrome in the area of the origin of the hand and finger muscles at the bony outer attachments of the humerus. Permanent overuse of the forearm muscles, which is caused by monotonous movements without adequate relief, is seen as the main trigger. Most tennis elbows heal with the right therapy; the limitation is rarely chronic.
You can find more information on this topic at: Tennis elbow
Golfer's elbow
The so-called golfer's elbow is an inflammation of the tendons of the flexors of the forearm muscles. Patients with golfers' elbows complain of pain on the inside of the elbow, where tendons attach, which increase when the fist is closed and the wrist is bent. The elbow pain usually radiates into the forearm and / or upper arm, so that the whole arm then hurts. Therapy for the golfer's arm is usually conservative, and surgery is only carried out in rare cases.
Read more on this topic at: Golfer's elbow
Mouse arm
The colloquial term "mouse arm" describes the unspecific clinical picture of the RSI syndrome (Repetitiv Strain Injury, German: Injury due to repeated stress). The term mouse arm covers various clinical pictures, such as pain or inflammation in nerves, tendons and muscles of the shoulder, elbow and hand. With the mouse arm, the movements in the arm and hands are very painful and restricted due to overload.
Read more on this topic at: Mouse arm
Injuries to the elbow

Torn ligament on the elbow
Movements that exceed normal levels can lead to overload injuries such as torn ligaments. These are mainly expressed in pain and swelling. When a ligament breaks in the elbow, the elbow joint is usually dislocated as well. In the case of a torn ligament in general, if it is a sports injury, an immediate sports break should be taken. Fast cooling is also important.
Find out more at: Torn ligament on the elbow - what now?
Dislocated elbow
You can dislocate your elbow joint through falls or sports accidents, so that either no more movement is possible in the joint or, if so, only very limited possible. In adults, the dislocation of the shoulder is more likely, but toddlers in particular suffer more often from a dislocated elbow, as their ligaments are even more elastic.
Read more on this topic at: Elbow dislocation
Specific diseases of the elbow
Panner's disease
The disease known under the term Panner's disease is bone necrosis that occurs in the area of the elbow joint. As a rule, children between the ages of 6 and 10 who play sports that put a lot of strain on the elbow joint are particularly affected.
The cause of this disease is a circulatory disorder of the growth plate in the area of the lower humerus or other bony structures of the elbow joint
Read more on this topic at: Panner's disease
Causes of pain in the elbow

Elbow pain can have a variety of causes.
Very often pain occurs after trauma. As a result of falls or accidents, muscles and ligaments can be pulled or otherwise injured or fractures (breaks) of the adjacent bones, i.e. humerus bones (Humerus) and forearm bones (radius or Ulna) occur. Furthermore, dislocations (dislocations) of the elbow are very often the cause of acute pain.
If the elbow joint is permanently overloaded, inflammation can be the cause of the pain. The tendons of the forearm extensor muscles and forearm flexor muscles - the tennis or golfer's elbow - that arise at the elbow are very often inflamed.
In addition to the tendons, an inflammation of the bursa can also be the source of the pain.
For chronic pain in the elbow joint that also affects other small joints such as arthritis caused by rheumatism should also be considered.
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the elbow
In addition to inflammation, prolonged overuse or improper use often results in osteoarthritis in the elbow joint, which is characterized by wear and tear on the cartilage. In contrast to the other causes of pain mentioned, here the pain occurs after longer periods of rest and improves with movement.
In addition to the external assessment, testing of the mobility and palpation of the structures involved, an initial suspected diagnosis can be made by describing the times of occurrence, the type and location of the pain. By other means such as X-rays, MRI, ultrasound or arthroscopy (Jointoscopy) the diagnosis can be completed.
Blood tests can also help, especially in the area of rheumatological diagnostics.
Dislocated elbows
A Elbow dislocation occurs much less often than one dislocation (Dislocation) of the shoulder. It often takes place with the application of external force, like that Fall on the outstretched or slightly pronated (palm is turned down) poor.
A dislocation is very common Accompanying injuries hand in hand.
In the event of a dislocation, the head of the spoke (caput radii) and / or the end of the facing the body slips Cubit, the olecranon, from the distal (facing away from the body) end of the Humerus (Humerus) that the three bone parts are no longer properly aligned with each other - they are postponed.
Basically one is dislocation in the Humeroulnars Joint, i.e. the articulated part between Humerus and ulna, more common than a dislocation between the spoke and humerus.
A shift backwards or backwards-outwards is very common. Of the Tape apparatus at the Elbow joint can just like the capsule tear in or off. Not infrequently do so Fractures (Broken bones) on the humerus, the olecranon of the ulna or the radial head. Unpleasant complications are injuries from Arteries, Veins and annoythat are near the joint to run.
There the humerus slips with its joint roller (Trochlea humeri) to the rear or rear-outside out of the bony hollow of the ulna, which is formed by the olecranon. But at the same time there is also one Shift in the connection between the upper arm and the spoke instead of. The joint surface of the radial head slips off the humeral head.
A ventral dislocation in which the Humerus pushes in front of ulna and radius.
A lateral or diverging dislocation also rarely occurs - Cubit and spoke move to different sides of the Humerus.
The Restoration (Reduction) of the original joint position Within a few hours to avoid consequential damage. This takes place under general anesthetic instead of moving the joint into the starting position with jerky movements, depending on the dislocation. After short Immobilization (1-2 weeks) he follows physiotherapy.
With possible accompanying injuries, such as Ligament and bone damage, is a surgery indicated to eliminate the damage.
A special form of Elbow dislocation is the Dislocation of the radial head in young children. There the head radii slips out of its articulated connection and is pinched by part of the ligament holding apparatus, the radial annular ligament. Often this happens when young children are held by the hand of their parents and are prevented from falling. The force that acts on the radial head cannot be held by the ligamentous apparatus, which is not yet very stable, and dislocation occurs. The children hold their arms in one after an incident like this Relieving posturewhere the poor and the hand slightly not turned inside are (pronation), hence the name pronatio dolorosa (painful pronation).
To restore the original position of the radial head is no surgery needed. It can be restored in a few simple steps by an experienced doctor.
Therapy for elbow pain
Taping
Taping for irritation in the elbow is said to help relieve the pain and increase blood flow to the affected areas. The increased blood flow is said to accelerate the healing process. It is hoped that the pain relief will result in the patient holding his arm less in a relieving position and thus avoiding cramps caused by abnormal positions.
Taping on the elbow is often used in the course of overload.
One possible application is the tennis elbow - the outer point of origin for the extensor muscles of the forearm is stimulated (lateral epicondyle). By sticking tapes over the back of the forearm from the bent wrist to the outer side of the elbow, the extensor muscles are relieved.
If the origins of the forearm flexors on the inner side of the elbow (epicondyle medialis) are irritated, taping can also be used. The tapes are affixed to the inside of the extended forearm along the flexor muscles up to the wrist.
In the event of further inflammation of the elbow, the muscle tummies of the upper arm extensor (triceps brachii muscle) attached to the elbow can also be taped.
Basically, only people who are familiar with the medical and anatomical principles of the elbow should tape. If used incorrectly, there is no supporting effect and in rare cases the problem can worsen.
Please also read our topic: Taping a tennis elbow
Elbow brace

Many muscles and tendons for the hand and forearm have their origin in the area of the elbow. In the event of irritation from one-sided movements or excessive strain, such as tennis elbow or golfer's elbow, a bandage on the elbow can have a supportive effect. The brace relieves and stabilizes the tendons and muscle origins.
A bandage can also be used to immobilize the elbow joint. The additional stability and immobilization can support the healing of an irritation.
In addition, a bandage can have a preventive effect before problems arise - it can be used prophylactically.
Read more on this topic at: Elbow bandage for a tennis elbow
Anatomy of the elbow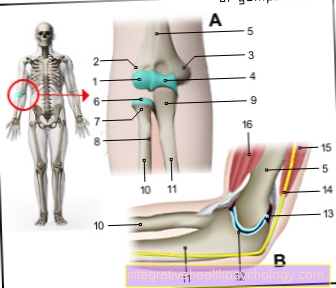
- Upper arm head -
Capitulum humeri - Outer femoral knot -
Lateral epycondilus - Inner femoral knot -
Epycondilus medialis - Upper arm roll - Trochlea humeri
- Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Spoke head - Caput radii
- Spoke neck - Collum radii
- Roughness of the spoke -
Radial tuberosity - Roughness of cubit -
Ulna tuberosity - Spoke shaft -
Corpus radii - Ellschaft -
Corpus ulnae - Articular cartilage
- Joint capsule -
Articular capsule - Ellen's nerve -
Ulnar nerve - Arm extensor -
Triceps brachii muscle - Upper arm muscle -
Biceps brachii muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Structure of the elbow
The elbow joint is made up of three bones:
- Upper arm bone (humerus)
- Ulna
- Spoke (radius)
By combining different types of joints (hinge, ball and pivot joint), the large degrees of movement and restrictions are possible. Since this joint is not constantly under load, wear and tear (osteoarthritis) without fractures or certain underlying diseases (e.g. rheumatism) are rare.