Swollen tonsils
definition
Whenever "swollen tonsils" are mentioned, inflammation of the paired tonsils is usually meant.
You can find out more about the topic here: Tonsillitis

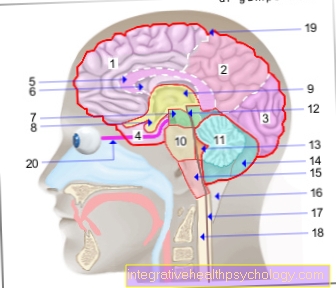
They are located in the back of the oral cavity on each side. According to their name, they look almond-shaped.
Since the oral cavity is in constant contact with the outside world and possible pathogens, the tonsils form a kind of "first defense barrier". In the event of a possible danger to the body, they activate the immune system and swell in the process. They are also known as the “guardians of the defense system”. However, they do not have to do this alone.
There are other tonsils in the mouth and throat. The unpaired pharyngeal tonsils, also called "polyps", are located on the roof of the pharynx. The paired tubular tonsils can be seen as a lateral continuation of the pharyngeal tonsils. Some also equate these with the "side strands". There is also a tongue almond. All together belong to the so-called Waldeyer throat ring. They are part of a relatively independent defense system and can swell as needed. However, in contrast to the lymph nodes, they only have so-called efferent connections that lead out. They are in close contact with the cervical lymph nodes.
causes
The causes of swollen tonsils are many.
The Tonsillitis usually arises initially through Viruses.
In the course can a bacterial inflammation to be added. But it is also possible that bacteria alone cause tonsillitis.
In many cases the viruses and bacteria enter the mouth and throat through the air we breathe. The acute, viral tonsillitis is often called Adenoviruses caused.
More acute and chronic tonsillitis are often caused by a specific group of bacteria known as Streptococci called, evoked. But other bacteria can also cause tonsillitis: staphylococci, pneumococci, Haemophilus influenza, Moraxella catharrhalis and Neisseria gonorrhae, among others.
Most of these bacteria are found in the mouth of healthy people and are harmless. They can only cause inflammation under certain circumstances. Because the swollen tonsils often subjectively a feeling of tightness trigger in the throat is also used by "angina"Spoken, which literally means" tightness ".
Depending on the causative agent, the Tonsillitis differently named. Also allergic processes and stress can lead to swollen tonsils. Often a weak, endogenous defense system favors the development of a Tonsillitis.
Find out more about the topic here: Tonsillitis
Swollen tonsils from stress
Swollen tonsils, as a sign of an activated body's own defense system, can through stress caused.
In stressful situations, the body releases various hormones that permanently influence the body's own defense system. Some studies report that it is more permanent negative stress, so-called Distress can lead to an increased susceptibility to infection. In addition, the interaction between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic the affect the body's own defense system, which can possibly also manifest itself in tonsillitis. The connections in detail are still being researched.
allergy
As part of a allergy swollen tonsils can occur. The tonsils can swell in the event of an allergic reaction with so-called histamine release and vasodilation. However, permanent inflammation of the mucous membranes due to allergies is also a risk factor for enlarged tonsils. The exact causes are still being researched. It has also been observed that enlarged tonsils can be caused by pain medication allergies.
diagnosis
First, the doctor systematically questions the person concerned.
In the Mirror examination he looks at the tonsils and throat. He can differentiate color, swelling and evidence.
He also tests how the tonsils react to pressure. He also palpates the mandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
If you suspect that Glandular Pfeiffer fever The neck and groin lymph nodes are also checked.
Through a Throat swab and a so-called Rapid streptococcal test the doctor can identify the pathogen. If the tonsillitis has been around for a few weeks, a so-called Antibody detection be useful.
If an allergy is suspected, one follows Allergy test. If Pfeiffer's glandular fever is suspected, an Ultrasound examination of the upper abdominal organs recommended.
Read more about the topic here: Glandular Pfeiffer fever
Concomitant symptoms
The swollen tonsils and the structures around the throat may be red.
Pus may leak from the tonsils. This can taste and smell unpleasant.
The bad breath can be strong. Furthermore, pain of various types can arise or not occur. In addition, it can become difficult to open the mouth, making it difficult to eat and speak. In addition, the lymph nodes in the neck and below the ear at the corner of the jaw can be swollen and painful.
Read more about the topic here: Lymph nodes on the neck
With glandular fever, the neck and inguinal lymph nodes can also be swollen. Furthermore, fever and fatigue may occur. Difficulty breathing and breathing noises, as well as a dry cough, can also occur.
If the swollen tonsils are dark red in children and a rash also occurs, and a shiny, characteristic "raspberry tongue" can be seen, scarlet fever should be considered. The rash usually develops between the 2nd and 3rd day of the illness. It is noticeable that the area around the mouth, as well as the soles of the feet and palms are left out.
You can find out more about the topic here: Scarlet fever
In the so-called Kawasaki syndrome, a "raspberry tongue" appears next to the swollen tonsils. But the rash particularly affects the palms of the hands and feet. First of all, redness can be seen here and then flaking. In addition, vomiting and diarrhea can occur in the context of Kawasaki syndrome. In these cases a doctor should be consulted.
Swollen tonsils and pain
Swollen tonsils arise as part of a defense process. This means that the body is fighting against a pathogen that it has classified as dangerous.
In the course of these defense reactions, various messenger substances can be released, which, among other things, can also trigger pain. If there is pain, it can be very different. The pain can also vary in quality. It can be burning or stinging. You may also experience difficulty swallowing and chewing pain.
You can find out more about the topic here: Causes of difficulty swallowing
In children, a sudden loss of appetite due to the pain when eating is noticeable. In babies, the pain manifests itself as a lack of drinking. The pain can also radiate into the ear, especially if the so-called side cords are affected.
The swollen lymph nodes are also often painful to the touch. Furthermore, mild to severe headaches can occur. In children, abdominal pain is often noticeable at the onset of tonsillitis.
You may also be interested in this article: Abscess on the head
Swollen tonsils and no pain
In some cases, the tonsils can swell painlessly and after a few days it will spontaneously decrease again without any consequential damage.
But also with permanently swollen tonsils, as part of a chronic tonsillitis, No pain.
Those affected often complain about you permanent unpleasant taste and odor in and out of the mouth. Intensive dental care does not usually alleviate the discomfort.
Even if chronic tonsillitis does not cause pain, it is important to treat it. Surgical removal of the tonsils is often advisable. If chronic tonsillitis is left untreated, the Bacteria in the blood of the person concerned. This allows them to to other organs be transported and severe complications trigger.
Find out more about the topic here: chronic tonsillitis
Swollen tonsils with pus
pus is always a Signs of bacterial inflammation.
A bacterial tonsillitis can therefore be characterized by the development of pus.
The so-called Tonsillar angina is often caused by the bacterium Strepptococcus pyogenes. Its name describes its properties: "Strepptococcus causing pus". Furthermore, the Plaut Vincent's angina, the Diphtheria angina and the Scarlet fever angina to the bacterial, purulent tonsillitis.
Pus consists of inflammatory cells called living and dead granulocytes, as well as body cells and bacteria. It basically shows the fight between bacteria and the body's own defense system. Pus shows up on the almonds as yellowish sticks or Toppings.
Some writers share one Tonsillitis in stages. According to this, the bacterial inflammations with yellowish pus are assigned to the 2nd stage, the so-called angina follicularis.
In the following 3rd stage, a so-called angina lacunaris, confluent, yellowish fibrin coatings appear.
At a chronic tonsillitis, you can also see a pulpy mass due to cell and tissue breakdown, the so-called detrius. Pus often comes out of the tonsils if the doctor presses on them during the exam. Most often the pus is very bad smelling.
In diphtheria angina this smells sweet.
Swollen tonsils without pus
A viral tonsillitis usually shows no foci of pus. Unless a so-called inflammation develops in addition to the viral inflammation Bacterial superinfection.
A purely viral tonsillitis is accompanied by no pus. Viruses have a different structure than bacteria and are fought by other cells in the body as well as by other mechanisms of the body's own defense system.
According to the staging, that counts viral tonsillitis to stage 1, the so-called angina catarrhalis. Are typical Redness and Swelling of the tonsils, without pus. This includes, for example Herpetic angina. It is common in teenagers. It is often characterized by recurrent inflammation of the tonsils and the pharynx. Those affected complain of burning Sore throat, headache, fatigue and Fever.
The tonsils are often only slightly swollen and reddened. At the onset of the disease, whitish-yellowish blisters are usually visible on the tonsils, on the palatal arches and on the cheek mucosa. The lymph nodes are often only slightly swollen. Herpetic angina heals by itself, usually after about a week.
In addition, monocyte angina is one of the Glandular Pfeiffer fever, to viral tonsillitis. But also with one allergy or as part of a HIV virus viral tonsillitis can develop without pus.
Swollen tonsils with a fever
Swollen tonsils, in the sense of tonsillitis, can be with fever accompanied. Children in particular have a higher fever with tonsillitis. Fever helps the body kill the pathogens.
Often the fever is with viral inflammation rather light to moderate. However, it works Pfeiffer's glandular fever mostly with high fever along with it, even if it was caused by viruses.
Furthermore, the fever can occur bacterial inflammation very high be. If you have a fever, a Arnt be visited.
Difficulty swallowing with swollen tonsils
Often it occurs at swollen tonsils difficulty swallowing. Also a swollen one Tongue almond triggers similar complaints.
The difficulty swallowing can be mild to severe.
Since the swollen tonsils narrow the exit of the oral cavity very strongly in some cases, the ingestion of food can be extremely painful or hardly possible. It should a doctor must be consulted. Until the treatment starts or takes effect soft food, such as yogurts, soups, and mashed potatoes are recommended. In addition, you should definitely use a adequate fluid intake ensured become.
Read more about the topic here: Causes of difficulty swallowing
shortness of breath
For example, if you have an allergic reaction, the tonsils and throat can swell so much that they become too shortness of breath can come. This is an emergency! An emergency doctor must be consulted immediately. The so-called "Kissing tonsills“Or enlarged tonsils trigger. Furthermore can Abscesses cause shortness of breath.
In very rare cases, the Tongue almond swell and cause shortness of breath.
therapy
Since the causes of swollen tonsils are varied, the treatments are also versatile. With slight, short-term tonsillitis, for example as part of a cold, certain Home remedies be enough. Often enough physical rest and adequate hydration. That too Sucking throat lozenges or lozenges can have a soothing effect. Also can Gargle solutions be pain reliever and anti-inflammatory.
Read more about the topic here: Tonsillitis- what helps?
If home remedies aren't enough, you can anti-inflammatory and analgesic, such as antipyretic drugs Create relief. If, after more than a week, the symptoms have not decreased or have worsened, a visit to a doctor is usually advisable.
Especially when there are abnormal breathing noises, breathing difficulties, fever, severe pain when chewing and swallowing and it is difficult to open the mouth. Also should be a Consulted a doctor if additional serious previous illnesses or acute rheumatic fever are known in the family.
At bacterial inflammation can Antibiotics support the body's own defense system in fighting the pathogens.
If there is a chronic tonsillitis has developed is usually one surgical removal of tonsils advisable. The point at which tonsillitis is classified as chronic and when an operation is recommended is controversial.
More on the subject: Almond removal
At Children under 4 years of age or the elderly will usually not advised to have surgery. At best, tonsils should not be removed until after puberty, since the tonsils play an important role in the immune system, especially in children. If children have massively enlarged tonsils that touch each other, an operation may be necessary in early childhood. Especially if the children are affected by these so-called "kissing tonsills“Suffer from severe swallowing and breathing difficulties. However, in this case the tonsils are usually only reduced in size with a laser and not completely removed. Imagines abscess on the tonsils and restricts the person's breathing, an operation is also recommended, regardless of age.
You can find out more about the topic here: Almond abscess
In some children, the tonsils are often bothersome and have to be removed. However, this operation is usually a smaller procedure, with less risk of bleeding, compared to the surgical removal of the tonsils.
Swollen almonds despite antibiotics
If, despite antibiotics, a purulent tonsillitis does not heal, one should definitely further diagnostics respectively.
It should viral diseases, including that Glandular Pfeiffer fever, be excluded. Antibiotics are ineffective for viral diseases. Instead, side effects may even increase. When taking the so-called ampicillin, a skin rash, a so-called rash can develop. This can occur even after antibiotic therapy is completed.
In addition, the prescribed antibiotic, despite confirmed diagnosis of bacterial inflammation, does not workn can. Since every body reacts very individually to medication and there are a large number of different antibiotics, it may well be that the right preparation was not selected straight away.
It should Under no circumstances should the antibiotic be discontinued independentlyas this can lead to complications. Instead, the attending physician should be consulted and a further course of action should be planned with him. Furthermore, the treatment of the chronic tonsillitis usually no longer successful with antibiotics. The drugs often no longer reach the diseased tissue.
Also are antibiotics for allergies and the so-called Kawasaki syndrome ineffective.
You can find out more about the topic here: Antibiotics for tonsillitis
Medication
The medication administration depends on the cause of the swollen tonsils, the accompanying complaints, but also on the age and general condition of the person affected.
Are the swollen tonsils part of a bacterial inflammation and a fever occurs at the same time, treatment with Antibiotics be advisable. Which antibiotic is used depends on various criteria.
Frequently becomes Penicillin V recommended. If you are allergic to penicillin, the so-called Cephalosporins can be used. In other cases, so-called Macrolides used. In certain cases you also use the so-called Clindamycin. W.
hen the swollen tonsils are the result of a viral disease, these drugs are not useful. Instead you can anti-inflammatory and anti-pain medicines have a soothing effect. If, however, in addition to the viral inflammation, there is a bacterial superinfection will come again Antibiotics, so-called Tetracyclines, recommended.
homeopathy
Homeopathic treatment is found to be effective by some sufferers with swollen tonsils.
Treatment should be individual, based on causes and symptoms. It is advisable to seek advice from a specialist. For example, can Phytolacca Can be used when the swollen tonsils are dark red, stabbing pain, difficulty swallowing, fatigue, the tongue is covered in the middle and hot drinks increase the pain.
Instead, you can Apis mellifica have a supportive effect when the swollen tonsils are fiery red, the uvula is swollen, the throat and throat feel swollen, the mouth is dry but not thirsty and the swallowing difficulties occur especially when eating and drinking.
Also can Hepar sulfuris have a supportive effect on purulent tonsillitis if there is intense, stabbing pain that radiates to the ear and sensitivity to cold and draft.
Moreover can Mercury be used for painful, purulent tonsillitis with bad breath and increased saliva formation.
Also can Lachesis for unilateral swollen tonsils and sore throats, which are aggravated by warm drinks, have a soothing effect.
Also can Belladonna and other substances have a supporting effect. As a rule, 5 globules are recommended 3 times a day, in a suitable potency agreed with the specialist.
If the Complaints do not improve or worsen, should definitely be one A doctor should be consulted. Homeopathic measures do not replace conventional medical treatment.
Home remedies
At a slight tonsillitis and one good body's defense system Home remedies can relieve the symptoms and facilitate the healing process.
For example, some sufferers feel Neck wrap as beneficial. These neck wraps can be filled with slightly warm cottage cheese, healing clay, onions or warm potatoes.
In addition, some sufferers find gargling with sage, chamomile or thyme tea beneficial. Others use for Gargle a few drops of aloe vera juice, salt or frankincense oil, which you mix in a cup with warm water.
In addition, those affected report relief from the Inhaling an infusion of sage. Furthermore, special, homemade Concoctions be beneficial and anti-inflammatory. For example, mixtures of a tablespoon of horseradish, a tablespoon of honey and a few cloves mixed with hot water can have a soothing effect. Some affected people also find mixtures with ginger beneficial. The mixtures should be left to steep for 10 to 15 minutes at a time. Drinking should be done in short sips and each sip of the drink should stay in the mouth for a minute if possible.
Another very old home remedy that sometimes seems effective is Baked apples with honeythat should be consumed warm.
Also can Propolis with a little sugar that can be melted on the tongue, help against swollen almonds. These can also be gargled with warm water several times a day as required.
Often is a neck kept warm beneficial with a scarf. Furthermore, the mucous membranes should, through moist room air and through adequate hydration, kept moist.
Water, warm or cold, and herbal teas as desired are recommended.
Should it no improvement with the help of home remedies or even one deterioration should come absolutely consulted a doctor become.
Duration
The duration of swollen tonsils can vary widely depending on the cause and circumstances.
With an uncomplicated, acute tonsillitis go the complaints mostly after 3-5 days back. The disease is common after 1-2 weeks completely healed without permanent damage.
In some cases, however, tonsillitis can occur longer than three months stop. Some authors refer to this as one chronic tonsillitis. Others already define tonsillitis that longer than two weeks last as a chronic condition.
Other authors speak of chronic tonsillitis when this several times a year occurrence. The number is also controversial. In addition, there are authors who make the definition of chronic tonsillitis dependent on the clinical picture, i.e. the symptoms of the person affected. Ultimately, it remains the responsibility of the attending physician to assess the individual situation and recommend appropriate measures.
Read more about the topic here: How long does tonsillitis last?
Are swollen tonsils contagious?
A Tonsillitis can about Droplet infection transmitted and is contagious. That is, by shaking hands, sneezing, coughing, and speaking, the inflammation can be passed on.
The risk of infection is particularly high in the first days very high. Even when taking an antibiotic there is a risk of infection in the first 2-3 days.
Read more about the topic here: This is how contagious tonsillitis is
A special tonsillitis called Plaut-Vincent-Angina is usually not infectious. Of course, swollen tonsils caused by allergies are also not.
Swollen tonsils- an indication of HIV?
First of all, with a HIV infection for a long time no complaints or unspecific complaints occur. As the immune system is affected, swollen, sore tonsils can also develop. Besides that you can Fatigue, fever for several days, Headache, joint pain and muscle pain, mouth sores and Rash on the back, chest or belly occur. In addition, those affected often notice a massive one Night sweats.
Since these symptoms are relatively unspecific, an HIV infection often goes undetected for a long time. If the symptoms mentioned above occur and there is a suspicion, this should be clarified by a doctor.
Read more on the subject here: Symptoms of HIV
Swollen tonsils during pregnancy
During pregnancy, an altered body's own immune system can be responsible for the fact that swollen tonsils and tonsillitis can occur frequently.
Often, however, these are harmless and heal by themselves without medication.
If the tonsillitis are more persistent, medication may be necessary. Since not all drugs can be taken during pregnancy in order not to harm the mother and the unborn child, a Medication intake must be discussed with the doctor become.
Swollen tonsils after a wisdom tooth operation
After wisdom tooth surgery, you may experience swollen tonsils and a sore throat. Since not everyone goes to the doctor afterwards, it is difficult to estimate how often these occur after a wisdom tooth operation. It is estimated that around 2 in 10 people who have wisdom tooth surgery have pain in their throat and throat.
As root cause one suspects a possible disruption of the natural environment in the mouth caused by a Injury to the mucous membraneoccurred during the surgical procedure. The mucous membrane consists of so-called lipids, immunoglobulins and proteins, all of which contribute to the defense against pathogens.
If the oral mucosa is injured, the susceptibility to infection can be higher. Besides, it can too inflammatory processes of the teeth that can spread to the tonsils. The tonsils usually swell on one side.
Read more about the topic here: Inflammation after a wisdom tooth operation
Swollen tonsils after angina
Frequent tonsillitis often leave their mark: the Almonds appear scarred and fissured. As a result, bacteria can easily penetrate, multiply and spread here. In addition, abscesses can develop after tonsillitis.
Furthermore, complications can arise after bacterial tonsillitis. It can too Middle ear and sinus infections, rheumatic fever or to Kidney corpuscle inflammation, called glomerulonephritis. In addition, a Endocarditis and at worst one sepsis develop. Such complications can easily be avoided if complaints are recognized and treated at an early stage.
You can find out more about the topic here: angina
Peiffer's glandular fever
The Glandular Pfeiffer fever is a febrile systemic lymphatic disease. In technical jargon they are also known as Mononucleosis. In this context, so-called monocyte angina can occur.
The Neck, neck and inguinal lymph nodes are often severely swollen. The liver and spleen are also affected. The Pfeifferian glandular fever is triggered by the so-called Epstein-Barr Virus. Those affected are mostly teenagers or young adults.
Antibiotics are ineffectiveunless a bacterial superinfection has developed in addition to the viral infection. Otherwise the glandular fever can only be with pain relievers and anti-inflammatory agents be treated. Some people also take Corticoids a. Its use is controversial in the context of Pfeiffer's glandular fever. Since there are no well-founded studies on the proven effectiveness in this context, opinions differ. Especially important physical conservation, as the liver and spleen can also swell. There is a risk of one life-threatening ruptured spleen.
You can find out more about the topic here: Glandular Pfeiffer fever
Single swollen tonsils
The tonsils are swollen on one side not that often in front like both sides swollen tonsils.
Unilateral swollen tonsils can have different causes. Often times they come under one-sided Tooth infections or Tooth root operations past Syphilis infections, tuberculosis or benign and malignant tumors.
In addition, they can go through unilateral bacterial inflammation arise. For example, a unilateral bacterial inflammation, a so-called Plaut-Vincent angina arise. It mostly only occurs in adults, often in men. It is triggered by an infection with so-called spirochetes (Borrelia vincentii) and so-called fusiform rod bacteria (Fusobacterium fusiforme). These pathogens are normally part of the healthy oral flora. For reasons that are not clear, these cause Plaut-Vincent angina in some cases. There is usually no risk of infection. The tonsils are reddened on one side and gray-whitish coatings can be seen. These plaques resemble an ulcer. They often smell unpleasant. In addition, there is often increased salivation, difficulty swallowing, swelling of the lymph nodes, fatigue and fever.
In addition, there is usually an inflammation of the oral mucosa, a so-called Stomatitis, recognizable. However, subjectively, this often causes minor complaints. The uncomplicated Plaut-Vincent angina usually lasts 8-10 days and heals without any consequential damage.
Almonds swollen on both sides
If the Pathogen tonsillitis from the outside into the oral cavity have occurred, then mostly the tonsils both sides - left and right - swollen. The reddening of the back of the throat is usually strongly reddened on both sides. Coatings and pus on the tonsils can usually be seen on the left and right side of a bilateral tonsillitis.