Swollen hollow of the knee
definition
Behind the swelling of the hollow of the knee there are numerous, different clinical pictures that have different causes and bring with them various accompanying symptoms. What causes the symptoms depends on many factors, such as various underlying diseases, accidents, lifestyle, age and gender.

Depending on the cause, the swelling may be the only symptom or it may be accompanied by pain, signs of inflammation, or joint stiffness. Accordingly, the diagnosis and treatment of the swollen hollow of the knee are very different.
Read more about this under: Swelling - what's behind it?
causes
The causes of the swollen hollow of the knee depend on the age, gender and living conditions of the patient. Often one solves over - or Incorrect strain on the knee the swelling out. This usually improves in peace. To Accidents and Fall ligaments, cartilage, bones or the capsule of the knee joint may be damaged, which is also expressed in swelling.
Permanent swelling that may be painful can indicate a Baker's cyst, i.e. a fluid-filled protrusion of the joint capsule.
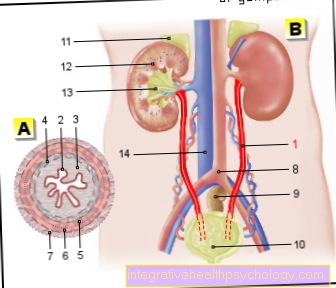
This accumulates on the floor of a previous rheumatic disease and tends to affect the elderly. One dreaded cause is this Deep vein thrombosis: This mainly affects women, can cause severe pain and dangerous complications. In rare cases, and especially in older men, a so-called poplietal aneurysm can be used for swelling of the hollow of the knee. This is a Bulging of the arteryrunning through the back of the knee.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
thrombosis
A thrombosis is a Blood clotsthat builds up in a vein and blocks it. Thromboses often form in the legs, as the blood "sinks" here when standing and sitting; Thromboses in the deep leg veins are more relevant than those in the superficial cutaneous veins (Phlebothrombosis).
The risk of developing a thrombosis increases through prolonged immobilitye.g. from sitting for long periods of time while traveling or wearing a cast on your leg. Smoking, especially when taking the pill at the same time, being overweight and being older also increases the risk of thrombosis. Women are affected significantly more often than men.
It is important to recognize a thrombosis and, if necessary, treat it, as it can lead to serious complications: If the clot loosens, it is carried away in the bloodstream and can then block a blood vessel in the lungs, less often in the heart or brain. If you suspect a thrombosis, you should therefore see a doctor immediately.
Symptoms
Depending on the cause and extent of the swelling, different symptoms are observed. The knee joint can hurt and feel unstable feel, which is particularly noticeable when the leg is loaded. Sometimes the Cracked skin and brittle Act. If the skin barrier is not intact, it can lead to bleeding or Inflammationto exit pus come.
With inflammatory processes, the knee appears reddened and overheated. If the swelling puts pressure on nerves or muscles, parts of the skin can expand deaf feel like the muscles are weakened. Often the mobility in the knee is limited. Bending the leg in particular can cause pain and is then not completely possible or even completely eliminated. The timing and connection of the complaints also depends on the underlying cause: If excessive or incorrect stress triggers the symptoms, these usually improve Immobilizing the leg. Inflammatory processes, on the other hand, can be alleviated by gentle exercise adapted to the pain.
Swollen hollow of the knee with pain
If pain occurs in addition to the swelling, the cause is usually either one trauma or one inflammatory process. Inflammatory processes particularly affect the tendon attachments of the muscles that run through the hollow of the knee (the so-called ischiocrural muscles); one speaks here of the Tendonitis of the muscle concerned.
The joint capsule can also hurt due to inflammatory processes. After trauma, bones, ligaments, muscles, and cartilage can be damaged and then hurt too. Often it is pain then load-dependent. Another painful clinical picture is the Baker cyst. This is a fluid-filled bulge in the joint capsule. Finally, thrombosis can also cause pain.
Swollen hollow of the knee without pain
Painless swellings in the hollow of the knee are far less common than those that cause pain. A so-called sarcoma can cause these symptoms. This is one malignant tumorwhich mostly arises from fat, bone or muscle cells, but is extremely rare. Another cause may be Poplietal aneurysm be: This is a bulging of the popliteal artery. This may or may not be painful. Water retentionwhich also cause painless swelling, affect the entire lower leg rather than localized the hollow of the knee.
diagnosis
The doctor can make a diagnosis by asking the Medical history of the patient, e.g. after injuries, Taking medication and Pre-existing illness is asked. The physical exam examines the degree of mobility and any pain. Imaging procedures like the Ultrasonic or one X-ray, represent soft tissues or bones in the hollow of the knee. In other cases, a MRI be necessary (diagnosis of anterior / posterior cruciate ligament tear or cartilage damage) or contrast agents are administered (visualization of diseases of the vessels, e.g. thrombosis or poplietal aneurysm).
therapy
The therapy for the swollen hollow of the knee varies greatly depending on the cause. In many cases, minor injuries or incorrect loads caused irritation or local inflammatory reactions. Then the leg should temporarily relieved and chilled until the discomfort subsides. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen or Voltaren ointment can also help.
In other cases, and especially when conservative therapy does not work, a surgical treatment become necessary: Serious injuries (e.g. torn ligaments, cartilage injuries, bone fractures) may have to be treated surgically.
Chronic processes that cause the swelling can go through Compression stockings and treatment of the underlying disease. If this conservative approach does not work, an operation may have to be carried out here as well. Treatment of thrombosis includes regular check-ups and drug therapy that inhibits blood clotting. Possibly. must also be operated on here to remove the thrombus.
homeopathy
In addition to conventional medicine, homeopathic treatment can be helpful. The taking of arnica has a pain relieving effect. Be after a fall or twisting of the knee joint Bryonia alba and Rhus toxicodendron recommended. Bryonia alba reaches the joint capsule and can also have a pain-relieving and irritation-relieving effect, Rhus toxicodendron generally improves dislocations and joint problems. However, one should know the limits of homeopathy. The Baker's cyst, for example, has to be treated with medication or surgically removed. The thrombosis can develop into a life-threatening emergency and therefore requires a quickly effective and reliable medical therapy.
Duration
How long it takes for the hollow of the knee to resolve depends to a large extent on the cause of the swelling. In general, a conservative approach, i.e. non-surgical treatment, is rather tedious. The swelling disappears as soon as the trigger, e.g. the underlying disease or injury has been treated, which can take a few weeks. An operation usually promises faster recovery: For example, if a Baker cyst has been surgically removed, the surgical area will still be swollen for a few days, but should soon look normal again.
Swollen hollow of the knee during pregnancy
If a swollen hollow of the knee (or a swollen lower leg) occurs during pregnancy, one must - in addition to the diseases mentioned above - the so-called pre-eclampsia think. It comes to the named Swelling, in this case Water retention, high blood pressure and one damage of the Kidneys.
In addition, those affected report on Drowsiness, Eye flicker, a headache and nausea. The disease can harm both mother and child, which is why they must be hospitalized. In extreme cases, childbirth must be initiated in order to successfully treat the disease.
Swollen hollow of the knee with involvement of the calves
If the swelling covers the entire calf, local inflammations, diseases of the veins or injuries are also possible. However, there are also some other clinical pictures that need to be clarified. Weaknesses of the heart or the liver (Heart failurezienz, Liver failure) can lead to water retention (Edema) that collect at the lowest point, i.e. in the lower legs.
Some medications can also cause edema. In these cases both calves are usually affected. If only one calf is swollen, a possible thrombosis should be reconsidered. The lymphatic system can also be damaged and lead to swelling of the calf, for example after surgery in the leg or groin or after radiation treatment. One then speaks of one Lymphedema. This is often the case after cancer treatment, when the affected lymph nodes have been removed.
Certain parasites, bacteria or viruses can also lead to a loss of lymphatic drainage with edema formation. Certain systemic diseases, e.g. some Forms of rheumatism, can cause calves to swell.
Swollen back of the knee after jogging
If the swelling occurs in the hollow of the knee after exercise, e.g. Jogging is often the cause of excessive strain or improper stress. The muscles in the hollow of the knee - clinically referred to as the hamstring muscles - can be irritated or even inflamed after excessive stress. The inflammatory process is then accompanied by swelling and pain. Incorrect strain on cartilage and ligaments or damage to them can also be a reason. In any case, the training should be reduced, and even paused completely at first. Cooling and elevating the leg and taking anti-inflammatories can help.
Swollen hollow of the knee from veins
Various diseases affecting the veins can cause the hollow of the knee to become swollen. There is an acute need for action here in the case of thrombosis of the deep veins in the leg. Chronic processes include inflammation (phlebitis) or weakening or bulging (Varicose veins, Varicose veins) of the veins. If this causes the blood to back up - often in the elderly or from standing for long periods - or if an inflammatory reaction takes place, local water retention can occur. These so-called edema lead to swelling and require clarification.
Swollen lymph nodes in the hollow of the knee
There are usually about six lymph nodes in the hollow of the knee. Like the rest of the lymphatic system, they mostly take over Defense tasks and help the body to recognize and fight germs and pathogens. Swollen lymph nodes can have a variety of causes, from harmless local infections to malignant cancers (which, however, are much rarer).
Swollen lymph nodes in the hollow of the knee are rather rare, mostly the lymph nodes of the neck or groin swell when infected. In the hollow of the knee they therefore indicate a local infection, e.g. after an injury. You should be further clarified, as there may be a therapy, in worse cases e.g. with antibiotics, may become necessary. Often they are then accompanied by other signs of inflammation such as pain, overheating, reddening or fever and are easy to move in the tissue. In cancer, enlarged lymph nodes tend not to hurt, but they cannot be moved in the tissue.





.jpg)