Gluten intolerance
definition
Gluten intolerance is a disease with many different names: Celiac disease is the most common name in the medical field. But the disease can also be referred to as native sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy.

As the German name suggests, the disease is one Gluten intolerance underlying. Symptoms range from abdominal pain and diarrhea to significant weight loss and vitamin deficiencies (see also: Vitamin deficiency). The only treatment option is to completely avoid gluten. If this diet is followed, the prognosis is very good.
causes
A gluten intolerance means that the body cannot tolerate gluten. Gluten is a protein found in numerous types of grain. The gluten intolerance has both parts of an allergy (see also: Food allergy) as well as an autoimmune disease, i.e. an excessive reaction of the immune system to gluten.
The result is that contact with gluten causes a permanent inflammatory reaction in the small intestine (see also: Inflammation of the small intestine). This leads to a partial destruction of the surface of the small intestine. This in turn means that numerous nutrients in the small intestine, including those that the body actually tolerates, can no longer be adequately absorbed.
Why gluten intolerance occurs has not yet been conclusively clarified. There seems to be a hereditary component. This can be deduced from the fact that if one of the twins of identical twins falls ill, the likelihood of illness for the other twin is significantly higher than in the general population. Relatives of sick people also have an increased risk of developing gluten intolerance. A genetic predisposition is currently assumed to be the main cause. However, research in this area is still ongoing.
Diagnosis
First of all, on the way to finding a diagnosis, the anamnese an important role. The attending physician will ask what symptoms are present, when they occur, which foods lead to the occurrence of the symptoms, whether there are similar symptoms in the family, whether there has been a weight loss and how long the symptoms have existed.
Then the physical examination. Among other things, the weight is checked here. If there is a suspicion of celiac disease, you can first Blood tests respectively. If there is a gluten intolerance, certain ones can be found here antibody prove. If this proof is provided, however, it is not sufficient for a reliable diagnosis. It also has to be a Gastroscopy respectively. After anesthesia of the throat or during a short anesthesia, a tube (gastroscope) is pushed over the throat and the esophagus into the stomach and down to the small intestine. Several samples must be taken from the small intestine (Biopsies) can be removed. These are examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Here it can be assessed whether the villi atrophy typical of gluten intolerance is occurring, i.e. a loss of certain surface features of the small intestinal mucosa. It can also be assessed whether and how many inflammatory cells are present in the intestinal mucosa. The diagnosis is only confirmed by such an examination of the mucous membrane samples.
What tests are there for gluten intolerance?
Specific tests that laypeople can carry out to find out whether they suffer from gluten intolerance have also been around for some time.
First, if you suspect gluten intolerance, you can try for Switch to a completely gluten-free diet for a few weeks. If this leads to a significant decrease in symptoms, the diagnosis is likely. The attending physician should then be consulted for final confirmation.
There are other tests such as the D-xylose testtrying to measure how limited the absorption of certain nutrients is in the small intestine. However, they are not sufficient for the diagnosis. For this, a sample from the small intestine is absolutely necessary. For some time there has been Blood tests that show certain antibodies can buy even for the layman. The test is similar to the blood test the doctor does. However, a negative result does not reliably rule out the presence of celiac disease.
What are signs of gluten intolerance?
The gluten intolerance will often discovered in childhood, when starting to feed grain products. It comes to Diarrhea and not infrequently too Fatty stools, that is, foul-smelling, shiny and voluminous stools that occur in the context of fat digestion disorders. The affected children often have little appetite. There is nausea and vomiting. It is not uncommon for one to develop over time Failure to thrive. The children are therefore underdeveloped in terms of their weight and size for their age. After an initially normal development curve, there is a kink. This can also be noticed for the first time during the check-ups at the pediatrician.
One is also typical for gluten intolerance in children bulging belly otherwise rather thin limbs. Also abnormalities on the teeth, such as stains, can occur in the case of gluten intolerance.
In adolescents and adults, the symptoms are often not that typical and pronounced. Here you can chronic fatigue, loss of appetite, bone pain, and paleness indicate a gluten intolerance in the context of anemia.
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to the typical diarrhea, as well as nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite, gluten intolerance can be permanent Fatigue, listlessness, increased irritability, pale skin, and bone and muscle pain demonstrate.
Symptoms on the skin
With gluten intolerance, it can Vitamin deficiencies come. These can cause numerous symptoms.
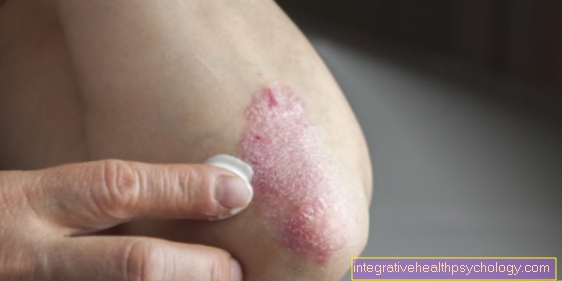
The skin can be noticeable dry be. Also one pale skin can occur, as it is not uncommon for one Anemia comes. This is through a Iron absorption disorder conditionally. Patients who suffer from gluten intolerance can also develop a certain skin disease. This is called Dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring. It occurs much more frequently in patients with celiac disease than in the general population. The condition is associated with different types of rash. It can too Blistering, redness, wheals and eczema with burning and itching come. The main locations of the rash are knee and elbows. Other parts of the body can also be affected less frequently.
skin rash
A skin disease with a name Dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring occurs almost exclusively in people who also suffer from glow intolerance. It shows up in various types of skin rashes. The gluten-free diet plays an important role in therapy.
Pimples
Normal single blackheads do not occur more frequently in the context of gluten intolerance than in the general population. However, some celiac patients have an additional skin condition called the Dermatits herpetiformis Duhring. With this you can numerous small pimples / blisters on the skin which can occur especially after eating cereal-based foods.
Weight gain
The gluten intolerance itself is usually not a cause of weight gain. Especially with children it can more likely to lead to weight loss come. However, some studies have shown that once diagnosed, following a gluten-free diet leads to weight gain in some people. However, there are various study data on this. Other studies show that there is no significant weight gain on a gluten-free diet.
nausea
Nausea is a symptom that can occur with gluten intolerance. Together with loss of appetite it comes especially in childhood in front. However, adults with celiac disease can also experience nausea. After changing your diet, the nausea will usually go away.
diarrhea
Diarrhea is the main symptom of gluten intolerance. Due to the chronic inflammation in the small intestine, the nutrients absorbed with food can no longer get enough into the blood. They therefore reach the large intestine, where they are broken down by the bacteria that live there. This creates gases and other substances. That leads to Diarrhea, gas, and abdominal pain. A fat digestive disorder can also lead to fat stools. These are greasy, shiny and smelly.
Symptoms in the child
The first symptoms are common when feeding grain products on. The children suffer from diarrhea, abdominal pain, gas, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, and do not gain enough weight.
treatment
Treatment for gluten intolerance is primarily one complete diet change. It must strictly renounces foods containing gluten become. Since gluten is found in most types of grain, such a diet is often not easy to implement at the beginning.
With a gluten-free diet, there is a slow recovery of the small intestinal mucosa and the symptoms are usually completely regressive.
Grains that must be strictly avoided are rye, barley and wheat, as well as spelled and oats. Since gluten is also often used as an emulsifier or for gelling, it must be ensured that finished products do not contain any gluten.
Grains such as millet, rice, corn and buckwheat are allowed in a gluten-free diet. Chestnut and soy flour can also be used alternatively. Potatoes and dairy products as well as meat, fish and eggs are no problem either.
Can gluten intolerance be curable?
In the conventional sense, gluten intolerance cannot be cured, as the symptoms keep recurring when foods containing gluten are consumed. However, the disease can be described as curable insofar as a strict gluten-free diet usually completely recovers the mucous membrane of the small intestine and leaves no symptoms.
What are the consequences of gluten intolerance?
Gluten intolerance can occur in children permanent tooth damage and one Growth retardation to lead. It can also lead to nutrient and vitamin deficiencies. This can lead to a reduced iron absorption. This can lead to anemia. Due to a lack of calcium and vitamin D, as part of the resorption disorder, the development of osteoporosis, i.e. increased bone fragility, can be promoted.
That too The risk of developing other autoimmune diseases is increased. These include, for example, thyroid diseases. In patients with celiac disease depression is more common. This is also the case with a gluten intolerance that goes untreated for decades Increased cancer risk.
However, most of these consequences can be prevented by following a gluten-free diet.
Which beer can I drink if I have gluten intolerance?
There are special gluten-free beersthat may be drunk if you have a known celiac disease. There are gluten-free beers that are made from gluten-free grains and those that are made from gluten-containing grains, but in which the gluten was largely broken down during the production process. Gluten free beer is more expensive than regular beer and most importantly available in health food stores / health food stores.
Which alcohol can I drink if I have gluten intolerance?
Generally should Types of alcohol that contain gluten are avoided. These include, for example, the conventional types of beer. However, there are now gluten-free beer that can be drunk by patients with celiac disease.
High-proof alcohol such as whiskey, vodka, rum, wine and sparkling wine do not contain gluten and can be drunk. Be careful with cocktails, as the additives are often not listed on the cocktail menu.