Carpal
Synonyms
Wrist, scaphoid bone, Scaphoid bone, Navicular bone, Moonbone, Lunate bone, Tripod, Os triquetum, large polygonal leg, Trapezium, small polygonal leg, Tapezoid bone, Head leg, Os capitatum, Hook leg, Hamate bone, Pea bone, Os pisiform
English: wrist

Figure carpal bones
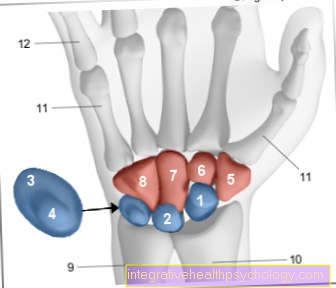
The eight carpal bones
Upper (proximal) row - blue
Lower (distal) row - red
- Scaphoid bone of the hand -
Scaphoid bone - Moonbone - Lunate bone
- Triangular leg - Os triquetrum
- Pea bone - Os pisiform
- Large polygonal leg
(Trapezoidal leg) - Trapezium - Small polygonal bone
(Trapezoid leg) -
Trapezoid bone - Head leg - Os capitatum
- Hook leg - Hamate bone
- Cubit - Ulna
- Spoke - radius
- Metacarpal bones - Metacarpals
- Phalanx - Ph. Proximalis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
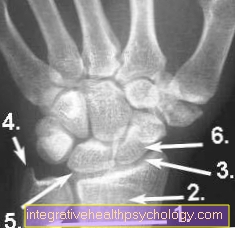
X-ray wrist
- Cubit (Ulna)
- Spoke (radius)
- wrist
- Stylus process (Ulna styloid process)
- Moonbone (Lunate bone)
- Scaphoid (Navicular bone)
anatomy
The so-called carpal lies between the end of the spoke (radius) and metacarpal (Metacapal bone) and is formed by the individual carpal bones. The carpal bones lie in two rows. The first row of carpal roots forms the wrist with the end of the spoke.
In the first row of the carpal roots (directly on the wrist), starting with the thumb, is the Scaphoid (Scaphoid bone, earlier Navicular bone), next to that Moon leg (Lunate bone), next to that Triangular leg (Os triquetum). The so-called Pea bone is most on the little finger side and is not a "real" carpal bone.
The second row of carpal roots (closer to the fingertips) is on the thumb side, starting with the large polygonal leg (Trapezium), next to that small polygonal bones (Trapezoid bone), next to that Head leg (Os capitatum) and on the little finger side that Hook leg (Hamate bone).
All the carpal bones are tightly connected by tight ligaments. The mobility of the individual bones against each other is limited.
Since the carpal bones are convex when viewed from the side, a longitudinal groove is formed on the palm side, which forms the carpal tunnel.
Also read: Carpal tunnel syndrome
The scaphoid
The scaphoid bone (Scaphoid bone) is the second largest Bones of the wrist and lies thumb side, in the row of bones close to the body. It is convex and has six sides. This connects it to the adjacent carpal bones and the radius of the forearm. Because of this many links is most of the scaphoid bone with cartilage covered, of which the articular surfaces are made. Of the Humps (Tuberculum ossis scaphoidei) of the navicular bone serves as the origin of the muscle and can be easily felt on the palm of the hand.
The moon leg
The moon bone (os lunatum) is located central in the back row of bones of the wrist and resembles, as the name suggests, roughly one Crescent moon. Towards the thumb it borders on the navicular bone and on the other side on the triangular bone. Like the scaphoid, it is also with the spoke of the forearm in articulated connection, as well as with the head and hook bones of the bone row distant from the body.
Falling on the hand can lead to so-called "perilunal dislocation“Come, whereby the connections to the other carpal bones tear off. However, this is rather rare.
The triangular leg
The triangular leg (Os triquetrum) is a roughly pyramidal bone the row of bones near the wrist. With its base, it borders on the side Moon legwith which it, along with the navicular bone, the Articulated connection to the spoke of the forearm. To the front it borders on the hook bone and has a small articular surface at its tip towards the palm of the hand. This is him on this one Pea bone superimposed.
The pea bone
The pea bone (Os pisiform) is the smallest bones the wrist. It rests on the triangular leg and is located at the end of the little finger ball near the body, where it also passes through the skin palpable is. Since it is in the tendon of the ulnar hand flexor (M. flexor carpi ulnaris) is embedded, it is one of the so-called Sesame bones. These act as spacers between the surrounding bones and the tendon and act as a kind Pulleywhich increases the strength of the muscle.
The large polygonal leg
The large polygon is lying thumb side in the row of carpal bones distant from the body. It forms this with the first metacarpal bone Saddle thumb joint. Its other articulations exist to the small polygonal bone and the scaphoid bone, as well as to the metacarpal bone via a small joint surface Index finger. Palpable when the back of the hand is pulled up (dorsiflexion), the large polygonal bone becomes through a small bone hump on its upper side.
The little polygonal bone
The small polygonal bones (Trapezoid bone) is located in the row of bones remote from the body between the large polygonal bone and the head bone, with which it is articulated. Furthermore, it borders on the metacarpal bones of the Index finger and thus forms one Part of the carpal-metacarpal joint.
The head leg
The Head leg (Os capitatum) represents the biggest of the eight carpal bones and is located in the row of bones distant from the body. On its sides it borders on the small polygonal bone as well as on the hooked bone. It is connected to the carpal row of bones near the body via the lunar bone and the scaphoid bone. His part in the Carpal-metacarpal joint it forms mainly via its connection to the metacarpal bone of the middle finger and via smaller articular surfaces to the second and fourth Metacarpal bones.
The hook leg
It owes its name Hook leg (Hamate bone) a hook-shaped bone protrusionwhich, starting from him, protrudes towards the palm of the hand. Together with the pea bone, this forms the Eminentia carpi ulnaris, which as a starting point for a tight Sliver (Flexor retinaculum) of the wrist. The hookbone is connected to the headbone as well as the triangular and lunar bones via joint surfaces. Like the other bones in the distal row of the wrist, it forms part of the Carpal-metacarpal joint. Its joint connections to the metacarpal bones of the Ring finger, as well as that of the little finger represent.
function
The Spoke (radius) forms the wrist with the first row of carpal roots.
The wrist is a so-called ellipsoid joint (egg joint with two skin axes, similar to a ball joint).
The wrist can be extended approx. 90 ° (back of the hand = extension) and bent approx. 70 ° (flexion).
On the little finger side, the wrist can be spread approx. 40 ° (ulnar abduction) and approx. 20 ° on the thumb side (radial abduction).
Due to the tight ligament connection within the individual carpal bones, there is only little mobility between the first and second carpal row (metacarpal joint).
The second row of carpal roots, together with the metacarpal bone of the hand, forms the carpal - metacarpal joint (carpometacarpal joint), which also has only a limited range of motion.
Wrist pain
Due to the complexity of the wrist and the multitude of structures that can be found in this area, pain in the wrist can result in a Variety of illnesses and injuries Clues. Often the circumstances of the complaint can narrow down the possible causes a little.
Was the pain e.g. a Fall ahead, bruises, sprains, ligament and tendon injuries as well as a scaphoid fracture or less often a lunar dislocation are likely to be the cause of the complaints.
Are the hands one for a long time? monotonous mechanical load, such as. working on the PC, exposed, come Tendinitis or muscle tension as a possible cause.
Diseases that primarily affect the joints are also very common, e.g. Joint inflammation, so one arthritis, and Joint wear, so-called. arthrosis.
Furthermore, the annoywhich are at hand to be the starting point of pain. These are mainly among the so-called Bottleneck Syndromes (e.g. Carpal tunnel syndrome) affected. In addition to pain, narrowing of the nerve usually also leads to loss of sensation and tingling in the fingers, as well as a reduction in strength in the muscles supplied by the nerve. In the case of long-term complaints, a doctor should always be consulted due to the multitude of possible causes. The doctor can then make a precise diagnosis with the help of a precise anamnesis, examination and, if necessary, imaging.
Carpal fracture
The reason for a wrist bone fracture is usually one Fall on the overstretched hand. This most often leads to a break in the so-called Scaphoid (Scaphoid bone).
This often leads to initially strong ones Painwhich reappeared relatively quickly in the course of improve. Hence, such an injury is also often called Wrist sprain misunderstood. This can be problematic if the breaklines heal incompletely or displaced and a so-called Pseudarthrosis forms. This can become premature over time Joint wear, Joint changes and permanent restrictions. Therefore, after such a fall, even with minor complaints, a doctor should be consulted to rule out a break.
The therapy depends on the severity of the fracture. If there is no or only a slight shift in the break lines, a Immobilization of the joint performed with the help of a plaster cast. The wearing time varies between 6 and 12 weeks. Another possibility, which allows the wrist to move again very quickly, is that minimally invasive screw connection. The bone is accessed through a small incision in the skin. In the case of severely displaced fractures, as well as a fracture in which several small fragments of the bone have formed, an open operational direction of the break become necessary.
Carpal arthrosis

Carpal arthrosis usually develops on the basis of other carpal diseases, as well as inflammation or fractures that have healed in misalignment. The radiocarpal joint between the spoke of the forearm (radius) and the carpal bones is primarily affected by osteoarthritis.
However, the joints between the individual carpal bones can also have osteoarthritis. It manifests itself in severe pain in the wrist, which leads to a functional impairment, a swelling of the back of the hand and partly. palpable bone additions to the joints. If the osteoarthritis is less severe, immobilization of the joint using a wrist cuff is often sufficient therapy. On the other hand, if the joint wear is already very pronounced, surgical stiffening of the joint may be necessary in order to reduce the symptoms.
Read more on the subject at: Wrist osteoarthritis
Taping the wrist
The wrist is a very stressed part of the body in many sports as well as in everyday life. To protect an already affected wrist from further damage from this Stress To protect and promote healing in minor injuries, a tape bandage can help in many cases. This is one Bandage made of adhesive plaster tape, who is essentially a Support function and should prevent hyperextension of the wrist. In contrast to other associations, it grants a right despite stabilization great mobility of the joint. Furthermore, in contrast to other types of dressing, it only leads to very little impairment of the blood circulation. Its area of application is above all that physical therapy as well as sports medicine.
Inflammation of the wrist
The most common carpal inflammations are those of the Tendon sheaths (Tendovaginitis). These are mainly caused by a permanent exposure by monotonous mechanical work, e.g. frequent work on the PC. Also Infections bacteria can cause inflammation. Since the tendon sheaths are not superficial structures, these are usually one Stab or cut injury ahead.
The complaints usually express themselves in one diffuse pain above the wrist, which can extend into the forearm, i.e. along the muscle vision. The so-called De Quervain's stenoscopic tendovaginitis This is a constriction of the tendon of the short thumb extensor caused by the inflammation and the longer ends of the thumb spreader in their tendon sliding bearings. Here, too, the cause is suspected to be mostly occupational overuse. Since this disease is mainly Postmenopausal women concerns, further causes are discussed. The pain is also expressed here above the wrist and is especially pronounced when holding and gripping objects. The therapy usually consists mainly of one Immobilization by means of a cuff or a bandage, as well as the gift of Medicationthat counteract inflammation. Cooling, rest, elevation and massages can all help to alleviate the symptoms. If there is a bacterial infection, therapy is also carried out Antibiotics.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.



.jpg)