Skin cancer - early detection and treatment
definition
Skin cancer is a malignant neoplasm of the skin.Different cells can be affected and depending on this, skin cancer is called more precisely. Most often the term "skin cancer" refers to malignant melanoma (Black Skincancer), but also basalioma or spinalioma can be meant.
You may also be interested in this article: White Skin Cancer
Epidemiology / frequency distribution
The most common types of skin cancer are basalioma and spinalioma, accounting for more than 90% of cases. 10% of all skin cancer cases are malignant melanoma.
With regard to the peak age, spinalioma is mainly found in 60 to 80 year olds; Basalioma also predominantly affects older patients. In malignant melanoma, on the other hand, the age range differs further, with the peak here at 30 to 70 year olds.
The incidence (Incidents) the skin cancer "basalioma" is 20 to 50 per 100,000 in Europe, that of spinalioma 25 to 30. The incidence of malignant melanoma in Germany is 12.3 per 100,000, with an increase of 8% per year.
In Australia, the incidence of skin cancer is much higher. It is 250 per 100,000 for basalioma and 60 for malignant melanoma. In sub-Saharan Africa, however, it is very low for malignant melanoma, namely 0.1 per 100,000.
The diagnosis of skin cancer

The diagnosis of “skin cancer” is made on the basis of the clinical picture, i.e. the appearance of the skin changes. This is supported by reflected light microscopy, a method for the enlarged representation of the suspicious changes in skin cancer. However, the diagnosis of "skin cancer" can only be confirmed through a microscopic examination (histology).
Read more on the subject at: How do you recognize skin cancer?
When assessing the clinical picture of malignant melanoma, the ABCD rule is also used. More under skin cancer symptoms. In this case, the letters stand for a criterion that suggests the malignancy of the skin lesion and thus skin cancer.
A classification is also important for the diagnosis of "malignant melanoma" (Staging) and an immunohistochemical examination of the affected tissue with certain antibodies (against Melan-A, MART-1).
During staging, the tumor thickness, the presence of possible metastases in the surrounding lymph nodes, the presence of distant metastases and certain markers in the blood (MIA protein = melanoma inhibiting activity protein, LDH = lactate dehydrogenase) are used as criteria.
The skin cancer screening
Skin cancer screening is used for the early detection of skin cancer so that treatment can be initiated at an early stage in the event of an illness. This results in a better prognosis for the sick patient. In the early stages, skin cancer is usually curable. In Germany, skin cancer screening is used for insured persons aged 35 and over every two years reimbursed by health insurance.
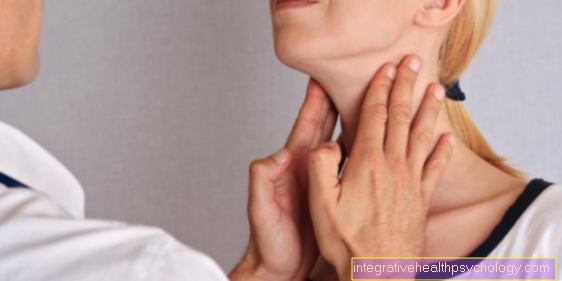
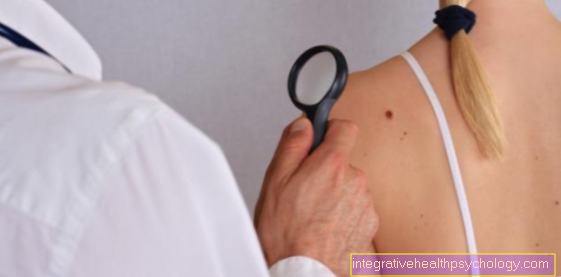
Examination procedure: The skin cancer screening is carried out by doctors who have acquired additional qualifications. Often these are general practitioners or dermatologists (Dermatologist). At the appointment, the doctor first records the patient's previous illnesses and general well-being. The entire surface of the body is then inspected. A targeted search is made for skin abnormalities that malignant melanoma (Black Skincancer), one Basal cell cancer or spinocellular carcinoma (White skin cancer) could correspond.
The doctor uses a lamp with bright light with which he illuminates the body parts in order to make skin changes visible. Since skin cancer can develop not only in parts of the body that are exposed to frequent sunlight, the oral mucous membranes and spaces between the toes are also inspected, as is the scalp. To do this, the hair is gradually parted so that the entire scalp can be seen as far as possible. Elaborate hairstyles should therefore be avoided on the day of the doctor's visit. The armpit and pubic region are also examined for abnormal areas of the skin, as skin cancer can also develop in these areas. Finger and toenails are also examined, which is why you should remove nail polish beforehand. Make-up, earrings and piercings should not be worn on the day of the examination so as not to cover the skin.
In addition to the physical exam, skin cancer screening includes education about skin cancer in general and its risk factors. The doctor explains how to deal with sunlight exposure and gives tips on how best to protect yourself against skin cancer.
Anomalies were discovered: If abnormal skin areas were discovered during the skin cancer screening, the attending physician can take a sample of the tissue, which is then sent in. The tissue sample is then prepared and cut so that it can be assessed under the microscope. A pathologist can then decide whether it is actually skin cancer or whether the tissue appears normal. Therapy is then based on this.
Read more on the topic: Skin cancer screening
How can you recognize skin cancer?
Regular self-examinations are of great importance in order to detect skin cancer early. Everyone should check their own body regularly for suspicious skin changes. Use a well-lit room or daylight, as this is the only way to see changes in the skin. Don't forget, too between the toes and under the feet to look for abnormalities. For the inspection of the back and parts of the body that are difficult to see, ask someone close to you to look.
Almost everyone has birthmarks on their body. In principle, these are harmless. Often they exist from birth, but they can also develop over a lifetime. Nevertheless, all birthmarks, especially from the age of 35, should be examined by a doctor as part of a skin cancer screening. You, too, can take care of your moles and check whether these change over time. It is considered noticeable if the birthmark suddenly increases in size, changes its shape and / or color, if it suddenly begins to itch or bleed. In this case, a medical clarification would be helpful.
As a guideline for self-examination of birthmarks, there is the so-called ABCDE rule, which you can use as a guide. If one of the following features occurs on your mole, a medical evaluation is recommended:
- A (= asymmetry): This applies if the birthmark irregularly shaped is, so it does not have a smooth, round / oval / elongated shape, but rather looks jagged and misshapen. This criterion is also considered to be met if a pre-existing birthmark begins to change shape.
- B (= limitation): It is considered conspicuous if the birthmark no sharp edge but is blurred or jagged with the surrounding skin. In the process, many smaller runners are often formed that shine into healthy skin. A sharp contour can no longer be defined.
- C (= Color): "Color"Translated from English means" color ". A birthmark is noticeable when it's out different colours exists, so it is not colored uniformly. Especially if the birthmark pink, gray or black spots or crusty deposits it should be examined by a dermatologist. It could be a malignant skin cancer.
- D (= diameter): In general, all moles that have a Diameter of 5mm exceed, to be assessed by a dermatologist. Same goes for birthmarks that take the shape of a Hemisphere to have.
- E (= evolution): Evolution in this case means something like further development. If the birthmark is in the last three months has suddenly changed in shape / color / texture, you should see a dermatologist.
If you are unsure, you should generally opt for a medical assessment of the relevant skin area. With your own skin examination and the two-year skin cancer screening from the age of 35, you are optimally prepared for the early detection of possible skin cancer.
Read more on the topic: Detect skin cancer
Detect early-stage skin cancer
The term skin cancer includes various malignant diseases of the skin.
The initial stage can differ significantly depending on the specific disease and type of degenerated cell. It is important to watch your own skin carefully because skin cancer, if detected in the early stages, is one very good prognosis Has. Careful examination of the skin, knowing the characteristics of skin cancer in the early stages, can be of great importance in the fight against skin cancer. All forms of skin cancer have in common that they affect a larger area of skin as the disease progresses. In particular, rapidly growing moles and moles should be carefully checked. In the early stages, skin cancer is usually small and relatively unremarkable. Any abnormalities can only be detected with a magnifying glass.
A distinction must be made between that black and the white Skin cancer. With so-called black skin cancer, there are several factors that should be taken into account and which can help to detect black skin cancer even in the early stages. Noticeable is one pigmented skin area whenever it is asymmetrical, fuzzy and very large (diameter over 5mm), has different colors and has changed in the last three months. Even if a pigmented area of skin begins to itch, a close examination of the skin should be carried out.
The so-called white skin cancer usually develops at an advanced age and in areas that are exposed to UV light (for example on the face or on the hands). In the early stages, there is often a hardening of the skin. The hardening is known as actinic keratosis. A gray, reddish or brownish nodule is also typical for the early stages of these skin cancer forms.
In general, symptoms in the early stages of skin cancer are only discreetly perceptible. Nevertheless, with the correct interpretation of the small changes in the skin, skin cancer can be detected and the affected person cured. A regular visit to a dermatologist including carrying out skin cancer screening is therefore generally recommended.
Proper skin cancer treatment
Treatment of black skin cancer (malignant melanoma): In the treatment of black skin cancer, the surgical removal of the diseased tissue is in the foreground. The exact therapy is adapted depending on the size of the findings. Skin cancer that is only superficial is removed with a safety margin of half a centimeter. If the thickness of the tumor is up to 2mm, the safety distance is 1cm, if the tumor is thicker than 2mm, the resection is performed with a safety distance of 2cm. This is done in order to completely remove the degenerated tissue with certainty. For skin cancer from 1mm in size, the nearest lymph node is also used in the Lymphatic drainage area removed (so-called sentinel lymph nodes) to see if it is already infected with tumor cells. If this is the case, the entire lymph node station must be cleared out. If the sentinel lymph node is tumor-free, no additional lymph nodes are removed.
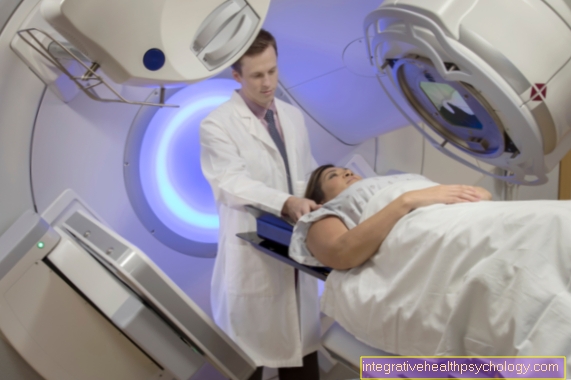
Has the tumor already settled (Metastases), these must also be surgically removed if possible. If it is not possible to completely remove the skin cancer or its metastases, radiation and / or chemotherapy are used. Various therapeutic agents are available for this purpose.
Treatment of white skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma): White skin cancer is also preferably treated surgically. The goal is the complete removal of the degenerated tissue.
For white skin cancer, however, there are alternative procedures that can be chosen if the cancer is in a very early stage or surgery is not possible due to the patient's advanced age or the location of the tumor. Very superficial or small basal cell carcinomas can be scraped off with a sharp spoon. The recurrence of skin cancer is higher with this procedure than with conventional surgical therapy.
Another alternative is photodynamic therapy (PDT), in which the affected skin area is first pretreated with a certain substance (for example with 5-aminolevulinic acid cream). This increases the light sensitivity of this skin area. This is followed by irradiation with red cold light, which then specifically destroys the malignant skin cancer cells.
In the case of superficial basal cell carcinoma, special creams can also be applied to the relevant skin area for several weeks, which then externally kill the tumor cells. Regular application of the cream is crucial for the success of the therapy. Possible side effects include strong inflammatory skin reactions to ingredients in the cream.
Last but not least, the degenerated tissue can also be frozen with liquid nitrogen. This procedure is known as cryotherapy. Added to this is nitrogen from -70 ° C to -196 ° C for use, which is applied directly to the tissue and kills the tumor cells. This procedure is particularly used for elderly patients who cannot be operated on.
A final alternative is the irradiation of white skin cancer.
Read more on this topic at: Skin cancer treatment
Aftercare
Ultimately, it is very important that patients with a history of skin cancer post their clinical healing regularly checked for over 10 years become. this will every three to six months Recommended, depending on the type of skin cancer and how it has spread, as these people are at increased risk of developing skin cancer another time in their life. Regular and consistent follow-up care can make these possible Second malignancies Detected early and given adequate therapy in good time, so that for the patient very good chances of recovery result.
prophylaxis

Consistent protection against solar radiation is important for the prevention of all types of skin cancer. In the case of basaliomas, the use of retinoids (substances similar to vitamin A) is also used for prevention.
Self-examination of suspicious skin cancer changes by the patient as well as participation in the skin cancer screening offered by dermatologists from the age of 35 (every 2 years) is also useful.
Note
An important means of preventing skin cancer is consistent protection from the sun.
forecast
The prognosis of the different types of skin cancer depends on the form.
- Basalioma: In general, the prognosis for the skin cancer "basalioma" is good. However, it depends on the localization and the type of treatment of the skin cancer. Usually the healing rate is over 90%. Recurrences occur in 5% of cases.
- Spinalioma: With spinalioma, the prognosis is also influenced by the location and the thickness of the skin cancer. The 5-year survival rate is 68 to 80%. If the skin cancer is on the mucous membrane or the skin-mucous membrane boundary, the prognosis is usually worse.
- Malignant melanoma: Even with malignant melanoma, the prognosis depends on the location, cancer thickness, metastasis and lymph node involvement. Skin cancer on the extremities is better than that on the trunk. Overall, the mortality rate for this type of skin cancer is 20%.
Localization of the skin cancer
Skin cancer on the face
The face is an area of the human body that is particularly exposed to sunlight and thus UV radiation.
Since the development of so-called white skin cancer can be associated with high UV exposure, this type of tumor is particularly common on the face.
But black skin cancer is also associated with UV exposure and occurs more frequently in the face area. When assessing the skin and looking for early stages of skin cancer, particular attention should be paid to the skin on the face. If birthmarks and moles change on the face or new marks appear, a doctor should be consulted to examine the areas.
Areas on the face that are particularly often affected by skin cancer are the ears and nose.Since these two areas of the face are at a direct angle to the incoming UV radiation, they are more frequently affected by skin cancer than other areas of the face. In addition to the face, the scalp should not be forgotten when examining the skin, as it is also often affected by skin cancer.
Read more on this topic at: Skin cancer on the face
Skin cancer on the nose
The nose is an area on the face that is particularly often affected by skin cancer. The reason for this is that the nose is rarely protected from the sun and thus UV radiation by an item of clothing.
Since UV radiation is the main cause of the development of malignant skin cancer, many types of skin cancer can be found in this part of the body. The nose is one of the so-called sun terraces on the face. The name is derived from the angle at which the nose is to the sun. In addition to the nose, for example, the ears and forehead also belong to this vulnerable group. Skin cancer does not always have to arise directly on the nose.
A skin cancer focus can also develop on the sides or near the nostrils. In general, if skin changes occur for no reason, a doctor should be consulted who will examine the area and make a diagnosis. This is especially true if the skin type is light and a high level of UV exposure is known.
Skin cancer in children
The typical forms of skin cancer that occur in adulthood are very rarely found in childhood.
In most cases, skin cancer that occurs in childhood is benign tumors. Nevertheless, malignant forms of skin cancer can also occur in childhood. As with all skin tumors, moles and moles should be monitored closely and a doctor should be consulted if the marks change.
The so-called melanomas usually only appear after puberty. It should be noted, however, that precautionary measures that can prevent the development of melanoma, such as the use of sunscreen, are useful even in childhood. Melanomas can develop in puberty or in adulthood, which can be traced back to high UV exposure in childhood.
More often, however, malignant skin tumors develop in children on the basis of skin changes that have genetic origins. Skin changes of genetic origin can be a risk for the development of malignant forms of skin cancer. For children and adolescents, too, general risk factors such as light skin type and high UV exposure are the main causes of skin cancer. In the past few years, particularly careless behavior towards UV radiation has led to the development of malignant skin cancer.
Read more at: Skin cancer in baby
Summary
Under Skin cancer one understands different forms of malignant neoplasm at the skin. These include the types of skin cancer "Basalioma“, „Spinalioma" such as "malignant melanoma“, Which show different clinical pictures. The diagnosis of "skin cancer" is made on the one hand on the basis of this image and on the other hand through a microscopic examination of the change. The skin cancer is primarily treated with excision. Other treatment options are available, depending on the stage and type of skin cancer.