Palpitations on inhalation
definition
"Heart pounding" is a very subjective term that describes a painful symptom. Most people understand a "heart attack" to be one burning, stech pain behind the breastbone.

Some people can also perceive an oppressive or constricting feeling as a "heartache". Overall, however, the feeling of a "palpitations" is very individual and strongly dependent on the sensation of the person concerned, so that a definition is difficult to define. "Heart pounding" can also be exacerbated when you breathe in, for example if breathing is difficult and makes extra effort.
Read about this too: Stinging in the chest when breathing
root cause
The causes for a "heart pounding" can be extremely diverse. A "heart pounding", which occurs when inhaling or is aggravated by it, cannot be assigned to a clear cause. In principle, a "stitch" can indicate a disease of the heart or the heart vessels. It often occurs in the context of the “angina pectoris” symptom complex, which many people are familiar with. A narrowing of the coronary arteries, for example through years of smoking, does not supply the heart with sufficient blood flow when the patient is exerted, which leads to a "stinging of the heart" as part of angina pectoris. Inhalation can also be more difficult and intensify the "heart pounding". Particularly in the case of severely constricted vessels, it is quite typical that "heart pounding" occurs when you inhale with the slightest effort or even at rest. Get examined by a cardiologist.
Read detailed information on the subject: Angina pectoris
For many people, fear of a heart attack exacerbates these symptoms even though there is no damage to the heart. Certainty can bring relief and calm. Anxiety, stress and the general psychological state can also be reasons for a "heart pounding" when inhaling, which are not all that rare. Since both the breathing rate and the heart rate increase during stress, the subjective impression of a heart pounding can arise. Other emotional and psychological stresses and fears can also trigger a "heart pounding" when inhaling. However, there is no harm to the heart. Tension in the auxiliary respiratory muscles and the muscles of the chest may cause stabbing pain when inhaling (pain when inhaling), which can feel like a "heart pounding".
Read more on the topic: Signs of a heart attack
diagnosis
First of all, it's important to stay calm. The best thing to do is to contact your GP and describe your symptoms and fears. They will refer you to the cardiologist who will check the health of your heart. Echocardiography, EKG examinations such as the stress EKG and other diagnostic measures can detect and reveal disorders of the heart rhythm or the organ. Further imaging examinations or even invasive measures such as cardiac catheters are also available for examining and treating the heart. If the heart is healthy and all relevant diseases are excluded, the search for the cause is steered in a different direction. The question of fears, stress or other psychological stress should be clarified. Possible causes such as tension in the muscles of the chest are also included.
Learn more about: Troponin Test
Symptoms
The accompanying symptoms of a "palpitations" when inhaling depend on the underlying cause. Heart disease can show many more symptoms.
Stinging of the heart when inhaling caused by angina pectoris
An angina pectoris, for example, which occurs in the context of coronary artery disease occurs, shows next to one Heart pounding also a Tightness the chest. Those affected often describe this with the comparison of an elephant sitting on the chest. Also nausea, Restlessness, fear and radiating chest pain are typical. The Pain can in the left arm, move, Lower jaw, neck or Upper abdomen radiate. The symptoms usually go away with rest.
Stinging of the heart when inhaling, caused by a heart attack
It is different with one real heart attackwhich can also manifest itself in a palpitation of the heart when inhaling. If you have a heart attack, they are Symptoms most of time stronger than with angina pectoris. Step accompanying it Fear of death, Sweats and partly too Vomit on. The pain is felt to be much stronger and the symptoms persist does not go away in peace. shortness of breath and a Drop in blood pressure such as Pale skin also occur. So it is a highly acute clinical picture.
Stinging of the heart when inhaling due to stress
However, "heart pounding" when inhaling can also occur due to stress or are related to psychological stress. Most of the time, the "palpitations" are not expressed in the same way as in angina pectoris or a heart attack. It occurs much more in stressful situations and is accompanied by anxiety, a high heart rate, sweating or dizziness. Other possible accompanying symptoms are muscular pain, for example in the chest or back muscles.
Palpitations on inhalation and back pain
"Heart pounding" when breathing in can occur in combination with back pain. Very severe pain, shortness of breath and sweating form the typical symptom combination of a heart attack. A radiation of the pain in the left arm, the upper abdomen or the neck and the upper jaw is also typical for a heart attack. Angina pectoris can also lead to "palpitations" when inhaling, which is accompanied by back pain. The symptoms are usually less pronounced than with a heart attack and recede after 10 to 20 minutes at rest. Back pain can persist on a muscular Tension of the back muscles be due. Some sufferers also report a kind of "heart pounding" that comes about through muscular tension. Formally, however, it is not a "heart pounding" because the heart is healthy. However, the subjective impression of a sharp chest pain can exist. It seldom appears stronger when inhaled. However, the connection can only be vaguely established. These are very subjective complaints that cannot necessarily be traced back to one another.
Heartache on inhalation and flu
A flu as such, it does not cause "heart pounding" when inhaling. Some respiratory infections such as one lung infection inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy) entail. This inflammation, in turn, is a possible cause of sharp chest pain, which most people refer to as "heart pounding". Typically, this "heart pounding" intensifies when you inhale. However, the flu usually does not lead to such symptoms.
Read more on the topic pleurisy
Palpitations on inhalation and cold
A simple cold does not cause a "heart pounding" when inhaling. In the case of pneumonia, however, inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy) can occur, which leads to chest pain that can appear like a "stitch of the heart". It is also typical that it is then a breath-dependent pain that increases when inhaled
Palpitations on inhalation and coughing
"Stinging the heart" is a very misleading term, as it is in very few cases a pain that actually comes from the heart. It is usually much more of a general chest pain that is felt to be stabbing. Typically this is what irritation of the pleura feels like. The pleura can be inflamed as part of pneumonia or acute bronchitis. A sharp pain in the chest on inhalation is typical, accompanied by a dry or productive cough. The latter denotes a cough with sputum. Can accompany fever, Exhaustion and a general feeling of illness occurs
Stinging of the heart when breathing in during pregnancy
In the pregnancy women are in a physical and psychological state of emergency. The whole life situation, the body and the stresses to be dealt with change. Stress during pregnancy can lead to "heart pounding" when you inhale. As the woman adjusts to pregnancy, her heart rate increases naturally. There is usually no damage to the heart or lungs. Hence this is not a cause for concern.However, an examination by a doctor should be carried out solely to reassure the pregnant woman and to provide security. Stretch pain or pain caused by irritation of the pleura can also mimic a palpitation of the heart when you inhale and is far more obvious than a disease of the heart or lungs.
Palpitation on inhalation while stooping
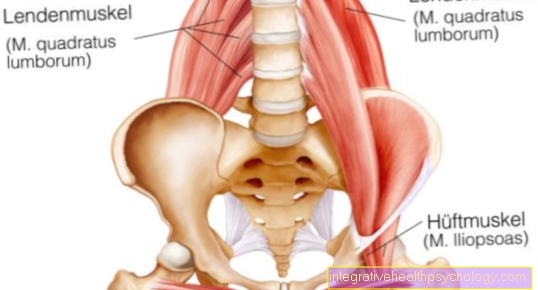
Also the posture can have an influence on the severity of the "heart pounding" when inhaling. The posture can, for example, increase muscular tension or change the subjective feeling of the "heart pounding". Muscle tension in the chest or back muscles can become noticeable, for example, when bending over and thus imitate a "heart pounding" when inhaling. However, it is difficult to derive a direct connection. As such, stooping has no effect on the heart and therefore one must not assume that it would in any way cause a "heart pounding" that actually comes from the heart. Rather, the posture can make breathing more difficult and, in the case of already existing tension or muscular dysfunction, intensify the impression of a "pounding heart" when breathing in.
therapy
Treatment for "palpitations" when you inhale depends on the underlying cause. Since various diseases or circumstances lead to a palpable heart attack when inhaling, there is of course no standard therapy. In the following section, the most important causes with regard to their therapy are briefly explained:
1. Coronary artery disease / angina pectoris: Coronary artery disease therapy comprises many different building blocks. Nitrates and so-called calcium antagonists or beta blockers are prescribed to relieve the symptoms and the aching heart.
Read more on the topic Therapy for angina pectoris
At a Occlusion of an artery or even a heart attack, a catheter is usually used to insert a stent into the affected vessel via the groin so that it is opened.
Read more on the topic Therapy for heart attack
2. Muscular tension: Muscular tension in the back or chest muscles can be relieved with the help of massages or physiotherapy. Breathing exercises can help to make optimal use of the auxiliary respiratory muscles and to improve the heart rate.
3. Stress / strain / "psychogenic heart pounding": The treatment of a "heart pounding" caused by stress or other psychological stress usually includes relaxation techniques and approaches to stress management. However, the therapy is very individual and adapted to the needs of the person concerned.
How long does the heart pounding when I breathe in?
The duration of a "heart pounding" when you inhale varies widely. Usually the symptoms only last a few minutes or even a few seconds. That depends on the underlying cause. Angina attacks usually last between 10 and 20 minutes, when treated with nitroglycerin, they subside after a short time. The length of time the symptoms persist depends on whether and how successful the treatment is. Therefore, no general information on the duration can be given. "Heart pounding" with psychological causes or in stressful situations can be brought under control by relaxation techniques, for example, so that the symptoms only appear less often or at some point no longer.