Homeopathy for nosebleeds
introduction
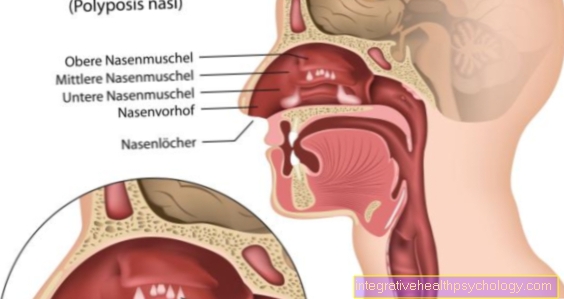
Nosebleeds (also called "epistaxis" in medical terms) can have many different causes, such as a traumatic effect (injury) or irritation of the nasal mucosa due to allergic reactions or the like.
However, it can also occur spontaneously without any recognizable cause.
What all cases have in common is that a superficial blood vessel in the nasal mucosa has burst.
Normally, the bleeding should stop by itself after a few mitings, namely when the body's natural hemostasis has been used.
If you tend to have frequent nosebleeds and prefer alternative healing methods, you can first try a treatment with homeopathic active ingredients. However, if this method of treatment does not work, a visit to the ENT doctor is inevitable.

Which active ingredients are used?
There are many different homeopathic active ingredients that can be used successfully for nosebleeds.
The following have proven particularly useful:
- Arnica montana,
- Ferrum phosphoricum and Phosphorus,
- Ammonium carbonicum,
- Bryonia alba or
- Carbo vegetabilis
When choosing the right active ingredient in the situation, it is important that the symptoms that occur with the nosebleed match the respective drug picture of the active ingredient.
This does not necessarily have to be a question of physical ailments, but also ailments or properties of psychological or character causes can be taken into account:
In short, the homeopathic remedy picture in homeopathy contains the entirety of the symptoms that indicate a “desire” of the person concerned for the respective active ingredient.
Arnica
Arnica montana is primarily used as a wound healing agent, i.e. for injuries such as sprains, contusions or strains.
It is also used in support of inflammation, cardiovascular diseases and bleeding or bleeding tendencies of any kind.
Arnica montana can therefore help with nosebleeds, but low potencies such as D3 should be avoided here.
The mother tincture should also not be used to treat nosebleeds.
Do you have an acute nosebleed and want to stop it?
- Find out what you can do: How can you stop nosebleeds?
Ferrum phosphoricum
A person who needs Ferrum phosphoricum usually appears anemic, as if suffering from anemia.
Specifically, this means that symptoms such as:
- pale skin,
- dark circles under the eyes,
- Sensitivity to cold and
- Tiredness or fatigue.
In addition, the drug picture often shows bleeding.
The properties of these appear spontaneously and are more light red than dark red, similar to the Phosphorus type.
Especially in children, a “desire” for Ferrum phosphoricum is often shown by spontaneous nosebleeds - but if it occurs frequently, spontaneously and for a long time, a doctor should definitely be consulted in the long term!
Would you like to know what you have to pay particular attention to in the case of nosebleeds in childhood?
- Find out more at: Nosebleeds in children
Phosphorus
Bleeding anywhere on the body is one of the typical main complaints of a person who does the homeopathic Phosphorus well.
Therefore, in addition to bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract or gums, Phosphorus can also help with nosebleeds.
The nosebleed (or bleeding and injuries in general) of the Phosphorus type (i.e. the person who could help this remedy) is described - similar to the Ferrum phosphoricum type - as strong and pulsating, long-lasting and of a bright red color.
These are all characteristics of arterial bleeding.
So if you find these characteristics in your own (spontaneously occurring and recurring) nosebleeds, you should visit an ENT doctor at short notice in addition to medication with homeopathic remedies.
Do you want to know where your nosebleeds are coming from?
- Find out more at: Causes of nosebleeds
Bach flowers
The so-called Bach flowers are 38 different flower extracts, which were compiled by the British Edward Bach, can also be used to treat recurrent nosebleeds.
Since different substances can be used, it is advisable to research the areas of application of the individual agents.
A frequently used remedy is, for example, Century (thousand herb), which can generally be used for weakness of the psyche or the tissue.
For nosebleeds that are associated with high blood pressure, cherry plum (cherry plum) or holly (holly) can help.
If the nosebleed leads to weakness, dizziness or drowsiness, the use of the substances olive or clematis can help.
Are you interested in therapy with Bach flowers?
- Find out more about the topic at: List of all Bach flowers
dosage
The potency D6 or D12 is mostly used to treat nosebleeds.
It is advisable to seek advice from an appropriate specialist in order to precisely match the dosage and active ingredients to the symptoms.
Anyone who is already familiar with homeopathy and would like to try their own medication first can start by taking five globules three times a day.
How quickly can an improvement be expected?
How long a homeopathic treatment has to last in order for the symptoms to improve depends heavily on various factors.
These include:
- the strength of the complaints,
- Type and dosage of the agent used,
- as well as the physical condition and nature of the person concerned.
In general, the homeopathic remedy should be discontinued when the symptoms no longer exist.
If the symptoms fail to respond after 4-6 weeks, at least a change in the remedy should be considered.
Treat nosebleeds in children with homeopathy
Statistically speaking, children and adolescents are more likely to have nosebleeds than adults.
In general, however, nosebleeds in children can be treated with the same homeopathic remedies as in adults, but Hamamelis virginiana or Millefolium can also be used, especially for children.
Witch hazel is recommended when the tendency to bleeding increases in warmth and moisture, while millefolium is used more when it is worsened by dry cold.
Here, too, you should inform yourself about the respective field of application and drug picture of the homeopathic before choosing the therapeutic agent, or you should consult a suitably trained specialist.
Would you like to know what you should pay particular attention to when you have a nosebleed in childhood?
- Find out more at: Nosebleeds in children
How do you treat nosebleeds conventionally?
When you have a nosebleed, a blood vessel in the lining of your nose has burst. Usually, the body should be able to stop the bleeding itself within several minutes. You can support the body with a cold cloth on the forehead or neck, as this slightly reduces the blood supply for the face and nose and it is easier for the body to stop bleeding.
In the case of frequent, heavy and long-lasting nosebleeds, a single, exposed vein in the nasal mucous membrane can sometimes be responsible: More precisely, a blood vessel in the plexus (network of blood vessels) called the Locus Kiesselbachi is usually affected.
Such an anatomical peculiarity is usually easy for the doctor to see.
Are you interested in more detailed information on the causes of nosebleeds?
- Read the article on this: Causes of nosebleeds
If the nosebleed affects the quality of life, the corresponding blood vessel can then be obliterated. The blood supply for the surrounding tissue is then still guaranteed through the other veins of the vascular plexus. The deserted area then forms scar tissue, which is more solid than the previous tissue and therefore less likely to burst and lead to bleeding.
Do you suspect that you may have to obliterate a vessel?
- Find out what you could expect: Nosebleeds cease to exist - what exactly is happening?
When should I not treat nosebleeds homeopathically and when is a doctor's visit necessary?
There are also some alarm symptoms to watch out for in the case of nosebleeds, for which a doctor should be consulted. Above all, these include symptoms that indicate arterial bleeding.
An artery is a blood vessel leading away from the heart, which transports oxygen-rich blood and is under higher tension. Arterial bleeding is therefore more severe and lasts longer.
Evidence of arterial bleeding can be an often recurring and spontaneous nosebleed that occurs without any recognizable external influence.
In addition, medical advice should be sought if the nosebleed lasts for a long time, i.e. more than 5 minutes, and the escaping blood is noticeably bright red.
These are both indications of an arterial origin of the nosebleed and should be clarified by an ear, nose and throat specialist in order to rule out the possibility of an anatomical peculiarity in the so-called "Locus Kiesselbachi", which is responsible for frequent nosebleeds in some people ( see above).
Recommendations from the editorial team:
- Nosebleeds while sleeping
- Epistaxis in young children
- Nosebleeds during pregnancy
- Stop nosebleeds
- Nosebleeds cease to exist