Astigmatism in children
definition
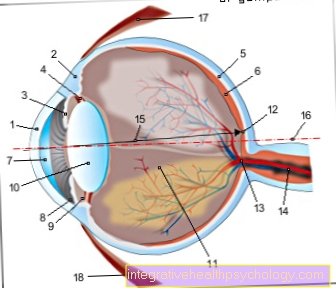
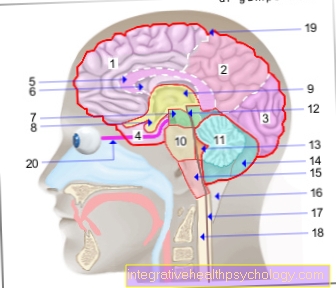
An astigmatism in children is a deformation of the cornea. The incident light is distorted on the retina and the children see blurred and blurred. Without early and adequate treatment, extensive developmental delays can occur. Most children who suffer from astigmatism are noticeable because they are significantly more clumsy than other children. An undetected visual defect is often the cause of this awkwardness.
Read more on the topic: Astigmatism in babies

Recognizing astigmatism in children
What are the symptoms of astigmatism in children?
The accompanying symptoms of astigmatism in children include, above all, clumsiness that is noticeable early on. Often this is the first symptom that can provide an indication of the presence of the disease. The children appear awkward, often trip and fall, and cannot purposefully grasp objects. Since seeing and processing the visual impressions is very exhausting for the children, they also often suffer from headaches, tension and dizziness. Many children have enormous difficulties seeing up close or at a distance, and they report images that appear blurry or double.
Read more on the topic: Symptoms of astigmatism
How is astigmatism diagnosed in children?
The procedure for diagnosing astigmatism depends on the age of the affected children.
Babies in particular can often not be adequately examined by the ophthalmologist with the help of the special examination equipment, as they are not yet ready to cooperate. In these cases, a so-called visual school usually tries playfully to diagnose a visual impairment.
From the 3rd to 4th Normal ophthalmological examinations can usually be carried out at the age of 16. A visual defect can be determined with a so-called objective refraction. An infrared image is projected onto the back of the child's eye and it is possible to measure whether the image is in focus. If this is not the case, various lenses are switched on until the image can be seen in focus.
The doctor can also use a measuring instrument, the so-called ophthalmometer, to measure the exact extent of the corneal curvature. Here, 2 crosses, a hollow and a line cross, are projected onto the cornea. On a normally curved cornea, the crosses would lie directly on top of one another. If they are bent, they will deviate from each other.
Treating astigmatism in the child
How is astigmatism treated in children?
Since the ametropia that arises from astigmatism can lead to far-reaching developmental delays, early and adequate treatment is particularly important.
In children, the astigmatism should be compensated for with the help of glasses. With the help of the glasses, the children's brain can compensate for the curvature and enable sharp vision. A correct fit and the exact calculation of the visual defect to be treated is extremely important.
If the curvature of the cornea is unilateral, the defect can be corrected by masking the healthy eye. This forces the brain to process the impressions of the weaker eye and to train it.
Can astigmatism in children be treated with laser therapy?
Another treatment option for astigmatism is laser therapy. However, it is largely not used in childhood. If the glasses supply does not show sufficient effects, this measure can be considered in consultation with the treating doctor.
Laser therapy is a surgical procedure in which the unevenness on the cornea is removed with the help of a hot light beam, creating a regular, smooth surface that enables sharp vision.
Read more on the topic: Laser therapy for astigmatism
Preventing astigmatism in children
What are the causes of astigmatism in children?
In most cases, astigmatism is congenital in children. If there is a hereditary component, multiple family members in different generations have an astigmatism. Particularly characteristic of a congenital astigmatism in children is a curved cornea that is particularly thinned. This is known as the keratoglobus.
Other causes that can lead to astigmatism are, for example, surgical interventions on the eye or the formation of scars or ulcers on the cornea. However, this occurs very rarely in children and is more often seen as the cause in adults.
Since astigmatism often only becomes noticeable late, it is particularly important to pay attention to the instructions early on and to examine the children for the presence of an astigmatism. Particularly in the case of a familial accumulation, you should see an ophthalmologist at an early stage so that any curvature that may be present can be recognized and treated early on.
Curvature of the cornea in children
Is astigmatism curable in children?
Astigmatism in children is usually not curable. If it is recognized at an early stage, the treatment is very successful in most cases and can often almost completely compensate for the existing error. However, it must be remembered that astigmatism in children is never 100% reversible. A certain visual defect that requires further correction using glasses or contact lenses always remains. The goal of treatment is to correct the visual defect so that the risk of developmental delay is minimized.
Can an astigmatism grow together in a child?
A corneal curvature in children can both decrease and increase as the eye grows. However, a complete fusion with 100% healing is not possible.Since the curvature of the cornea and the associated ametropia can change as a child grows, it is important to have regular checkups by an ophthalmologist and to readjust the therapy if necessary.
Another question about astigmatism in children
Do you need glasses with astigmatism in children?
By using glasses to correct a curvature of the cornea in children, missing nerve pathways can develop and compensate for the ametropia. It is particularly important to start treatment early.
The glasses used by children must have certain properties. Since children romp around a lot and often fall, the glasses should contain unbreakable plastic lenses. This significantly reduces the risk of injury. In addition, the bridge should be made of silicone so that it can adapt to the nose and does not cause pressure points or pinch the nose. For smaller children, elastic straps can be used instead of hangers.
Read more about this: Glasses
Can you do that without glasses?
The best possible treatment for astigmatism in children is to use glasses. If the curvature has not progressed too far and the other eye does not show any ametropia, another therapy can be considered first. In this case the child's brain can be forced to process the impressions of the weakened eye as well as possible by tying off or masking off the healthy eye. This trains the weakened eye and the visual defect can sometimes be compensated for over time.
In the case of congenital astigmatism, however, this treatment is not sufficient in many cases and must be supplemented with the use of glasses.