Hypercholesterolemia
Definition / ICD
Hypercholesterolemia refers to the Increase in total cholesterol above a certain limit. Is the cholesterol level in the blood? over 200 mg / dl, this corresponds to hypercholesterolemia. A high cholesterol level has been shown to increase the risk of developing arteriosclerosis, a thickening and hardening of the arterial walls.

Most of the cholesterol is produced by the body. It fulfills various functions in Structure of cell membranes and accepts Metabolic processes part. A small proportion of the cholesterol is supplied through the diet through animal products. The distribution of cholesterol in the body takes place through the Incorporation in so-called lipoproteins. These consist mainly of protein and fats. The co-determination of the HDL and LDL proportion on total cholesterol contributes to the precise assessment of the risk profile. While LDL, the “bad” cholesterol, remains in the tissue, it is transported HDL the cholesterol back to the liver. There it is broken down and excreted via the bile acid. One also speaks of “good” cholesterol.
To ICD, the international classification of diseases, pure hypercholesterolemia is associated with the Section E.78.0 Mistake. Numerous sub-categories that specify a familial disposition or the elevation of a certain lipoprotein fall under the same point. Is that Total cholesterol between 200 and 230 mg / dl and / or the LDL value over 160 mg / dlone speaks to one increased cholesterol.
causes
There are basically two different causes that can lead to high cholesterol levels. The so-called secondary hypercholesterolemia is by far the most common form. It can appear as a result of various diseases or with long-term, high-fat diets. The hypothyroidism (Hypothyroidism), Diabetes mellitus and kidney disease known as nephrotic syndrome are chronic diseases with an increased risk of hypercholesterolemia. Alcohol abuse is also seen in connection with the secondary form. A high-fat diet, which contains a large proportion of animal products, is a major cause of high total cholesterol. Saturated fatty acids and trans fatty acids increase LDL cholesterol.
Primary or familial hypercholesterolemia can be traced back to a genetic disposition in which there is a deficiency or even an absence of receptors for LDL lipoproteins. The LDL cholesterol circulating in the blood is not absorbed by the cells and remains in the bloodstream. It can be measured as high cholesterol. In many cases of lipid metabolism disorder, genetic predisposition plays a role. Usually manifests itself only in an unhealthy lifestyle.
Read more about the topic here: Lipid Metabolism Disorder and What is Oxidative Stress?
Symptoms
Those affected show hypercholesterolemia in the first few years no visible symptoms. Often it is one Incidental finding, which is determined in the course of a family doctor check-up. Significantly increased cholesterol levels are evident here. The consequences of increased total cholesterol and an increased LDL level manifest themselves gradually. Circulating in the blood LDL cholesterol is deposited on the blood vessel walls of the arteries. In the further course so-called Plaquesassociated with hardening and thickening of the arterial walls. They are the starting point for symptomatic hypercholesterolemia. Symptoms as a consequence occur depending on the arteries affected.
Angina pectoris Complaints are closely related to the increasing calcification of the coronary arteries. They are mostly load-dependent and occur in the heart area or in the area behind the sternum. When moving, the heart muscle's need for oxygen increases. If the supplying vessels are no longer adequately supplied with blood as a result of the vascular deposits, this leads to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the muscles (Ischemia). Burning, stabbing, sometimes cramp-like pain are the consequence.
If the vessel diameter narrows further, a persistent ischemia. It is a myocardial resp. Heart attack, which is a life-threatening event for the person concerned. It is often triggered by a blood clot that has formed on arteriosclerotic changes in the vessel walls. Chest pain with radiation in the upper left half of the body, Sweats and nausea are among the typical symptoms.
A stroke (Apoplex) can also be a sequel to arteriosclerosis caused by hypercholesterolemia. Usually it is one ischemic strokein which an acute Reduced blood flow to the brain present. This can be triggered, among other things, by a constriction of the arteries supplying it or blocked blood clots. Neurological symptoms in the form of visual, speech and word finding disorders can be observed. Dizziness, signs of paralysis in various parts of the body can also occur.
If the vessels supplying the heart and the brain are narrowed, there is often one at the same time peripheral arterial disease, PAOD, before. The decreasing diameter of the vessels in the leg arteries does not initially cause any symptoms and is often only noticeable in more advanced stages. Affected people complain about decreasing pain-free walking distances and in late stages feel severe pain even at rest with increasing skin involvement.
The small arteries of the kidneys can also be affected by the fatty deposits. As a result, increased pressure is necessary for complete blood flow to the kidneys. In the course this leads to arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) and can terminate in kidney failure.
The pure familial hypercholesterolemia If left untreated, it also shows visible symptoms. These include so-called Xanthelasma and Xanthomas. It concerns the slightly yellow spots on the eyelids and similar colored nodules on the skin. There is also a yellowish ring around the iris of the eyes.
diagnosis
As part of a GP examination become different Laboratory parameters certainly. The blood sample is taken morning and sober. When diagnosing hypercholesterolemia, this plays alongside Total cholesterol, also the height of the LDL and HDL cholesterol an important role. If the total cholesterol and / or the LDL cholesterol is above a certain limit value, all other possible triggers must first be excluded.
The Cardiovascular Event Risk, such as a heart attack or stroke, is collected with the help of other diagnostic tools. The measurement of the Blood pressure and blood sugar counts as well as that Preparation of an EKG and possibly one Exercise EKGs. In this way, the attending physician can obtain an assessment of the overall risk. Also be other risk factors such as smoking, alcohol abuse, obesity and comorbidities detected. The target values of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol are determined depending on the overall risk.
therapy
Just like the diagnosis of hypercholesterolemia, the therapy is directed according to the individual risk profile of the patient. The goal is Lowering cholesterol. In addition to the Reduction of risk factors, treatment of triggers and a healthy lifestyle in the foreground. All of these measures reduce the likelihood of possible cardiovascular events. A healthy lifestyle is made possible by a adequate level of physical activity and a conscious diet Achieved with low levels of saturated fat and trans fats.
Is there a causal factor Hypothyroidism, a Diabetes mellitus or one Kidney disease before, this should be addressed. It is also important to minimize risk factors. Clear decreased alcohol consumption, No nicotine and Weight reduction play an important role in overweight. Medication come to lower cholesterol with unchanged high values used despite conservative measures and familial hypercholesterolemia.
Medication
The most common drugs used to lower cholesterol are statins. They have been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks and contribute to a reduction in overall mortality. Their mode of action is based on the inhibition of an enzyme which is involved in the formation of new LDL cholesterol. Statin representatives include atorvastatin and simvastatin.
Other drugs used to lower LDL cholesterol are so-called anion exchange resins, such as cholestyramine, and fibrates, which promote the breakdown of fatty acids. If therapy with statins alone is not sufficient, a nicotinic acid derivative can also lower the cholesterol level. In the familial form, the administration of ezetimibe, which inhibits the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine, together with a statin can bring about the desired therapeutic success.
Also read the article on the topic: Cholestyramine
values
The exact limits for total cholesterol levels vary from laboratory to laboratory. Values between 200 and 230 mg / dl are commonly called too high viewed. The interpretation the total cholesterol value is always done depending on the levels of the lipoproteins HDL and LDL. The LDL cholesterol should below the limit of 160 mg / dl while the HDL cholesterol should not be lower than 40 mg / dl. A high HDL value is considered protective factor for strokes and heart attacks.
If such an event occurred in the past, the limit value of the LDL should be reduced to values below 100 mg / dl as a preventive measure. Tobacco consumption, high blood pressure, a familial predisposition to cardiovascular events and diabetes mellitus are also indicators of the lowest possible LDL value.
consequences

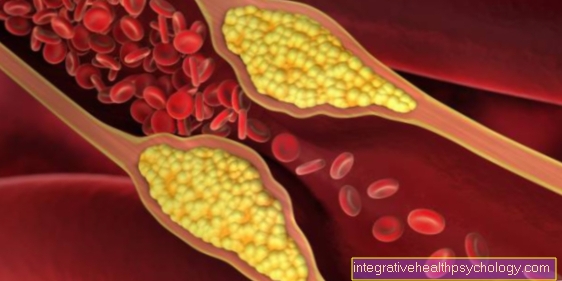
If more LDL cholesterol circulates through the bloodstream over a longer period of time, the likelihood of it sticking to the vessel walls increases. The Fat deposits on the walls the arteries are called Plaques designated. They also consist of connective tissue, thrombi and, to a small extent, calcium phosphate. Colloquially one speaks of a Hardening of the arteries. However, it is rather a degenerative process with hardened and thickened vessel walls. The final stage includes the emergence of so-called Foam cellsthat contain a large amount of LDL and one chronic inflammation have as a consequence. Connective tissue plaques with a core of fats develop. If a plaque breaks up, the arterial diameter continues to decrease, as a clotting reaction of the blood is triggered.
The consequences of arteriosclerosis make up the largest proportion of causes of death in the western world. A Heart attack occurs when the coronary arteries are obstructed and the heart muscle is no longer adequately supplied with oxygen. A stroke is triggered by a reduced blood supply to the vessels supplying the brain. These are other common consequences Aortic aneurysm, a bulging of the abdominal artery and the so-called PAD. The latter stands for peripheral arterial disease and denotes the increasing obstruction of the leg arteries. Those affected complain of load-dependent pain that is associated with a significantly restricted walking distance.
pregnancy
Elevated cholesterol levels are not uncommon during pregnancy. Changes in hormone levels let the cholesterol level, as well as the triglycerides rise significantly. This is especially true in the case of familial hypercholesterolemia.
So far it is medication high levels of fat in the blood during pregnancy Subject of discussion. It is also unclear whether there is any potential harm to the child as a result of the hypercholesterolemia. The Taking most cholesterol lowering drugs is used during pregnancy and while breastfeeding not recommended. These include statins, nicotinic acid, ezetimibe and fibrates. If possible, such therapy should already be Terminated one to three months before conception become. Therapy with anion exchange resins, on the other hand, is a possible alternative.
nutrition
Cholesterol levels can be lowered not only through exercise and weight loss, but above all through one healthy diet. That plays an important role Amount of ingested fats and the choice of the right fatty acids. In general, the Amount of energy supplied daily half from carbohydrates, too 30 percent from fats and 20 percent from proteins should exist. Converted, this corresponds to a weight of 70 to 90 grams Fat.
This should include the Half of the "good" fatty acidn included. The other half can be supplied in the form of saturated and trans fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids are mainly found in sausage, cheese and baked goods. Trans fatty acids are also known as "hardened" fatty acids and are found in industrially manufactured products such as puff pastry, frying fats, sweet spreads and snacks.
The "bad" fatty acids, which are also contained in palm and coconut fat, contribute to the increase in LDL cholesterol. The daily intake should be kept as low as possible. One can also help here Low-fat preparation of meals.
A positive influence on the Fat metabolism to have monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. They help lower cholesterol. Naturally, they mostly come in Fish and vegetable fats in front. Next Olive and rapeseed oil own in particular Linseed, grapeseed, walnut and sunflower oils a high proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids.