Incontinence after a herniated disc
introduction
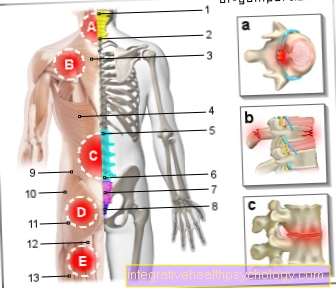
Incontinence after a herniated disc is a typical, but not necessarily common, phenomenon.The reason for this is irritation or damage to nerve fibers from the herniated disc.
The degree of incontinence can also be different and does not always have to mean that you can no longer hold the water. Often there are only a few drops.

Why can incontinence occur with a herniated disc in the lumbar spine?
The continence of the human bladder is based on a complex interplay of voluntary and autonomous muscles. Furthermore, the filling level of the bladder and the activity level of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system also play a major role in holding the urine.
All of these components are controlled or supplied by nerves that make their way to the urinary bladder or from the urinary bladder to the brain via the spinal cord. The herniated disc in the lumbar region now ensures that certain of these fiber connections between the urinary bladder and the brain are disturbed or, in the worst case, even destroyed. The transmission can no longer work without problems.
As a rule, incontinence is a combination of the failure of the arbitrarily controllable muscles - namely those of the pelvic floor and urinary bladder muscles, which are controlled by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, the so-called vegetative nervous system.
The pelvic floor muscles, which can be consciously tensed, are used to deliberately close the urethra. Anyone who has had to urgently hold their urine at some point probably knows the feeling that the body actually sets all signals to "let go", but you can still hold back by tensing the pelvic floor muscles. If the nerve connections to the pelvic floor muscles are disrupted, it may no longer be possible to keep to these sensitive situations. So that you don't have to permanently tense your pelvic floor, this is normally done by the autonomic nervous system - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. They control a urethral closure muscle that is located slightly above the pelvic floor. Normally this muscle is contracted - completely unconsciously for humans - and thus blocks the way to the urethra. The muscles of the urinary bladder are relaxed. If the urinary bladder now reaches an individually limited level, pressure sensors send signals from the urinary bladder to the brain. Humans feel this as an urge to urinate.
If you now decide to give in to the urge to urinate, or if the bladder is too full, the autonomic nervous system begins to work again.
The urethral closure muscle expands and opens the way through the urethra to the pelvic floor. In addition, the muscles around the urinary bladder begin to contract - they are virtually wrung out.
If the arbitrary decision to relax the pelvic floor is made, the urine can pass the entire urethra and is excreted. It is therefore obvious that there are a number of possibilities which can result in incontinence in a disorder. Depending on where the spinal cord or the exiting nerves were damaged and how severe the damage was.
When does incontinence occur?
Unfortunately, when exactly or with whom exactly incontinence can occur cannot be said in general terms. Not every herniated disc of the lumbar spine is the same. Depending on where the protruding intervertebral disk of the spine is pressing, completely different areas of action or perception are affected.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Duration of incontinence
A statement about the duration of incontinence is just as difficult as a statement about who is affected by it. On the one hand, it depends on whether the damage is reversible and, on the other hand, which treatment of the herniated disc is used. If the nerve pathway controlling the bladder function is irreversibly damaged, the person affected will have to spend the rest of his life with this problem - at least from today's medical standards. If the nerve pathway is not irreversibly damaged, a stiffening of the vertebrae can either manifest the problem or, if necessary, resolve it again. Unfortunately, a general statement is not possible in this regard either.
You may also be interested in the next topic: Disc herniation of L3 / L4
What can you do about incontinence?
Unfortunately, incontinence itself cannot be treated promptly with medication or the like. As a rule, one has to deal with the prevention of too big "accidents". Wearing diaper pants or using sanitary towels are the most common methods to prevent uncontrolled urination, which in the worst case could show through the pants.
In the further course the operation of the herniated disc can bring an improvement of the problem. However, this is not the same in every case, but varies greatly from person to person. Depending on the extent and duration of the damage to the corresponding nerves. Last but not least, simply waiting after the operation can bring about an improvement. If the damage to the nerves was not too severe, there is a certain potential for regeneration, which can ensure that the nerve fibers can largely resume their old functions.