Internal bleeding
Definition - What is Internal Bleeding?
With internal bleeding, there is vascular damage that is not visible from the outside. There is a source of bleeding inside the body. If rapid and high blood loss occurs from this source of bleeding, this constitutes a medical emergency. In most cases, a traumatic event is the cause of the bleeding. However, there are other causes, for example caused by inflammation, which lead to so-called oozing bleeding. This means that very little blood escapes through the damaged tissue, but this does so continuously. This can lead to chronic anemia, which is accompanied by a feeling of tiredness and fatigue.

causes
There are many different causes that can trigger internal bleeding. In principle, the injury to any internal organ can cause internal bleeding. Some examples are given below.
Traumatic events, such as a car accident or a violent act, can lead to internal organ damage. In traffic accidents, for example, the blunt abdominal trauma often leads to a rupture of the spleen. Since the spleen is a very well perfused organ, a rupture can lead to massive blood loss and is a medical emergency.
Here it goes to: These symptoms indicate a ruptured spleen
Another cause is hemorrhagic fever. This is an infection that can be triggered by various viruses, which can lead to an increased tendency to bleed. Triggers are, for example, the dengue, yellow fever or Ebola virus. In addition to flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache and muscle pain, internal bleeding can also occur.
You can find one here Overview page on tropical diseases
Another symptom that can cause internal bleeding is oozing gastric bleeding. It often affects older people whose gastric mucosa has been irritated for a long period of time. The cause for this can be a chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which can be bacterial or a side effect of medication. A stomach tumor can also lead to gastric bleeding.
The so-called aortic dissection can also lead to massive blood loss. This is a splitting of the vessel wall of the main artery (aorta). As a result, blood flows between the layers of the aorta or the vessel ruptures completely. Aortic dissection is a life-threatening clinical picture and should be treated immediately.
Read here: Symptoms of aortic dissection
A low number of platelets can also cause internal bleeding. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting. If they are not available in sufficient numbers, the slightest trauma that would normally not cause bleeding, as small vascular injuries are normally blocked by the platelets, can lead to bleeding.
diagnosis
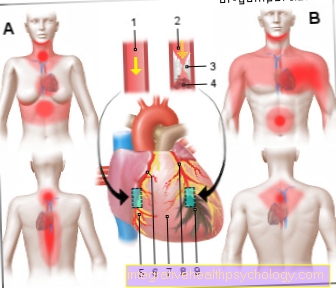
The diagnosis can be made in different ways. Which diagnostic procedure is used depends on the medical history. If external influences are the reason for the internal bleeding, the first thing to consider is the body. External injuries could provide clues as to the location of the bleeding. Other symptoms, such as the patient's blood pressure and heart rate, also need to be considered. The course of the accident must also not be ignored. Performing an emergency ultrasound can be very helpful. The most important internal structures that can be affected by internal bleeding are shown using sonography: heart and lungs, as well as liver, spleen and pelvis.
In the case of gastric bleeding, clinical evidence is of great importance. The patient should be asked about typical symptoms such as tiredness and fatigue. A pale appearance can also indicate chronic blood loss. In addition, it is typical with gastric bleeding that the stool of the person concerned has a black color. This is because blood that comes in contact with stomach acid turns black. To confirm the diagnosis, endoscopy can be done, i. Using a special device that contains a camera, the bleeding can be displayed and, if necessary, immediately closed.
In the case of aortic dissection, the diagnosis is made on the basis of a physical examination, laboratory tests, EKG and, if necessary, imaging, for example a representation of the aorta using computed tomography.
The suspicion that there may be a tropical disease arises from a survey on the last travel location. If the symptoms suggest a hemorrhagic fever, this can be confirmed by a laboratory test in which the pathogen is detected.
I recognize internal bleeding from these symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the cause. If high blood loss occurs quickly, this usually results in shock symptoms. The blood pressure drops as the blood volume decreases. To compensate, the heart rate rises sharply. Loss of consciousness may occur, and if the bleeding is chronic, symptoms of chronic anemia develop. Those affected are often pale, tired and less productive. Depending on the cause, other, more specific symptoms can occur.
As mentioned above, gastric bleeding leads to the appearance of black stools. Pain in the stomach area can also occur. An aortic dissection is often accompanied by sudden, very severe pain in the chest area. These can radiate into the back and stomach. If the blood loss is very high, shock symptoms can also occur in this case.
Also read: Symptoms of shock
In hemorrhagic fever, bleeding can take different forms. For example, skin bleeding, bloody diarrhea or blood in the urine may occur. In addition, there are usually flu-like symptoms such as fever, tiredness, headache and aching limbs.
therapy
Therapy depends on the underlying cause. In general, however, the bleeding should be stopped. In the event of accidents causing the bleeding, in many cases it must be treated surgically. If the injuries are less severe, it may be sufficient to monitor the patient in the hospital and to assess the patient's condition with regular laboratory checks, which can be used to make a statement about the blood loss. As part of the monitoring, blood pressure and heart rate should be continuously monitored. The blood pressure can be stabilized, for example, by administering infusions with a venous system. If the blood loss is particularly massive, it may also be necessary to administer foreign blood in the form of a blood transfusion.
Endoscopic hemostasis is also possible, in which bleeding vessels are obliterated. This procedure can be performed, for example, when the stomach is bleeding. Since gastric bleeding can go unnoticed for a long time, it is possible that the person has already lost a large amount of blood, which can result in an iron deficiency. In this case, iron substitution can be carried out to support adequate blood formation. Iron is an important part of the blood and can be administered in the form of tablets or as an infusion.
In the case of major vascular damage, such as aortic dissection, it may be necessary to supply the vessel with a vascular prosthesis. The implantation takes place during a surgical procedure.
Duration / forecast
No general statement can be made about duration and prognosis. These depend on the cause of the internal bleeding and the previous illnesses and health status of the patient. If the bleeding has to be treated surgically, the patient may have to be monitored in the hospital for several days or even weeks. This depends on the blood loss and the organ damage that may have occurred. The younger the person affected and the fewer previous illnesses they have, the better the prognosis.
For example, with ruptured spleen, the death rate is 0-15%. It varies greatly as the outcome depends on the accompanying injuries, the age of the patient, and the blood loss. Even with aortic dissection, the prognosis correlates with the severity of the clinical picture. It also depends on the therapy chosen. Depending on the type of dissection, surgery or conservative therapy can be beneficial. There is also no uniform prognosis for bleeding from other organs. If the bleeding is only due to inflammation, the prognosis is good with the right therapy. However, if an organ bleeds due to the presence of a tumor, the prognosis again depends on the stage of the disease.
Course of disease
As mentioned above, the course of the disease can vary depending on the cause of the internal bleeding. If the person concerned loses a large amount of blood in a short period of time, the body may no longer be able to compensate for this blood loss. This then leads to a drop in blood pressure, which can lead to an inadequate supply of vital organs. This blood loss should be counteracted immediately by drinking fluids.
Other types of blood loss may present very differently clinically. If only a small amount of blood emerges from a vessel leak over a long period of time, this can go unnoticed for a long time. The body can usually counteract this loss of blood by producing more blood. However, the compensation mechanisms are also exhausted after a certain period of time. This then results in symptoms of anemia (anemia). These are i.a. Fatigue and listlessness and can appear insidious, so that they may not be noticed by the person affected until late.
Read what the Symptoms of anemia are.
How contagious is that?
Internal bleeding is a symptom that can have various causes. There is no risk of infection for the symptom "internal bleeding". However, the underlying disease that caused the internal bleeding can be contagious. This applies to the Ebola virus, for example. If a person is infected, he can infect others through body fluids and excretions. The dengue and yellow fever virus, on the other hand, are only transmitted by mosquitoes and not from person to person.











.jpg)