Insulin resistance
introduction
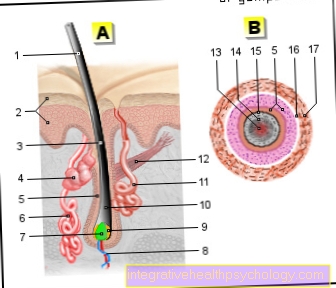
In the presence of insulin resistance, the hormone insulin, which is produced by the organism itself, has little or no regulatory influence on body cells.
Just cells from
- Musculature
- Adipose tissue or
- liver
show a reduced responsiveness to the proteohormone in the case of insulin resistance.
Read more about the Duties of insulin.
In general, insulin resistance doesn't just affect you endogenous Insulin. From externally substituted insulin preparations can hardly have any effect. Insulin resistance was defined as a condition in which the beta cells of the pancreas to maintain the regulatory tasks of the hormone, about 200 I.U. per day produce and retire.
However, these amounts cannot be synthesized even by a healthy pancreas. As a result, those affected experience one increased Blood sugar level (Blood glucose level).
Causes of Insulin Resistance
The occurrence of insulin resistance is primarily typical of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Even in the preliminary stages of this disease, insulin resistance can be demonstrated in some cases, which increases over the course and which Responsibility of the insulin receptors gradually reduce.
So far it has not been possible to conclusively prove the mechanisms to which insulin resistance is attributable.
1. Obesity
Although both Type 2 diabetes, as well as their preliminary stages in a close connection Obesity (Obesity) can also slim people get this type of diabetes. Nevertheless, obesity is probably the most important risk factor in connection with the development of insulin resistance.
2. Hereditary disposition
In addition, it has been assumed for a long time that hereditary components are involved in the development of insulin resistance. There is evidence of those in children a parent with type 2 diabetes suffers, a 50% risk getting diabetic yourself. In those cases in those both parents affected this probability increases 80% on.
3. Diet / amount of exercise
This is another cause of the development of insulin resistance disproportion between carbohydrate intake (respectively Calorie intake) and exercise Excessive amounts of calories and too little exercise lead to an increase in free fatty acids in the blood.
this in turn throttles sugar utilization in muscle and fat cells. In the long term, the consequence is a reduction in the responsiveness of muscle and fat cells to insulin (insulin resistance). The organism then stimulates the B cells of the pancreas, there is an increased release of insulin. The increased insulin supply then provokes a downregulation of the insulin receptors on the cells, and the insulin resistance increases steadily.
4. Medicines
The development of insulin resistance can also be due to ingestion various medicines to be led back. Especially the application of Cortisol, the antagonist of insulin, can lead to a reduction in the effectiveness of insulin. Since there is various infectious diseases If there is an increased release of cortisol, also apply Infections as a possible cause an insulin resistance.
Other reasons for the occurrence of insulin resistance:
- Metabolic disorders with high levels of fat in the blood
- Diseases that lead to an increase in production lead to contra-insulin hormones (for example: acromegaly)
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (short: PCOS)
- Long-lasting malnutrition
Diagnosing insulin resistance
Many people with insulin resistance have an increased body weight. Abdominal fat plays an important role here. The waist circumference can be determined as a measure of the amount of belly fat. The so-called body mass index (BMI for short) is also used to determine nutritional status.
In addition, if insulin resistance is suspected, the amount of triglycerides (blood lipids) dissolved in the blood should be determined. If the values are higher than 2.44 mmol / liter (215 mg / dl), further diagnostics should urgently be connected.
Furthermore, a reduced production of the hormone adiponectin produced by fat cells is an important indicator of the presence of insulin resistance. Further resistance tests are the so-called sugar exposure test (oral glucose tolerance test, oGTT for short) and measuring the fasting insulin level.
Find out more about the sugar exposure test at: Glucose Tolerance Test - What You Should Know!
Therapy of insulin resistance
A suitable and comprehensive therapy for insulin resistance consists of several components. For classic type 2 diabetics, the Adherence to a low-calorie diet (so-called hypocaloric diet) should be sought.
This means the daily calorie intake in women a value of 1400 kilocalories should not exceed. Male type 2 diabetic allowed during the day approximately 1800 kilocalories to take in.
In addition to adhering to a diet, this is the main factor Increase in physical activity affected patients play a major role in insulin resistance therapy.
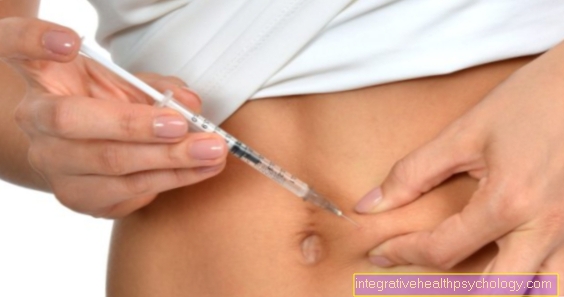
In addition, the temporary one applies Increase in insulin intake to very high doses at short intervals as a way of breaking insulin resistance. The administration of insulin can both subcutaneous (under the skin) or intravenous (into the vein). Come with this form of insulin resistance therapy Normal and / or analog insulins as suitable preparations in question. It has been proven that after the initially high doses, a reduction in the amount of insulin administered is possible after just a few days.
Furthermore there is various medicinesthat are specifically used to treat insulin resistance. Among the most famous drugs are
- the biguanide Metformin
- of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose or
- the insulin sensitizer Pioglitazone.
All of these drugs belong to the group of so-called oral anti-diabetic drugs. One of the most important side effects is the risk of developing one Hypoglycaemia (Hypoglycemia) that the regular Blood sugar control taking most oral anti-diabetic drugs.
It is precisely in this fact that the great advantage of the most commonly used metformin lies. Due to its mechanism of action, this does not involve the risk of hypoglycemia and is therefore essential less often for metabolic imbalances.
Is insulin resistance curable?
Insulin resistance usually develops over a longer period of time and, in addition to genetic factors, depends very much on diet and physical activity. Excessive calorie intake and insufficient physical activity lead to an ever-increasing increase in insulin resistance over time, so that the chances of recovery are reduced. With the onset of insulin resistance, on the other hand, the insulin sensitivity can often be increased again through a conscious and healthy diet and physical activity, so that these measures offer the prospect of a cure. In many cases, taking tablets or even injecting insulin can be avoided. The mentioned lifestyle change measures are always useful to counteract at least a further progression of insulin resistance.
What is the point of losing weight if you are insulin resistant?
In the development of insulin resistance, a vicious circle consisting of a high-calorie diet and insufficient exercise plays an important role. A mismatch between the calories ingested and the body's energy consumption leads to an increase in blood lipid and blood sugar levels. The body tries to counteract this by increasing the release of insulin. This in turn leads to increased storage of excess calories in the fat cells. As a result, people continue to gain weight, which also restricts physical activity and performance. It is therefore particularly important to lose weight in overweight people with an insulin resistance. This can often break the vicious circle. The blood sugar and blood fat levels drop. In addition, the insulin sensitivity increases again. However, the pathological changes in insulin resistance are only reversible to a certain extent. At least weight loss can counteract an increase in insulin resistance.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCO)
Insulin resistance is an essential part in the development of the Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCO). This disease is a metabolic disorder in women which, in addition to insulin resistance and obesity, is often associated with masculinization due to an excess of male sex hormones. A lack of ovulation and cysts in the ovaries can also form part of the disease. How exactly the connection between insulin resistance and the other possible symptoms of PCO is has not yet been established with certainty. Affected women, however, have an increased risk of developing diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
For women with PCO and overweight, the primary goal should be weight loss through a healthy diet and sufficient physical activity. These measures can often improve the symptoms, including insulin resistance. If the symptoms of PCO cannot be alleviated by natural measures, hormone treatment is often the only therapeutic option. The insulin resistance often has to be treated with medication in the case of elevated sugar levels.
Read more on the topic: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome











.jpg)