Is an MRI dangerous during pregnancy - what should you watch out for?
synonym
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- NMR
definition
Under the term MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) one understands an imaging process that is used to represent the human body. The MRI will be used, as will the Computed Tomography (CT), belongs to the group of cross-sectional imaging techniques.
introduction

MRI is a diagnostic technique that is used to visualize internal organs and various tissue structures. The MRI works with magnetic fields and radio waves. The patient to be examined is not exposed to any X-rays in this imaging process.
However, there are also restrictions when it comes to making an MRI. For this reason, for example, people who have an implanted pacemaker cannot be diagnosed using an MRI.
In assessing the question of whether performing an MRI scan during pregnancy can be harmful to the unborn child, there is so far only limited experience.
An MRI during pregnancy must always be carefully considered. However, due to the lack of radiation harmful to the fetus, an MRI during pregnancy is possible under certain conditions.
Today it is assumed that, in contrast to the production of X-rays, the MRI examination during pregnancy does not pose any risk from radiation.
Nevertheless, before each MRI examination, it should be checked whether it is actually necessary to produce cross-sectional images using magnetic resonance imaging.
This is especially true during the first trimester of pregnancy.
How the MRI works
The functionality of a magnetic resonance tomograph is based on the formation of a very strong magnetic field. With the help of this magnetic field, the atomic nuclei, especially the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, can be aligned.In the course of this, the atomic nuclei change from a low-energy to a high-energy state.
The atomic nuclei excited by the magnetic field are then set into oscillation. Of the Magnetic resonance tomograph (MRT) can switch off the magnetic field it generates at regular intervals. In this way, the previously excited atomic nuclei fall back into their low-energy basic state and give off energy in the process. It is precisely this energy that can be recorded by the MRT and converted into sectional images.
The production of such sectional images with the aid of a magnetic resonance tomograph can be useful for various reasons.
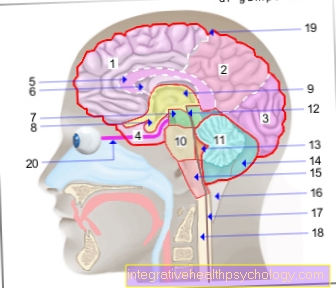
A main reason for using this imaging method is the targeted and differentiated display of all body tissues. In contrast to conventional X-rays, MRI is able to depict non-osseous structures such as soft tissues, organs, articular cartilage, intervertebral discs or the brain. In addition, detailed images of the heart can now be made.
With the help of magnetic resonance tomography (MRT), even minor changes in the body, such as inflammatory processes or small growths, can be reliably detected. Anatomical structures that only have a low water content, for example bones or the air-filled lungs, on the other hand, cannot be optimally represented with the MRI.
Here a special MRI of the lungs has to be made, in which the contrast is improved by helium.
preparation
During the preparation of the sectional images, the patient has to approximate depending on the body region to be examined 70 to 100 centimeters long, closed tube lie.
Patients who are under Claustrophobia (claustrophobia) suffer, should inform the caring staff of this before the examination.
If you suffer from claustrophobia, read our topic MRI for claustrophobiaHow an MRI can be performed despite existing claustrophobia.
An alternative to conventional magnetic resonance imaging during pregnancy is the so-called open MRI The new magnetic resonance tomographs have an open recording station that enables a panoramic view from the device. In this way, the MRI can also be carried out on pregnant patients who suffer from severe claustrophobia without taking a sedative.
During the actual examination, regardless of whether it is a conventional or an open MRI, the device loud knocking noises generated. Since the majority of patients find this extremely uncomfortable, the patient to be examined receives special Soundproof headphones or earplugs.
In addition, before starting the examination, it must be noted that magnetic objects can significantly disrupt the functioning of the magnetic resonance tomograph. For this reason, all electromagnetic objects must be placed in front of the examination room. This is especially true for Glasses, Dentures, contact lenses, Hearing aids, Hair clips, Rings, key and Clocks.
application areas
Even during the pregnancy the production of sectional images using MRI can be useful for various reasons.
A MRI of the pelvis can, for example, indicate the presence of gynecological tumors, altered lymph nodes, Rectal carcinomas, Inflammation in the area of the Hip joint or Cysts deliver to the ovaries.
In addition, with the help of an MRI examination free liquid can be reliably detected in the pelvic area. This can especially occur if there are complications during pregnancy or if the presence of one is suspected Ectopic pregnancy be helpful.
The production of MRI slices of the breast however, serves primarily as a supplement to Mammography and Sonography (Ultrasonic).
With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, both Ulcers (Tumors), as well as inflammatory processes within the mammary gland tissue.
In this context, however, it should be noted that the production of additional MRT cross-sectional images during the pregnancy should be carefully thought out.
It is assumed that carrying out an MRI scan during pregnancy poses no risk to the unborn child, but no extensive studies are available to support this assumption.
If there is a suspicion of impairment of the arterial and / or venous vessels during pregnancy, an MRI scan can be helpful if this seems unavoidable. That way you can inflammatory processes along the Vessel walls, Widenings or Closures (e.g. blood clots) can be reliably detected.
Even after traumatic events, for example one traffic accident, the preparation of MRI cross-sectional images during pregnancy can be essential and useful.
Other reasons that may justify performing an MRI scan during pregnancy include:
- Tumors
- Ischemic processes (e.g. stroke)
- disc prolapse with strong symptoms such as Paralysis during pregnancy
- Vertebral body fractures
free fluid in the abdomen
Treatment process
The duration of the preparation of MRI cross-sectional images depends primarily on the body region to be imaged. In direct comparison to the usual imaging methods, for example Computed Tomography or conventional X-ray, the MRI examination takes relatively long Long. Depending on the region of the body, the duration can be approximately 15 to 30 minutes can be assumed.
During the entire examination, the region of the body to be examined must be positioned in a narrow tube. When investigating the thorax, the abdominal or pelvic area and the head, the patient must be pushed into the MRI tube on a special couch. The Tightness the MRI tube and those generated by the device Knocking noises as uncomfortable for many patients. In addition, the available space within the MRT machine is additionally restricted during pregnancy.
During the examination, the magnetic resonance tomograph generates an extremely strong magnetic field. Such a high resolution of the individual sectional images can only be generated by the formation of such a strong magnetic field.
As a rule, the patient to be examined becomes a special one ear protection created. In this way, the examination can usually be carried out in a much more relaxed manner. During the entire admission period it is important that the patient perfectly calm lingers in one position. Even the smallest movements during the examination can lead to the MRT cross-sectional images becoming blurred and therefore not very meaningful.
In patients who are under strong Claustrophobia (claustrophobia) should therefore also be given a light dose during pregnancy Sedative to be thought about. If this is not possible, an application can be made to the health insurance company to cover costs for an MRI examination in open MRI be asked.
Since there are severe restrictions on the use of various drugs during pregnancy and therefore not taken any sedative This application is usually granted.
Contraindication
When performing an MRI scan during pregnancy, the following generally apply general contraindications.
Since a magnetic resonance tomograph works with a strong magnetic field, people who have electromagnetic products in their bodies must not be examined in an MRI.
The following groups of people may not be examined by MRI (further contraindications): Patients with:
- Pacemaker (such as a cardiac or bladder pacemaker)
- implanted insulin or pain pumps
- recently implanted joint prostheses
- Metal vessel clips
- Neurostimulators
- Cochlear implant
- older middle ear implants
- magnetically adhering Dentures.
Although it is believed that performing an MRI scan during pregnancy for the unborn child without hesitation is, the first trimester of pregnancy applies (Early pregnancy, the first three months pregnancy) as a contraindication for the preparation of MRI cross-sectional images.
In general, however, an MRI scan may only be performed during late pregnancy if strictly indicated.
Risk to pregnancy

According to the current state of knowledge, there is no particular risk involved in making MRI cross-sectional images during pregnancy. This means that it cannot be assumed that the strong magnetic field will damage the unborn child.
However, it is advisable not to perform an MRI scan, especially during early pregnancy, i.e. during the first three months of pregnancy. However, in order to ensure that a previously undetected risk remains as low as possible during late pregnancy, MRI examinations should only be carried out on expectant mothers in urgent cases.
However, the general risk applies to female patients during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding women should also ensure that breastfeeding is suspended for at least 24 hours after the administration of a contrast agent. Otherwise there is a risk of contrast agent intoxication for the breast-fed child.
In healthy people, regardless of whether they are pregnant or not, no long-term risks and side effects can be expected.
In contrast to computed tomography or conventional x-rays, magnetic resonance tomography even offers the advantage that the patient to be examined does not have to be exposed to x-rays.
As a result, MRI during pregnancy does not pose a risk of malformations in the unborn child caused by X-rays.
Only for patients with electromagnetic foreign bodies is there a certain risk when performing an MRI scan. For this reason, magnetic foreign objects such as coins, keys, pieces of jewelry or hair clips should be removed before the examination and stored outside the examination room.
Otherwise, the strong magnetic field could draw these objects into the magnetic resonance tomograph, accelerate them within the examination tube and injure the patient.
In this context one speaks of a so-called projectile effect.
Read more on the subject at: Is an MRI harmful?
Contrast media
Because different types of tissue, for example Muscles and Blood vessels appear in a similar manner in conventional MRI images Shades of gray and for this reason they are difficult to distinguish from one another. With the help of a special Contrast agent however, blood vessels can better represent. The reason for this is one enrichment of the contrast medium in the area of the vessels.
However, in order to enable a better differentiation between the different tissue types, the contrast medium has to be introduced into the arm vein a few minutes before the start of the MRI examination injected become. The contrast agent can then be distributed throughout the body via the bloodstream. Also in the area of Tumors and Metastases (Daughter ulcers) the contrast agent accumulates more strongly. For this reason, such changes in the Contrast MRI clearly visible.
In most cases, the contrast agent is tolerated by the patient without any problems and it only occurs extremely rarely side effects on. In some cases, however, it occurred after the administration of a contrast agent a headache, malaise, warmth- or Feeling cold, tingle and Skin irritation at the puncture site. Also allergic reaction tend to be a rarity after the administration of a contrast agent.
Nevertheless, the use of a contrast medium must be used both during pregnancy and while breastfeeding thoroughly thought out become. During pregnancy, when performing a contrast medium MRI, the Ratio of benefit and risk be weighed. The main reason for this is the fact that many of the contrast media used today containing iodine are. For this reason, their use during pregnancy may affect the maturation and / or function of the Thyroid gland of the unborn child influence.
In this context, it must also be noted that patients who are pregnant with a known Thyroid dysfunction under no circumstances should a contrast agent containing iodine be administered.
Guidelines / guidelines
According to the guidelines / guidelines, a MRI-Examination during pregnancy only in exceptions be performed.
During the Early pregnancy, that means, during the first three months of pregnancy, according to guidelines / guidelines, the preparation of MRI cross-sectional images should be completely avoided.
According to the guidelines / guidelines, no harmful influence of the Magnetic field can be demonstrated on the unborn child. However, due to a lack of studies, a risk cannot be excluded with certainty.
For this reason, the guidelines / guidelines place particular emphasis on the fact that when considering whether an MRI should be performed, an Benefit-risk analysis should be done.
Only in cases in which the benefit for the expectant mother outweighs the risk for the unborn child and no alternative diagnostic measures (e.g. a Ultrasound examination) are effective, an MRI scan should be performed during the pregnancy be performed.
What can be seen on the MRI of the pelvis during pregnancy?
The MRI can during the pregnancy can also be used to measure the pelvis of the expectant mother. This examination method helps to see how much space there is in the Birth canal is present for the baby. In case of doubt, this in turn can provide information about whether a vaginal birth is even possible or whether it is due to the to narrow pelvis problems can arise.
That way one can Pelvic MRI help determine if a caesarean section should be initiated during pregnancy. Due to the fact that a disproportion between the unborn child's head and the birth canal is one of the most common causes of long-lasting births, it can make sense to do a pelvic MRI during pregnancy and before birth.
You can find more information under our topic: MRI of the pelvis










.jpg)