Iodine allergy - what to watch out for
What is an iodine allergy?
An iodine allergy is a relatively rare allergic reaction that occurs when exposed to large amounts of iodine. At the same time, iodine is an essential substance that the body needs in order to produce thyroid hormones, for example. People with an iodine allergy usually do not react to the iodine in food, so that despite the allergy they can get enough iodine through their food. The allergic reaction is more likely to occur if, for example, a disinfectant containing iodine is used, as well as after contact with X-ray contrast media or after taking iodine-containing medication.
What causes the iodine allergy?
If iodine is supplied to the body, it is absorbed by the body through a mucous membrane. The immune system checks whether it is a dangerous or harmless substance. Sometimes this distinction is not reliable and iodine is mistakenly perceived as a dangerous substance. This is called awareness. An allergy is only spoken of when symptoms appear. The allergy to iodine belongs to the group of allergies of the late type (type 4). Upon first contact with iodine, it is absorbed and specific cells (T lymphocytes) are formed in the lymph nodes, which react sensitively to iodine (sensitization phase). The trigger or effector phase does not begin until the next contact with iodine. The T lymphocytes recognize the iodine and trigger a cascade of immune reactions. In connection with this immune reaction, messenger substances are released, which in turn promote inflammation in the tissue and thus lead to the known symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Further information on the development of an allergy can be found at: Allergic reaction
How can an iodine allergy be determined?
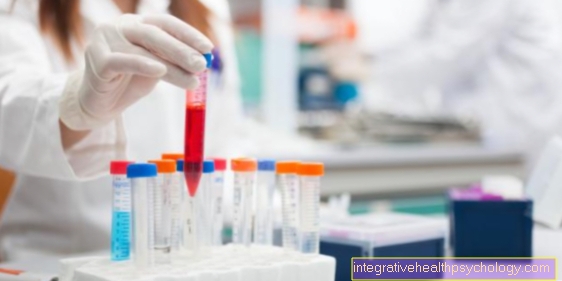
The diagnosis is usually made by an allergist. A detailed conversation can be used to discuss the situations in which the allergic reaction occurs. This allows the triggering substances to be identified. In the case of iodine allergy, this can sometimes be difficult, since most patients do not react to the iodine in food, but only show a reaction to the intake of large amounts of iodine, as for example during a contrast examination. In an analysis of the blood, substances can be identified that are found to be higher in an allergy. The next step would be to do a provocation test by applying some iodine to an area of skin and waiting for the reaction.
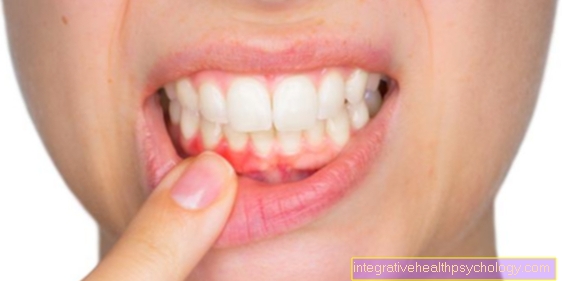
I recognize an iodine allergy by these symptoms
When you first come into contact with iodine, there are no symptoms of an iodine allergy. Only after the second contact is the immune system already sensitized to iodine and triggers various symptoms within 12 to 48 hours after contact with iodine. For this reason, iodine allergy is also classified as a type 4 reaction, as the symptoms only appear with a delay. The focus is on the development of eczema. Eczema is a certain type of rash that presents with redness and the formation of blisters. The rash can also ooze and itch. In some cases, the rash changes over time, creating scabs or scales. The rash particularly affects the areas around the head, such as the skin behind the ears and the area around the eyes. Skin reactions on the trunk as well as the arms and legs can also be observed. In addition to reactions on the skin, an iodine allergy can manifest itself with all kinds of unspecific symptoms, such as cough, malaise and headache. A reaction of the airways is also possible with an iodine allergy. The airways narrow and a feeling of shortness of breath arises. In extreme cases, the iodine allergy can also trigger an anaphylactic shock. It is the result of the maximum overreaction of the immune system and a serious condition that needs to be treated in hospital.
You might also be interested in: Anaphylactic shock
Treatment of an iodine allergy
Therapy depends on the severity of the allergic reaction. In the case of skin symptoms alone, these can be treated with antihistamines or a cream containing cortisone from the pharmacy. For further care of the skin areas, it is recommended to treat them with greasy cream ointments. In the case of stronger reactions involving the airways, treatment with the stress hormone epinephrine may be necessary to widen the airways again. In the event of such a reaction, the patient should be carefully monitored in order to identify further problems of the circulatory system at an early stage and to initiate appropriate measures. If the allergic reaction occurs after an examination with contrast agent, the patient should definitely be treated by an emergency doctor in the hospital. The risk of the patient suffering an anaphylactic shock cannot be neglected. Here it is important to constantly measure the vital parameters such as blood pressure and pulse and, in the event of deterioration, to give acute medical treatment quickly.
Duration of an iodine allergy
An iodine allergy is an acute reaction of the immune system and is usually not of prolonged duration. With appropriate treatment, the skin reactions should subside within a few days. If the airways are narrowed and treated with epinephrine, the symptoms will improve within a very short time. However, caution is still required, as one has to observe how the symptoms present themselves when the epinephrine has been broken down by the body. Anaphylactic shock alone can result in lengthy hospital treatment, but it also varies from person to person.
This must be taken into account if you are allergic to contrast media
People with an iodine allergy react particularly to some contrast media. The reason for this is that these contrast media contain larger amounts of iodine. Contrast media are used in imaging to better represent certain structures of the body and are part of the standard diagnosis. Iodine allergy sufferers would be advised against such a contrast agent examination and try to find an alternative. In some cases, however, the administration of contrast agent can be essential so that other, dangerous diagnoses can be diagnosed or excluded with certainty. If this is not an emergency, the patient is given cortisone twelve and two hours before the examination. The cortisone inhibits the immune system so that an excessive allergic reaction is less likely. The cortisone can also be given once via the vein six hours before the examination. Immediately before the examination, an antihistamine is administered to the patient via the vein to block the effect of the "allergy hormone" histamine. If it is an emergency, you cannot wait for the cortisone to take effect before imaging. In this case you would only give the antihistamine.
Also read: Contrast agent allergy
This must be taken into account during an operation
You can use other disinfectants during an operation if you are allergic to iodine. These offer the same protection against germs and thus avoid any skin reactions. Before the operation, there will be talks with the surgeon and the anesthetist. It is important to mention here that you have an iodine allergy so that another disinfectant can be provided in preparation for the operation.
Iodine allergy and thyroid gland - how are they related?
In the thyroid gland, iodine is absorbed from the blood and fed into the cells of the thyroid gland.A chemical reaction occurs there, which leads to the iodine being incorporated into the thyroid hormone. This is then stored in the thyroid gland until it is used. If the thyroid gland receives a signal that thyroid hormone is required in the body, the thyroid gland releases hormones, including iodine.
Also read: Thyroid hormones
Can i get an iodine allergy from iodized salt?
You cannot get an iodine allergy through iodized salt. The iodine contained in salt is too small to provoke a reaction in the immune system. In contrast media or disinfectants, the iodine is present in larger particles, which is why an allergic reaction can occur here.










.jpg)