Sphenoid sinusitis
definition
Since the sphenoid sinuses (Sinus sphenoidales) are two connected, air-filled cavities in the sphenoid bone of the skull and are lined with nasal mucous membrane, they, like the frontal and maxillary sinuses and the ethmoid cells, belong to the so-called paranasal sinuses. Like all paranasal sinuses, they serve to reduce the weight of the cranial bone system and as a resonance space for voices and sounds. Only the ethmoid cells are already created at birth, all other paranasal sinuses develop only with advancing childhood: the sphenoid sinuses are the second development point and form - after the frontal sinuses and in front of the maxillary sinuses - around the 3rd-6th. Year of life.

The sphenoid sinuses are anatomically aligned with the upper one Turbinate in connection and have a close spatial proximity to the Pituitary gland - the pituitary gland (it lies directly above the sphenoid sinusesso that access through the paranasal sinus system can be selected during a surgical procedure). A sphenoid sinusitis is one of the through Viruses or bacteria triggered sinus infections (Sinusitis), with the involvement of the sphenoid sinuses rather seldom occurs (the most common are the Maxillary sinuses (Sinusitis maxillires) and the Ethmoid cells (Ethmoid sinusitis) (see also: Inflammation of the ethmoid cells) infested. It can be acute or chronic over a long period of time.
Is Sinus Infection Contagious? Find out more at How contagious is a sinus infection
root cause
The causes of the development of a sphenoid sinusitis are identical to those of all other sinus infections: in the vast majority of cases it is one secondary infection of the Sinus lining by Viruses or, less commonly, bacteriathat differ from one already existing respiratory diseases (Inflammation of the nose and throat such as a sniff) about the Nasal passages spread into the sinus system. The triggering pathogens are usually transmitted by a Droplet infection. In 70-80% of the cases this is a cold virus such as Rhinoviruses or adenoviruses. A sole infection by bacteria is rather rare, mostly it is a species "Additional infection", since the attacked and swollen by the viral infection Sinus lining forms an optimal breeding ground for bacteria (e.g. for Haemophilus influenza or Streptococcus pneumoniae).
Inflammation of the sinuses may be less common also alone, without previous respiratory disease as primary infection occur, being sick Tooth roots (dentogenic sinusitis), pathogens in bath water (bath sinusitis) or extreme fluctuations in pressure while diving or To fly (Barosinusitis) should be considered the causes. But also in the context of Allergies sinus involvement can certainly occur.
Various anatomical features can promote the development of a sinus infection (sphenoid infection) and are therefore considered a type of risk factor. For one thing, a crooked nasal septum (congenital or acquired) and on the other hand so-called Nasal polyps the removal of what has formed in the sinuses Slime obstruct via the nasal passages into the nasal cavity. This leads to a build-up of mucus in the sinus system, causing this narrowed and less well ventilated. Everything together favors the settlement, survival and multiplication of Viruses and bacteria and may be the emergence of a first acute, but later also one chronic Sinus infection will result if the risk factors are not eliminated.
Symptoms
Above all, they are characteristic of acute sinusitis Headachen mostly in the form of a piercing, pulsating or stabbing Feeling of pressure, the exact location of the complaints from the respective affected sinuses depends. So if the sphenoid sinuses are inflamed, the feeling of pressure or headache is more in the area of the Back of the head (back of the head) but it can also be a diffuse headache that cannot be precisely localized. In addition, head complaints can often worsen as soon as the Upper body tilted forward and the Head down to be led. Often there is a parallel sniff (Rhinitis) before as well as obstructed nasal breathing, restricted odor and Sense of taste, an altered nasal language and an enhanced one Discharge from the nose and in the throat, whereby the secretion is usually watery at the beginning, later thick and even with an additional bacterial infection purulent-yellow-greenish may be discolored.
In addition, the general infection can also fever, Body aches, fatigue and cough are added, the latter preferably through at night Exiting mucus along the throat and airways causes irritation. If there is chronic inflammation of the sphenoid sinus / sinusitis, the headache is more likely to come with a intermittent and lower intensity on (sometimes stronger, sometimes weaker) the physical performance limited and those affected often suffer from chronic Fatigue syndrome. The symptoms of acute sinusitis (of the sphenoid sinuses) usually subside after a short time (on average 2 weeks), but at the latest it should follow 8-12 weeks to be endured. If it doesn't and the symptoms are still after 2-3 months present, one speaks of a chronic sinus infection.
diagnosis
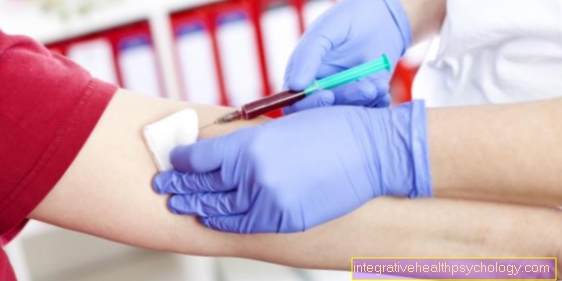
The diagnosis of inflammation of the sphenoid sinus or paranasal sinuses is usually obvious when the person concerned reports the characteristic complaints / symptoms (Headache, runny nose, smell / taste disorders, stuffy, runny nose). To further solidify the diagnosis, a endoscopic examination done by a doctor who uses an endoscope inserted through the nostrils or mouth to visually visualize the sinuses. In this way it can be determined exactly which sinus (s) is / are affected and whether there are any anatomical features that could represent a possible cause. In addition, is a Collection of sinus secretions possible during the endoscopy, so that this - if necessary - is sent to a laboratory and the causative agent be determined microbiologically. Knowing the exact pathogen enables a completely targeted therapy, as this can then be optimally adjusted to the germ.
If the diagnosis proves difficult due to the anamnesis and the endoscopy or if the resulting findings are inconclusive, further imaging methods can be used: CT (computed tomography) is the best method of choice because the resulting sectional images are a possible one Secretion congestion, inflammatory reactions, anatomical features and swelling of the mucous membranes in the respective sinus affected. In addition, the preparation of CT images prior to any planned surgical therapy measure indispensableto get an accurate overview of the spatial expansion of inflammation.
therapy
In the treatment of sphenoid sinusitis or sinus infections in general, both conservative and surgical therapeutic measures are available. In many cases, the symptoms sound like acute sinusitis after a few days even on its own, so that no or only supportive therapy is necessary. On the other hand, chronic sinusitis that persists for a long time, often only through an operation be eliminated.
Used in acute sinusitis by one viral origin assumed, a decongestant is usually used first Nasal spray (or Nasal drops) prescribed by the attending physician. The decongestant ingredient may also be combined with cortisone to create a anti-inflammatory To enable effect. Also nasal showers Sea salt base and warm Overhead steam baths can help to drain the stuck secretion. Other expectorant drugs (e.g. ACC) can be taken as support, although one Healing acceleration this is not entirely undisputed. Are there other symptoms of infection such as fever, can also be antipyretic and anti-inflammatory at the same time Painkiller be taken (e.g. Ibuprofen, Paracetamol).
Since it's usually a virus acts, the instant gift is one Antibiotic ineffective. Only in cases where it can be proven that a primary bacterial infection or there is a suspected additional bacterial infection (usually when the secretion purulent yellow-green is discolored), is the Administration of antibiotics indexed. Is the cause of an acute or even one chronic sinusitis an allergy, are therefore Antiallergic drugs and a Desensitization a suitable therapy option. If the symptoms cannot be relieved by all of these remedies and / or if there is a chronic sinus infection, various surgical interventions can still provide a remedy: on the one hand, one can Sinus puncture can be made to allow the accumulated secretion to drain, on the other hand anatomical peculiarities can be eliminated. These include the Nasal septum straightening, the removal of Nasal polyps or downsizing the Turbinates. The surgical interventions are usually carried out under general anesthesia and using an endoscope.