Dead body poison in the tooth
introduction
The term “corpse poison” of a tooth describes the fact that there are still tissue residues and cells as well as their metabolic products in the tooth when the nerve has already died. This biomass in the root canal system of a tooth can secrete substances that cause inflammation.
Whereby the term "corpse poison" in relation to the teeth is out of date and very imprecise, since the tooth itself is preserved and only the pulp (ie nerves and blood vessels) of the tooth dies and is broken down; that is, the tooth nerve "decays". Medically more correct would be: 'Pulp necrosis' or "putrefaction of the dead tooth nerve".
Read more on the topic: Dead tooth
Causes - Why does corpse poison form in the tooth?
In general, root canal treatment is only ever an attempt to save a tooth.
The anatomy of the canal system makes complete removal of residual tissue and disinfection difficult due to the strong ramifications and side canals in the area of the root tip. As a result, residual tissue almost always remains in the tooth root. This residual tissue can be metabolized by bacteria and thereby Toxins (Cell toxins) produce.
The toxins like Mercaptans and biogenic amines arise in inflammatory processes and are natural metabolic products that occur in almost all living organisms. Mercaptans are found in garlic or asparagus and biogenic amines in fresh fish.
In the case of a market-dead tooth, toxins are constantly released due to the tissue remaining, which lead to inflammatory reactions. In general, it is true that inflammations within the oral cavity, including below the root tip, are capable of affecting the entire organism and causing cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the affected teeth should be treated as soon as possible to remove the inflammatory cells.
Also read: Pulp necrosis - causes and therapy
What are the symptoms of dead body poison in the tooth?
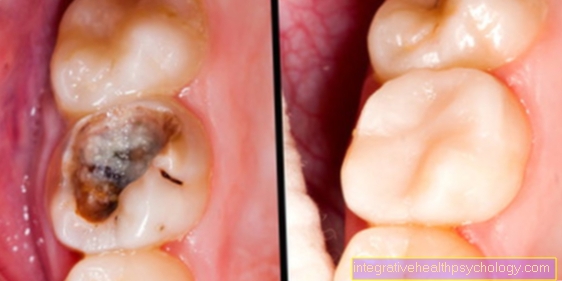
Classic symptoms of dead teeth can be bite pain and tenderness. Furthermore, a devitalized tooth can also be completely symptom-free, which is why it is not noticed. After a while, it can turn dark when the blood contained in the blood vessels releases iron after it has been broken down and this turns the tooth gray. Only then will the patient notice the dead tooth.
In naturopathy, many homeopaths are of the opinion that complaints of any kind and part of the body can be caused by the "corpse poison" of a tooth that has not been marketed or that has undergone a root canal treatment and why these teeth should be eliminated. However, this assumption has not been proven by any studies, which is why the attending dentist should always be consulted.
Find out more at: These are the symptoms of pulp necrosis and pulpitis
Treatment - what can be done about corpse poison?
A market-dead tooth is treated with a root canal treatment. The root canal can be filled with thermoplastic or stable root filling material, which means that either prefabricated posts are inserted or are compacted with a liquid filling material.
Teeth that are already root-filled and have persistent chronic inflammation can either be performed by revising the old filling and renewed root filling or by a root tip resection, in which the root tip is surgically separated.
Only if the above treatments do not work is it necessary to remove the tooth.
How long will the treatment take?
The duration of a root canal treatment is usually three appointments approximately every week. During these appointments, the canal system is prepared and disinfected and the root canal filling is finally placed in the now clean environment.
The root tip resection is a one-time appointment that can last three quarters to one and a half hours. After both procedures, you have to wait about two to four weeks to see whether the treatment has worked, the healing has taken place and the tooth has become symptom-free.
diagnosis
The concentration of mercaptans and thioethers can be determined diagnostically by testing the sulcus fluid of the affected tooth. However, these only signal that an inflammatory process is present.
Usually the dentist will feel the oral cavity and take an X-ray of the suspect tooth.
Chronic inflammation under the root tip of the tooth becomes clear through a bone dissolution as a brightening in the X-ray image. Furthermore, the affected tooth may respond to knocking with a pain response, which is also a apical periodontal disease, an inflammation under the tip of the root, speaks.
our recommendations for you
- Pulp necrosis - causes and therapy
- These are the symptoms of pulp necrosis
- Root canal treatment
- Apical resection








.jpg)