Photosensitive eyes - what can be behind it?
What is light-sensitive eyes?
A light-sensitive eye reacts sensitively even to low light stimuli. For this reason, those affected avoid light and are reluctant to go to the sun. This situation is described in medical terminology as photophobia.
Photobia can be triggered by various underlying diseases, such as neurological, psychological or ophthalmological - i.e. diseases that affect the eye. It can also occur with pain, watery eyes, headache and dizziness.

The reasons
The causes of an eye's sensitivity to light are not fully understood and vary depending on the underlying diseases.
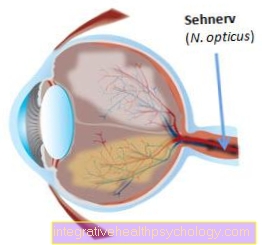
The most common causes are neurological diseases. The optic nerve can be irritated by an inflammation. This inflammation is called retrobulbar neuritis in medical terminology and can be triggered by multiple sclerosis, intoxication or infectious diseases. A migraine can also cause photobia.
In addition, diseases of the eye such as uveitis (inflammation of the skin of the eye) or inflammation of the retina can lead to sensitivity to light. The inflammatory reaction of the eye also leads to irritation of the optic nerve. In addition to the illnesses mentioned, psychological triggers such as depressive episodes should be taken into account.
Find out more about the topic here: The optic nerve inflammation.
The vitamin deficiency as the cause
A vitamin deficiency as the cause is rather unlikely and only occurs later on. The vitamin deficiency must have existed for a long time and has usually triggered other symptoms before it becomes noticeable in the eyes.
Vitamins that are particularly important for the eye are vitamin A and vitamin B12. A vitamin A deficiency leads to poor vision, especially in the dark - so-called night blindness. In addition, the eye dries out faster and becomes very sensitive. In the course of this, photosensitivity can also arise.
A vitamin B12 deficiency, on the other hand, can damage peripheral nerves, the spinal cord and the brain. Vitamin B12 is involved in building a protective covering (myelin sheath) around the nerves. This shell leads to an improved transmission of nerve impulses. If the shell is damaged, these impulses can no longer be properly transmitted and sensory disturbances and paralysis can occur. If the optic nerve has been damaged, blurred vision and sensitivity to light develop.
The thyroid as the cause
The thyroid produces hormones that are essential for the regulation of metabolic processes. If this balance is disturbed, the entire body can be affected. The eye in particular is a sensitive organ and is often affected.
Both an overactive thyroid and an underactive thyroid can negatively affect the eye. The most common disease in this case is the autoimmune disease Graves' disease, which leads to hyperfunction and triggers what is known as endocrine orbitopathy. The eyes protrude and the lids are pulled up. This leads to dehydration of the eye and associated sensitivity. Bright light or cold drafts are perceived painfully. In addition to Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis can also cause these symptoms. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is also an autoimmune disease, but it leads to an underactive thyroid.
The symptoms in the eyes can regress again through successful treatment of the underlying disease or through a balanced thyroid hormone concentration.
Also read the articles:
- The overactive thyroid
- The hypothyroidism
The contact lenses as the cause
Unfortunately, some people cannot tolerate contact lenses. You suffer from reddened and itchy eyes. In addition, one can have a foreign body sensation in the eye and the eyelids can swell. The inflammatory reaction causes dry eyes, which leads to sensitivity of the eye. As a result, environmental stimuli such as cold air or too much light are perceived as painful.
If there is a suspicion of contact lens intolerance, it is recommended to wear glasses. If the symptoms regress again, one can assume an intolerance. In this case you should go to the optician, as changing the contact lens brand sometimes leads to an improvement.
Find out all about the topic here: The contact lens intolerance.
The accompanying symptoms
Depending on the underlying disease, the symptoms can be quite different.
If there is inflammation of the optic nerve, blurred vision occurs. Headaches and a feeling of pressure in the eyeball can also accompany this. Visual disturbances in the form of flashes of light or zigzag lines can occur with a migraine. Other symptoms of a migraine include tiredness, trouble sleeping, nausea and vomiting. Paralysis and sensitivity to noise can also occur. In the presence of multiple sclerosis, the symptoms vary widely. Sensitivity disorders, symptoms of paralysis, depressive moods, headaches or concentration problems can occur. The symptoms are therefore dependent on the area of the brain that is damaged, as each area in the brain fulfills a different task.
In the case of a disease of the eye, such as inflammation of the skin of the eye or the retina, there is reddening, increased tearing and a feeling of foreign bodies in the eye. In addition, visual acuity is reduced. If the photophobia is triggered by mental illness, the accompanying symptoms are also variable. Sleep problems, concentration problems and headaches can occur.
Blurred vision as an accompanying symptom
Blurred vision is a symptom that is often associated with sensitivity to light in the eyes. The cause of this is the irritation or damage to the optic nerve (optic nerve). The optic nerve normally perceives incident light stimuli and forwards them to the brain for information processing. However, if the nerve is irritated by an inflammation, such as in retrobulbar neuritis or an inflammation of the choroid, this process can no longer proceed properly. The light stimuli are perceived more intensely and trigger pain. In addition, the surroundings can no longer be seen clearly, as this leads to dysregulation. How exactly this dysregulation occurs is, however, unclear.
Damage to the optic nerve, as is the case with multiple sclerosis, also leads to blurred vision. However, there is a risk of going blind due to severe nerve damage. For this reason, it is important to see a doctor if you have photosensitivity and blurred vision so that the disease can be clarified.
Find out more about the topic here: The optic nerve inflammation in MS.
The headache as an accompanying symptom
Headaches are also a frequent accompanying symptom. Neurological diseases in particular can trigger headaches. The best known illness in this context is migraine. Affected people complain of one-sided headaches that occur in attacks and that are particularly pronounced.
Furthermore, infectious diseases such as meningitis, i.e. meningitis, can cause severe headaches. The meninges (meninges) are supplied by numerous nerves. These can be irritated by the inflammatory reaction triggered by the infection and cause severe pain. Comparatively mild headaches can be caused by retrobulbar neuritis, an inflammation of the optic nerve.
Can I be depressed?
An increased sensitivity of the eyes to light can indicate depression, but it is not a typical symptom. If symptoms such as listlessness, sleep disorders, and social isolation occur, the likelihood of depression is significantly increased.
The causes and the exact mechanism that leads to depression are not fully understood. Genetic predispositions and environmental factors are discussed. The interaction of these factors leads to a metabolic disorder of the brain. Comparatively low concentrations of messenger substances such as serotonin or dopamine are found. This imbalance of messenger substances leads to a dysfunction of the brain. This can also lead to functional disorders of the eye. Successful treatment of depression can cause symptoms to regress.
Symptoms of Depression? Read more about this here.
Can I have multiple sclerosis?
Sensitivity to light accompanied by blurred vision and pain when moving the eyes suggests retrobulbar neuritis. Retrobulbar neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve (optic nerve). It is often the first symptom of multiple sclerosis and should be clarified.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that causes myelin damage. Myelin is a substance that forms a protective covering around nerves and improves the transmission of nerve impulses. If the myelin sheaths are damaged, the impulses can no longer be passed on correctly and functional failures such as paralysis occur. Permanent damage to the optic nerve can lead to blindness.
More information on the subject multiple sclerosis you'll find here.
The diagnosis
An increased sensitivity to light that persists over a longer period of time requires medical clarification. Especially if the sensitivity to light is accompanied by pain and blurred vision, an ophthalmologist should definitely be consulted. In this case, there could be retrobulbar neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve), which an ophthalmologist can diagnose through dysregulation of the pupils. If multiple sclerosis is suspected, an MRI scan of the head should also be performed.
But inflammation of the skin of the eyes or the retina should also be clarified, as they require therapy. This is noticeable through painful, reddened eyes. An ophthalmologist can diagnose this with various eye tests and a slit lamp examination.
If you suspect an overactive or underactive thyroid, you should consult your family doctor. This can determine the concentration of thyroid hormones through a blood test.
The treatment
The treatment for increased photosensitivity depends on the underlying disease. If there is inflammation of the skin of the eye (uveitis), eye drops containing cortisone can be used. With retrobulbar neuritis, i.e. inflammation of the optic nerve, multiple sclerosis should first be ruled out, as this is treated with glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants. If the neuritis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are given. If the genesis is unclear, glucocorticoids are administered to reduce the inflammatory reaction.
The treatment of acute migraines can be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or by giving triptans. Use ß-blockers such as metoprolol or bisoprolol for the prophylaxis of a migraine attack. In the presence of depression, antidepressants can be used. Psychotherapy is also recommended.
If an imbalance in the thyroid hormones is found, this can be restored with medication. If the thyroid is underactive, L-thyroxine, the thyroid hormone, can be substituted. An overfunction can be alleviated by anti-thyroid drugs. Anti-thyroid drugs are drugs that inhibit thyroid hormone production.
A vitamin A deficiency can be remedied by taking in vitamin A. An advanced vitamin B12 deficiency with functional failures can unfortunately no longer be remedied - a substitution of vitamin B12 can prevent progression.
Also read the article: The therapy of multiple sclerosis.
The glasses as a treatment option
Glasses can be suitable for treatment of contact lens intolerance. Unfortunately, some people are very sensitive to contact lenses - the eyes are red and itchy. A change of contact lens brand can be undertaken. If this does not help either, we recommend wearing glasses.
If you suffer from inflammation of the skin of your eyes and you normally wear contact lenses, they should not be worn until they have healed. Wearing glasses is also recommended here.
The duration
The duration of the illness cannot be answered across the board. It depends on the underlying disease. Inflammation of the skin around the eyes usually heals within a few weeks. The inflammation of the optic nerve (retrobulbar neuritis) can heal within a few weeks if it is bacterial. However, if it is caused by multiple sclerosis, the disease can recur.
If the sensitivity to light is caused by an acute migraine attack, it disappears on its own after the acute phase. In the presence of a thyroid disease, it usually takes several weeks, as the optimal concentration of thyroid hormones must first be set. Even in the case of depression, it can take several weeks for the symptoms to subside, as the medication must first be applied.