Tonsillitis
Synonyms
Tonsillitis; Tonsillar angina
definition
The tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils (Tonsils). This is triggered by viruses or bacteria.
In most cases it is the pathogen "Streptococcus type A". This is mainly transmitted during the cold season by means of droplet infection.
The affected person suffers from a sore throat, fever and a general feeling of illness. The tonsils are swollen and reddened.
If purulent coatings are visible on the tonsils, an antibiotic should be prescribed. The most important differential diagnosis is glandular Pfeiffer fever.
Chronic tonsillitis can develop as a complication.In rare cases, the purulent tonsillitis leads to the development of a rheumatic fever.

Stages
- Angina catarrhalis: the tonsils are only red and swollen. There are still no deposits on it.
- Angina follicularis: so-called stipple formation occurs on the tonsils. These are small, whitish deposits.
- Angina lacunaris: the coverings enlarge and merge to form flat surfaces.
However, these stages can also merge into one another.
Illustration of tonsillitis

A - tonsillitis - Tonsilitis
B - Simple catharrhal angina -
Angina catarrhalis
C - throat findings in diphtheria
D - ulcers in bacterial
Forms of angina
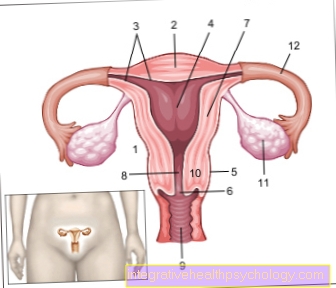
- Palatine almond bay -
Tonsillar fossa - Hard palate -
Palatum durum - Posterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatopharyngeus - Anterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatoglossus - Palatine almond -
Palatine tonsil - Back of tongue -
Dorsum linguae - Uvula + soft palate
(Soft palate) -
Uvula palatina + palatum molle - Meandering -
Isthmus faucium - Throat (back wall) -
Pharynx
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
root cause
As a causative agent of tonsillitis come on the one hand Viruses, on the other hand bacteria into consideration. Children suffer from viral tonsillitis more often, adults are more prone to bacterial tonsillitis.
The most common germ is that Type A streptococcus bacteria. This bacterium is round and prefers to line up in chains, hence the name "Streptos - twisted, arranged in a chain" and "Coconut - core". However, a number of other bacteria can also be used, e.g. Staphylococci, Haemophilus influenzae, or pneumococci.
Children are significantly more likely to be of that acute tonsillitis affected as adults as their immune system is still developing. Children can several times a year get tonsillitis.
Transmission routes
These pathogenic germs can already be found in the normal flora of the mouth and throat. If there is now a weakening of the defense situation, e.g. by stress, Cold, virus attack and Colds, so these germs can multiply in the throat and lead to the development of tonsillitis.
On the other hand, a sick person is contagious because they are in it saliva There are tons of bacteria that are distributed in the form of tiny droplets when you speak and cough. This is the principle of droplet infection.
The patient is contagious for up to two to three weeks without treatment; this can vary greatly depending on the pathogen. With an effective antibiotic If you have a bacterial tonsillitis, you are no longer contagious after one or two days.
Risk of contagion

Typically, tonsillitis is caused by the spherical bacterium Group A streptococcus triggered. These are transmitted bacteria via a so-called Droplet infection. That means the bacteria that are in Salivary and mucous secretions are located, from coughing or sneezing can be transferred to other persons. The bacteria can also first settle on the skin and then later, possibly by your own hands, come into contact with the mucous membranes, which can lead to an infection, e.g. at a Greetings with a handshake the case is. Situations where many people are in confined spaces, for example in buses or classrooms, are a high risk of infection with this type of transmission and should be strictly avoided if you have known tonsillitis.
For the same reason is also on a strict hand hygiene to pay attention. Depending on the pathogen, tonsillitis can be contagious for different lengths of time. In the case of streptococcal type A infection, the following applies 24 hours after antibiotic therapy started, the greatest number of pathogens has been killed, and the person affected no longer contagious to others. However, a certain bacterial population is still present, so the antibiotic should always be used to avoid bacterial resistance and other complications taken to an end become. Without antibiotic therapy, a Infection up to three weeks after the start of the infection to be possible.
The incubation periodThe time in which there are no typical symptoms of tonsillitis, but an infection with the bacterium has already taken place, is approximately in the case of tonsillitis two to four days. During this period, despite the lack of symptoms, one is already contagious because the bacteria are already in the saliva.
If there is a suspicion of tonsillitis, it is important to consult a doctor and, if the diagnosis of bacterial tonsillitis is confirmed, therapy with Antibiotics to begin, as this kills the bacteria and minimizes the risk of infection. Therefore, after about 24 hours after starting therapy with an antibiotic the patient with tonsillitis is usually no longer contagious.
Chronic tonsillitis represents a special form, in which there is also a risk of infection. However, the response to antibacterial therapy is not guaranteed, which is why infection can occur during therapy.
It is important to note that in the case of a present viral tonsillitis a treatment with Antibiotics don't make sense and the period in which a sick person is contagious is longer.
In order to avoid infecting others, it is essential as a sick person to follow some guidelines. Since infection occurs through droplets, one should always be Handkerchief or the Elbow at the Sneeze or cough held in front of your mouth. As often as possible, the hands should also be disinfected to avoid contamination of frequently used surfaces (door handles, railings). Rooms in which large crowds of people are in a tight space (bus, school, office) should also be avoided.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of tonsillitis are sore throats. These can be moderate to severe. The sore throat is typically bilateral, but it can also be more pronounced on one side.
The swelling of the tonsils often leads to a lumpy language. The person concerned may find speaking exhausting.
The inflammation in the throat area leads to pain and thus to swallowing difficulties, since the food has to pass precisely through the inflamed areas. The firmer and drier the food, the more difficult it is to swallow.
There is an increased flow of saliva, and the difficulty swallowing it makes it harder to swallow it.
In addition, the cervical lymph nodes swell, especially those in the corner of the jaw. This can cause a new painful swelling in the neck area, which the patient and the doctor can feel.
Read more on the topic: Swelling on the side of the neck
There is a connection between the throat and the middle ear, the so-called Tuba auditiva or Eustachian tubewhich is used to equalize pressure in the middle ear. However, as part of tonsillitis, the tube swells up, causing pressure on the ears with hearing loss and an uncomfortable stinging in the ear when swallowing. (see also: Pain when swallowing)
Fever often accompanies this. The fever is usually higher in children than in adults.
The general symptoms of illness are fatigue, pain in the limbs and headaches and a sometimes pronounced feeling of illness.
Read more on the topic: Fever, dizziness and headache
The symptoms typically last three to seven days, depending on the pathogen and immune system of the person affected.
Read more on the topic: Symptoms of tonsillitis
More signs of tonsillitis
To the typical signs of tonsillitis count primarily those local neck symptoms: are common severely reddened and swollen tonsils visible in the oral cavity that too difficulties swallowing (by the painfulness) and even in some cases too Difficulty breathing (by narrowing the transition from the mouth to the throat).
In addition, the swollen tonsils usually lead to a lumpy language as another indication.
Can stand out too Suppuration on the tonsils, mostly in the form of small stipples or even larger surface coverings, as well as a few Mucosal defects.
The optically changed almonds can also be accompanied by swollen, tender, movable lymph nodes in the neck and lower jaw area as well as one Bad breathcaused by the mostly bacterial colonization of the almonds.
Further general symptoms that may occur in parallel can be fever, headache and body aches, fatigue and tiredness.
Purulent tonsillitis
To a Accumulation of pus on tonsils in the context of tonsillitis it always occurs when bacteria are in play. pus represents a Accumulation of submerged tissue and immune cells (leukocytes) that have migrated into the inflamed area infected by bacteria and is thus a Signs of an ongoing bacterial defense reaction.
As part of a simple tonsillitis in the Initial stage (Angina catarrhalis) are the Almonds just swollen and reddened, at a Angina follicularis gets involved Pin-shaped yellowish-white pus in the furrows of the tonsils to be recorded. Is there a so-called Angina lacunaris before, can even larger pus patches stand out.
However, if the deposits are so large that they cover the entire tonsils or even go beyond the tonsils and differ in color from the classic pus coloration, various differential diagnoses should be considered, which require immediate, usually special therapy initiation (e.g. diphtheria, Angina-Plaut-Vincenti, angina agranulocytotica, Pfeiffer's glandular fever / mononucleosis)
Duration
The duration of acute tonsillitis is differently. Initially the incubation period, the time from infection to inflammation, which about 2-4 days amounts. Then symptoms become noticeable and the diagnosis of acute tonsillitis is made.
The Duration of illness total about a week or two, depends on the Type and fitness of the patient. This information applies to one under Antibiotic treatment standing tonsillitis. The duration of the illness will often perceived as shorter. That's because the symptoms sometimes subside after a few dayswhich, however, does not mean that one is healthy. Hence it is important that prescribed length of medication intake to be observed. Will the antibiotics discontinued early, the remaining pathogens and acute tonsillitis multiply breaks out again. There is also the option of Chronification. From one Duration of 3 months or complaints that occur several times in a short period of time, tonsillitis is classified as chronic. Here's some advice on one Removal of the tonsils (Tonsillectomy) advisable.
therapy

The conservative general treatment of symptoms is independent of the cause (bacterial or viral infection) and of the course and usually includes the same therapy options.
So can at the beginning of every tonsillitis first try the Relieve symptoms independently. Should the Sore throat, however, very strong persist excessively long, or other symptoms (such as Pus formation on the tonsils) should be added at the latest A doctor should be consulted (First of all, the Consultation of the family doctor, there is no need to go to an ENT doctor).
So what helps first is Throat rinses and solutions to gargle, the pain reliever and / or disinfectant ingredients and can thus fight the sore throat and support the defense against bacteria. The almonds can also be served locally with a antiseptic to be brushed (Pyktanine solution). Also help cold neck wrapsto relieve the sore throat.
Against possibly accompanying fever may use an antipyretic pain reliever such as B. Ibuprofen or Paracetamol be taken, which also combats the sore throat at the same time. In terms of nutrition, should occur in the acute stage of tonsillitis softer and cooler food can be accessed as well Avoid spicy or acidic foods so as not to additionally irritate the oropharynx. A copious fluid intake, especially in the form of pain relieving teas (sage, chamomile), can maintain the fluid balance with an existing fever and also help against the sore throat.
If one Antibiotic therapy is necessary, however, depends largely on the causative agent of tonsillitis. Since it is in the vast majority of cases it is bacteria and less often viruses are the trigger, the treating doctor usually prescribes an antibiotic.
This is a acute, uncomplicated tonsillitis around a 7-10 days of taking a penicillin (In the event of intolerance or ineffectiveness, the gift is also a 1st or 2nd generation cephalosporins or Macrolids possible). For recurring complaints or one chronic tonsillitis an extended antibiotic therapy is tried first (Amoxicillin & Clavulanic acid), in some cases it can also refer to the surgical removal of tonsils (Tonsillectomy) can be used as a last resort.
If tonsillitis is viral, there is no causal factor Treatment option. Make sure you drink enough water or tea.
Sufficient physical rest is important in order not to drag on tonsillitis and thus unnecessarily the risk of a rheumatic fever to increase!
If you have pronounced swallowing difficulties, you should initially avoid hard solid foods and switch to porridge and soups.
Strongly acidic juices and foods can irritate the almonds and should be avoided temporarily. Mouth and throat rinses with sage or chamomile tea also have a calming and disinfecting effect.
Against that fever can use antipyretic drugs like Paracetamol can be used. Household items like leg wraps can also be very helpful.
Ibuprofen is pain reliever and anti-inflammatory at the same time.
In the event of severe or persistent pain, purulent plaque, high fever or even difficulty breathing, a doctor must be consulted.
In the case of a bacterial cause - recognizable by the purulent coverings - antibiotics are prescribed. It is best known penicillin. Alternatively, cephalosporins or, if you are allergic to these two, macrolides can also be used.
It is important that antibiotic Always to take until the end of the prescription - even if the symptoms subside much faster - as bacteria still linger in the depths of the tonsils and can quickly lead to acute inflammation again.
With a one-time acute tonsillitis surgery is out of the question. However, if a patient suffers from chronic purulent tonsillitis that occurs more than three times a year, it becomes one Tonsillectomy carried out. This is the surgical removal of the tonsils by the ear, nose and throat specialist.
Also read our relevant topics:
- Treatment of tonsillitis
- Antibiotics for tonsillitis
- Tonsillitis - what works best?
Antibiotic therapy for tonsillitis

If the tonsillitis is bacterial, it can be assumed that the pathogen belongs to group A. Streptococci heard.Streptococci are spherical bacteria that occur mainly in the nose / throat area and can cause tonsillitis there, among other things. If tonsillitis is suspected, a doctor should be consulted who can confirm the disease and initiate therapy. The attending doctor will try to find out the exact reason for the occurrence of tonsillitis. The most important thing here is whether a bacterial or viral pathogen is behind the individual disease. If a viral background has been excluded, antibacterial therapy with antibiotics is initiated. The common antibiotic for an existing tonsillitis is Penicillin V. It is to be taken orally and is usually prescribed for a period of 10 to 14 days. The reason for choosing this antibiotic is that the streptococci, which in most cases are bacterial meningitis represent the cause of the disease, are almost always sensitive to this drug, so can be wiped out with it. Penicillin V is generally well tolerated, but there may be some allergies to the drug. Within the German population, about 3% suffer from such an allergy, which is noticeable by the sudden appearance of red blisters on the skin.
If there is a penicillin allergy, alternative antibiotics can be prescribed, such as Clarithromycinwhich belongs to the group of Macrolide-Antibiotics heard.
It is important to strictly adhere to the duration of therapy prescribed by the doctor. Although the risk of infection is greatly reduced after just 24 hours and the symptoms of tonsillitis get better, antibiotic therapy should always be completed. This can prevent another tonsillitis from breaking out within a few days or weeks and requiring renewed therapy.
If the antibacterial therapy is inadequate, serious complications can also arise if the tonsillitis is caused by the bacterium streptococcus. Without sufficient destruction of this bacterium it can lead to the clinical picture of rheumatic fever as well as a bacterial one Endocarditis come. Since permanent damage, such as damaged heart valves, can remain, therapy with antibiotics is essential for tonsillitis.
Chronic tonsillitis is a special form of bacterial therapy for tonsillitis. This form of tonsillitis is also caused by bacteria that can be treated with antibiotics. However, the elimination of the bacteria with antibiotics is much less successful than with acute tonsillitis. The causative bacteria in this case are mostly Haemophilus influenzae or Staphylococcus aureus. If antibiotic therapy is unsuccessful, removal of the tonsils can help.
Home remedies for tonsillitis
Most Home remedies to treat tonsillitis should the relieve associated discomfort. Proven home remedies, depending on the severity of the infection, can make the disease much more pleasant. It is important to note, however, that in the event of an infection caused by streptococci, a Seeking doctor and taking antibiotics should be. A strep infection could occur without the use of antibiotics severe complications how rheumatic fever or cause glomerulonephritis, which can be prevented with antibiotic therapy. If the symptoms do not improve in the first two days after the onset of symptoms, a doctor should also be consulted for other pathogens.
In general, the Body spared and as far as possible Bed rest observed become. Symptoms like difficulties swallowing can be relieved by lozenges, which stimulate the flow of saliva. Often so-called Neck wrap used to treat the commonly associated tonsillitis Relieve sore throat. These promote blood circulation and thus help the inflammation to heal. Serve the same purpose Scarves and shawlsthat can be worn around the neck.
Gargle solutions from certain teas can help against the pain, but also against the inflammation. Sage tea intended to be disinfectant and Camomile tea have an anti-inflammatory effect. Against fever, especially in children, calf compresses can be very effective. These cold wipes naturally help lower body temperature. Other more or less effective home remedies for fighting tonsillitis are salt water solutions for gargling, honey and Onion extract.
diagnosis
Most important for making a diagnosis are the patient's clinical complaints. The doctor will first ask about this in an anamnesis.
This is followed by the physical examination. The family doctor will Cervical lymph nodes Palpate, measure a fever, shine an ear mirror into your ears and look at the throat. He does this with the help of a wooden spatula, possibly also with a lamp and a mirror. During the examination, he can determine a fever and detect enlarged, overheated cervical lymph nodes. He will also recognize a whitish coated tongue and be able to determine whether the palatine tonsils are enlarged, reddened or coated with pus.
If there is a suspicion of a rare pathogen or in spite of one Antibiotic therapy Non-healing tonsillitis, a smear is taken from the tonsils with a swab and examined so that specific antibiotic therapy can be initiated. However, this is only necessary in the rarest of cases.
A blood test for antibodies is not required in a simple tonsillitis, but is important if one is suspected rheumatic fever.
Differential diagnoses
- Pfeiffer's glandular fever (infectious mononucleosis): Pfeiffer's glandular fever is the most common alternative diagnosis to tonsillitis. It is an infection with EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) which mainly affects young people. Since the virus is transmitted when kissing, for example, Pfeiffer's glandular fever is also known as "kissing disease". It expresses itself very similarly to a bacterial tonsillitis with sore throat, lymph node swelling, difficulty swallowing. However, the spleen and liver can also swell here and the number of white blood cells changes. The course of the disease is very variable. Some get infected and don't even notice anything about the disease - others struggle for weeks with tiredness, sore throat or stomach pain with enlarged liver or spleen (see also: swollen liver). In the worst case, the spleen can even tear, which entails surgical removal of the spleen. Therefore, if Pfeiffer's glandular fever is suspected, the abdomen may only be palpated extremely carefully and only by experienced doctors! Antipyretics (antipyretic drugs), increased fluid intake, and bed rest are recommended therapy. The use of an antibiotic is pointless, as the pathogen is a virus and these basically do not respond to antibiotics. However, bacterial colonization of the attacked almonds can occur in the further course. In this case, an antibiotic is prescribed (because it affects bacteria). It is important that ampicillin should not be administered in the case of Pfeiffer's glandular fever, as otherwise a pronounced red rash can occur all over the body!
Read more on the topic: Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Angina Plaut-Vincent: There is an infection with two different bacteria: so-called spirils and fusiform bacteria. This happens almost exclusively with poor oral hygiene. There is strong bad breath and a crater-shaped ulcer on a palatine tonsil. This is covered by pseudo-membranes. These are thin membranes that bleed when they are stripped. Thorough disinfection and an improvement in oral hygiene are usually sufficient therapy.
Complications of tonsillitis
- Chronic tonsillitis: see topic chronic tonsillitis. If acute tonsillitis is delayed, e.g. due to premature discontinuation of antibiotic therapy, chronic tonsillitis can occur. This is defined as a purulent tonsillitis lasting at least three months.
- Peritonsillar abscess: The connective tissue around a palatine tonsil becomes inflamed. A pus-filled abscess with a capsule forms. The patient feels severe pain on one side, has difficulty swallowing and has a rising fever again. Obstructed jaw opening and breathing difficulties can occur. If you look into the throat, you can see a one-sided bulging of the palate with strong reddening, the uvula is pushed to the opposite side. As treatment, an operative abscess dissection must be carried out and an antibiotic must be given at the same time. Otherwise the abscess can spread into the chest or cause thrombosis of the jugular vein! (see also: Almond abscess)
- Rheumatic fever: One to three weeks after tonsillitis caused by type A streptococci, rheumatic fever can develop. Nowadays this has become rare in industrialized nations, but it still represents a major threat in third world countries. Antibodies are formed against components of the bacterium, which are then directed against the body's own organs. This can lead to inflammation of the heart muscle, fever, joint inflammation with pain, especially in the large joints, as well as inflammation of the kidneys. In addition, children can even develop a temporary movement disorder. Heart and kidney inflammation in particular is very dangerous and can lead to scarring on heart valves and loss of kidney function. This rare clinical picture is detected by the symptoms, a throat swab for type A streptococci and the antistreptolysin titer, i.e. the antibody level, in the blood.
Read more on the topic: Rheumatic fever
- Sepsis after tonsillitis: Bacteria can invade the bloodstream from tonsillitis. The patient gets very high fever and chills. Sepsis, i.e. blood poisoning, is a life-threatening clinical picture and primarily affects patients with a weakened immune system. Therapy consists of an immediate surgical removal of the tonsils and administration of high doses of highly effective antibiotics via the vein.
Smoking with tonsillitis
Of the Smoke from a cigarette contains a large amount of substances that most Harm tissues of the body. However, this effect is particularly clear where the greatest dose of smoke occurs. Since the tonsils are in the throat, they are the smoke very exposed. If you have tonsillitis, you should therefore, in order not to aggravate the inflammation significantly, on the Refrain from smoking cigarettes or the like so that the natural healing processes of the Immune system are not hindered, since in addition to the bacterial infection, the foreign substances that are present in cigarette smoke are attacked by the immune system. It should also be noted that smoking during tonsillitis is the most common anyway Difficulty swallowing worsens can.
Even before the infection breaks out, the smoke and the substances it contains weakens the immune system, so that in the event of an infection with a few pathogens in smokers, tonsillitis may already break out, whereas the immune system of people who do not smoke might have been able to fight off the infection.
Also the consumption of chewing tobacco represents no alternative because the substances it contains also reach the mucous membrane in the affected area and significantly slow down the healing of the infection.
Since it is often not possible for many to completely abstain from nicotine, it could be considered as a substitute in the case of an existing infection, Nicotine patches to apply, which increase the nicotine level, but do not disturb the body in the fight against tonsillitis due to the harmful cigarette smoke.
The symptoms of tonsillitis, especially the Sore throat, are also evident from the tobacco smoke reinforced. Also the Throat irritation is caused by the consumption of cigarettes reinforcedwhich can cause other problems such as difficulty sleeping.
A tip for non-smokers who have tonsillitis is to stay away from places where they would be exposed to other people's cigarette smoke. Smoking bars or other places with particularly high levels of cigarette smoke in the air can also slow down the healing process for non-smokers. Parents of children with existing tonsillitis should pay particular attention to this, as tonsillitis in children should heal as quickly as possible in order to avoid an undesirable worsening of the disease and a possible accompanying hospital stay.
Tonsillitis in pregnancy
A pregnancy means a greater burden for the body and for the immune system. Because a tonsillitis often triggered by bacteria that multiply well especially when the body's own immune system is already under strain, tonsillitis during pregnancy not particularly rare. As a rule, there is no danger to the child or the mother. The Therapy, however, is a bit more complicated than with non-pregnant sufferers.
Most tonsillitis are with consistent self-therapy easy to get to grips with. In terms of medication, each intake should be discussed with the attending physician so that a Eliminate danger to the child's development to be able to.
In some cases, drug therapy is useful, as infections caused by the bacterial pathogen streptococcus can lead to complications if left untreated, which may also pose a risk to the child. Such infections can be treated with antibiotics that do not pose a threat to either the mother or the child. In any case, it is necessary to consult the attending physician and find out a suitable, individual therapy for tonsillitis.