nose
Synonyms
Olfactory bulb, olfactory organ, nasal tip, nostrils, nasal septum, bridge of the nose, nosebleeds
English: nose
definition
The nose is one of the individual characteristics of every person. Depending on
- Culture
- Age and
- gender
the nose can be long or snub-nosed, narrow or wide, delicate or hook-shaped. However, all noses have nostrils, nostrils and a nasal septum that divides the nasal cavity into two halves. From the outside, a distinction is made between the root of the nose (pyramid of the nose, nasal radix), the bridge of the nose (dorsum nasi), the tip of the nose (apex nasi) and the wings of the nose (alae nasi).

The outer nose

The nose consists of a bony and a cartilaginous part. The hard, bony part is called Root of the nose or nasal pyramid and represents a kind of foundation for the cartilaginous part of the nose sitting on it. It consists of an extension of the frontal bone (pars nasalis ossis frontalis) at the top and extensions of the Maxillary bone (Processus frontalis maxillae) and in the middle from the nasal bone (Os nasale).
The cartilaginous part of the nose is mobile and consists of triangular cartilage (Cartilago triangularis, Cartilago nasi lateralis) on both sides. It sits on the bony bridge of the nose and connects to other cartilaginous parts of the nose.
Together with the Nasal tip cartilage (Cartilago alaris major), which consists of the nasal bridge (Columelle, Crus mediale) and the nostrils (Crus laterale), is the shape of the Nostrils certainly.
The triangular cartilage also has a connection to the nasal septum (septum nasi) located in the middle of the nose.
The cartilaginous Nasal septum (Cartilago septi nasi) determines the height of the nose tip and can e.g. lead to a crooked nose. The actual shape of the nose is mainly due to the bony part, the nasal bone (os nasale). Together with the cartilaginous parts, a misshapen nasal bone can make up a humped nose or a saddle nose.
On the outside, the nose is covered with skin. As in other parts of the body, the skin has sebum glands and hair, that's why pubescent people often have ugly blackheads and in the area of the nose acne.
Figure nose
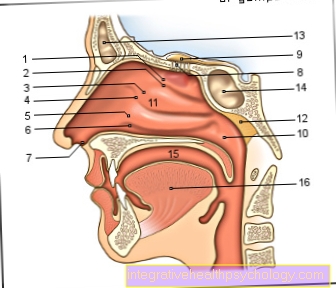
- Upper turbinate -
Concha nasi superior - Upper nasal passage -
Superior nasal meatus - Middle turbinate -
Concha nasi media - Middle nasal passage -
Meatus nasi medius - Lower turbinate -
Concha nasi inferior - Lower nasal passage -
Meatus nasi inferior - Atrium of the nasal cavity -
Nasal vestibule - Olfactory threads - Fila olfactoria
- Olfactory bulb - Olfactory bulb
- Rear opening of the
Nasal cavity - Choana - Nasal cavity - Cavitas nasi
- Pharyngeal almond -
Pharyngeal tonsil - Frontal sinus - Frontal sinus
- Sphenoid sinus -
Sphenoid sinus - Oral cavity - Cavitas oris
- Tongue - Lingua
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
The inner nose
Although all noses are very different from the outside, we always find the same structure inside the nose.
The inner part of the nose is larger than what one might think when looking at the nose from the outside. Because here you can find it Nasal cavitythat through the Nasal septum (Septum nasi) is divided into two halves.
The front part of the nasal septum consists of cartilage (Lamina quadrangularis, Cartilago septi nasi) and the rear part of non-deformable bone (Lamina perpendicularis). The bony portion in turn consists of extensions from other facial skull bones.
This is called Ethmoid bone (Os, because it is actually perforated in one place like a sieve by the olfactory nerves and the ploughshare (vomer). The main nasal cavity begins at the front with the nasal valve and ends with two adjacent openings, the Choans or also called "inner nostrils", in the throat. This causes the inhaled air to flow into the throat.
Like the outer nose, the main nasal cavity has boundaries on all sides. The roof is made up of the nasal bone (os nasale), part of the ethmoid bone (lamina cribrosa) and the body of the sphenoid bone. The bottom borders on our palate.
If we move our tongue from the back near the uvula forwards towards the incisors, we notice a transition to a hard structure. We call this hard palate (Palatum durum), which forms the lower limit of the main nasal cavity to our oral cavity.
On the side there are bony structures that consist of parts of the facial skull. Parts of the upper jaw (maxilla), the lacrimal bone (os lacrimale), the palatine bone (pallatum) and the sphenoid bone (os sphenoidale) are involved in this limitation. Here are the so-called Turbinatesthat actually look like such when viewed from the side. The turbinates serve to increase the surface area Nasal mucosa and limit the nasal passages.
On each side there are three turbinates, an upper one (Concha nasi superior), a middle one (Concha nasi media) and a lower turbinate (Concha nasi inferior).
Between them are the Nasal passages (Meatus nasi superior, medius, inferior), through which the cold inhaled air can flow.
Another important fact for the doctor is that the lower turbinate consists of an independent bone, while the overlying middle and upper turbinate consist of extensions of the ethmoid bone.
Function of the nose
A healthy nose can serve three main functions.
On the one hand, she should die Inhaled air warm up, pre-clean and moisten. We also identify numerous everyday ones Smells with our fine sense of smell. Therefore our nose also fulfills a certain sense of direction.
Pleasant smells of delicious food even stimulate our appetite and the production of Stomach acid on.
Unpleasant smells warn us e.g. from spoiled food.
Anyone who has a bad cold or who keeps both nostrils closed notices how our voice changes and becomes more “nasal”. Namely, the nose cares with its big Resonance space for a language education.
In addition, a cold for swelling of the Nasal mucosa and our sense of smell lets us down at times.
Our lung Actually only tolerates warm, moist and clean air. There is therefore a short wreath in each nostril Nose hairsthat aim to provide a rough pre-cleaning of the air and can hold back dust.
Smaller hair that we bare with eye could not recognize (ciliated epithelium) cover the entire mucous membrane of the nose and are also able to pack strokes in the direction throat execute.
Anyone who has a cold certainly knows the unpleasant situation of having a slimy throat. However, the body wants to keep the nose free for breathing and forces people to either unconsciously swallow the mucus transported into the throat, which is not a problem, or to spit it out.
In addition to dust, mucus contains many viruses and bacteria that keep our cold going, but stomach acid kills almost every pathogen.
The constantly moist mucous membrane (regio respiratoria) is located between the ciliated epithelium and humidifies the dry inhaled air. The goblet cells form the moisture film, which actually look like a simple, light drinking cup under the microscope.
The warming of the inhaled air comes about through a kind of own heating system of the nose.
This is formed by a network of very small blood vessels that are embedded directly in the nasal mucosa. As with central heating, this vascular network is regulated centrally.
In cold air, the air should be warmed up, the blood vessels are now more supplied with blood. Warm air leads to down regulation of the blood flow.
The special sense Smell to be able to fulfill the olfactory mucous membrane (Regio olfactoria). It is located near the upper turbinate, the roof of the nose and the upper part of the nasal septum. Olfactory nerves (Nn. Olfactorii) collect the information of the odor and bring it through a sieve-like structure (Lamina cribrosa) through the ethmoid to the brain. If we want to perceive a subtle smell and, for example, smell a flower, then we begin to "sniff". This slow and short drawing in of air brings a lot of flow into exactly this area in which the olfactory cells are located. If we just put our nose to the rose and inhale deeply, we would hardly be able to perceive the smell.
Diseases of the nose
sniff
The common one sniff (Rhinitis), which we all go through at least once in one of the cold seasons, is a harmless infection from you virus. Mostly it concerns viruses from the group of rhinoviruses (rhinoviruses) or adenoviruses.
Further information on this topic is available at: sniff
Sinus infection
Under one Sinusitis / sinus infection one usually understands bacterial inflammation of the sinuses.
Further information on this topic is available at: Sinus infection
Curvature of the septum
A Curvature of the septum (Septal deviation) is an alteration of the Nasal septum (septum nasi). In most cases the nasal septum is laterally displaced from birth or has been injured nose (e.g. a blow on the nose with Broken nose) moved from their normal position.
Further information on this topic is available at: Curvature of the septum
snoring
The loud breathing sounds like a good night's sleep snoring become a torture for everyone involved. The sawing noises arise in the upper airways. Swinging movements of the palate, the uvula or the base of the tongue or the deeper throat produce such sounds when snoring.
Further information on this topic is available at: snoring
Polyps
With the popularly named Nasal polyps it is swollen, bilateral enlargements (hyperplasia) of the nasal mucosa or the mucous membrane of the Sinuses.
They are called polyps because the mucous membrane enlarges like a mushroom looks like on a tree trunk.
Further information on this topic is available at: Polyps
Smelly nose
The (Ozaena) is characterized by a degeneration of the nasal mucous membrane with a loss of smell (anosmia). In the nose there are tough, smelly slime and numerous crusts and barks.
For more information, see our topic: Smelly nose
Nasal furuncle
At the Nasal furuncle a bacterial infection of a hair root (hair follicle) at the nasal entrance occurs. There is a danger if the pus produced in a nasal furuncle melts into the surrounding tissue.
Further information on this topic is available at: Nasal furuncle
Nose blocked / nose closed
Once the nose is blocked, it becomes noticeable with swollen mucous membranes, increased to excessive mucus production and the typical symptoms of a runny nose.
First and foremost, all of these signs are very useful for the body, because any pathogens that may be present can be removed more effectively from the nose with the help of the mucus.
The nose is blocked if, for example, viruses that cause respiratory infections (please refer Colds, colds), settle in the facial area, but also due to certain allergens that actually do not pose a threat to the organism, but cause a defense reaction as if they were harmful and the body should protect itself from them.
In addition, there are theories that say that even if we do not even consciously notice the process, the mucous membrane of the nose regularly swells; this procedure is quite normal for up to 80% of the population and is known as the "nasal cycle".
In response to the body's own signals, the mucous membranes on one side of the nose thicken, so that the air flow then increasingly flows through the other side. This may have the advantage that both halves of the nose could take turns in their task of cleaning the air from foreign matter.
So far, however, there is no definitive evidence for this theory. T
What to do with a stuffy nose
Despite all the advantages and protective mechanisms for the body, the breathing restriction, which in most cases is associated with a blocked nose, remains extremely unpleasant. So what can you do when your nose closes?
The first step is to think about the most likely cause of your nasal congestion. If the problem is an allergy, a thorough and detailed allergy test with a precise determination of the substances that trigger the symptom is recommended. These should then be avoided if possible or at least only be present in the environment to a lesser extent.
In addition, there are various options for allergy therapy, see also “Allergy”.
If a cold is the cause of the blocked nose, there is very little that can be done about the cause. Inhaling hot water vapor - either with special devices with a nose attachment or over a pot of hot water, which can be mixed with tea tree or chamomile oil - and humidifying the ambient air have a symptom-relieving effect.
This can be achieved very well, for example, with wet towels that are placed over the heating element.
Finally, of course, there is also the option of using special nasal sprays that are either mixed with a medicinal substance that constricts the blood vessels and therefore has a decongestant effect, a sea salt solution or something similar. A nasal rinse is also recommended for short-term, timely improvement.
You can find out more about the topic here: Swollen nasal lining
Broken nose
Another problem that is very often seen in connection with the nose is fractures of all kinds.
Due to its exposed, protruding position on the face, the nose is particularly at risk of being injured by trauma. Bumps, blows or even impact injuries after falling or falling are conceivable here.
As the nose about two thirds of bone and Rest of cartilage characteristic structures break more often. A distinction is made between fractions (Fractures) the nose open from closed Fractures of the nasal bone (Nasal bone), both of which are often associated with an injury to the nasal septum called the septum.
The term "open break“Means that parts of the bone have broken through the skin and are visible on the surface.
This means that open fractures are clear and usually easy to recognize.
At a closed fracture on the other hand, the skin can be completely uninjured on the outside or only show a small laceration or a bruise. These breaks are then also more difficult and not quite as clearly recognizable.
How do you generally recognize a fracture of the nasal bone?
As already mentioned, the diagnosis is often more difficult to confirm with certainty only externally. That said, there are a few pointers to look out for:
If one can notice external changes, there is usually one above all else Inclination of the bridge of the nose noticeable. With direct force from the front one often sees a widened, rather flat nose.
It seems to be pushed apart. In almost all cases there are also typical side effects such as Epistaxis, a bruise (Hematoma) in the affected area, pain (mostly pulsating and lasting for a long time) and severe swelling of the nose.
All of this naturally leads to a deterioration in the air supply with breathing problems and a significantly reduced ability to smell. The swelling of the surrounding tissue is often the reason why a fracture cannot be reliably assessed from the outside.
If the pain of the patient leaves it, one can also try to move the nose a little under certain circumstances. In the event of a fracture, it is much more mobile as a whole compared to an intact nose. If the Nasal septum In the following, there is an increased susceptibility to infections and inflammation in the nasopharynx, frequent nosebleeds and new snoring.
In many cases the suspected diagnosis is clear based on the course of the accident; to secure this and confirm it is still recommended X-ray image of the skull of the face. This also serves to prevent further fractures, for example of the cheekbone (please refer: Cheekbone fracture) or in the area of the jawbone.
How is a broken nose treated?
After this diagnosis, further therapy is required for the patient. In many cases one chooses one conservative Therapy, i.e. for treatment without surgical intervention.
This is always possible when individual fragments are not or only slightly displaced and can be pushed back into the correct position by the attending physician. The nose is then supplied with a plaster cast or splint and should be protected afterwards.
The further healing process then usually takes about two weeks.
In the case of severely displaced fractures or shattered bone parts, one should opt for a surgical Decide therapy. Ideally, the operation should be performed on the day of the accident and the aim is to restore the original shape and position of the bones. With quick treatment, the chances are generally pretty good that the nasal fracture will heal completely, leave no permanent damage and also no longer be visible externally after a while.
However, if the bones are not straightened again (repositioned) or if an error occurs, a so-called saddle or crooked nose can occur. This picture is seldom associated with impaired breathing, usually only a cosmetic-aesthetic problem remains. (please refer: Rhinoplasty)
The operation is usually performed through the nostrils with the assistance of a camera. In the process, a small incision on the inner wall of the nose may be necessary. All fragments are intra-operatively (during the operation) reassembled and returned to the original position. In general, the patient also needs a plaster of paris or a splint afterwards so that the nasal fracture heals without consequences.
Rinse your nose
Under one Rinsing the nose (also possible with specially developed nasal showers) one understands the introduction of large amounts of liquid, which then flows off again without delay, into the nose.
Most of the time, the aqueous liquid that is used for this is an isotonic saline solution, i.e. water to which salt has been added in the natural proportions of the body.
Nasal rinsing is used for the so-called Rhinitis, so the Inflammation of the lining of the nose With sniff and increased mucus production, but also prophylactically as a preventive measure against those symptoms as well as against sinus infections and other illnesses in the mouth, nose and throat area.
To rinse your nose you bend your head to one side and let isotonic saline solution (ready to buy or by dissolving 9gr salt in one liter of water to make yourself) flow in and out of the other nostril.
It is best to stand bent over a sink. The same procedure then follows on the other side. You should make sure that you continue to breathe through your mouth as calmly and normally as possible so that the water is not inhaled but can flow passively through it. During nasal rinsing, the inside of the nose, especially the mucous membranes in the nose, which is covered with fine hairs, should be cleaned mechanically. In addition, it is intended to stimulate the natural cleaning function and thus improve the defense against pathogens. There are several studies that have shown significant prophylactic results. However, studies are also known in which the condition of asthma patients with recurring sinus infections even worsened when using nasal rinses.