Side effects of chemotherapy for breast cancer
introduction
Chemotherapy, as used for many cancers, has many and often serious side effects due to its mode of action. However, it is often used because it helps many people with healing, pain relief, stopping tumor growth or shrinking the tumor. The side effects that occur depend on the individual patient. There are also different types of chemotherapy and the substances used.

Side effects
In high-dose chemotherapy, the mucous membranes in all parts of the body often dry out, especially in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth. Diarrhea or constipation, as well as nausea and vomiting, often occur.
At the root of the nail there are very divisive cells that are attacked by chemotherapy in some patients. Many patients therefore suffer from brittle nails, which also have white stripes, as well as longitudinal and transverse grooves. The hair is also mostly affected and the patients then suffer from hair loss.
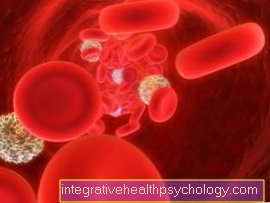
In addition, chemotherapy also results in changes in the blood count in some people. Most of the time the white blood cells change (Leukocytes) in their number. As they are essential for the functioning immune system, this blood value is strictly controlled. If the number of leukocytes (white blood cells) is too low, chemotherapy must be paused or the intervals between cycles increased. In addition to the white blood cells, the number of red blood cells (Erythrocytes) be disturbed, as these are formed in the bone marrow and the formation here is often not sufficiently guaranteed. Red blood cells are important for the transport of oxygen. If too few erythrocytes are present, one speaks of anemia or anemia. The efficiency is often greatly reduced and the patients are very tired.
Read more on the topic: Chemotherapy side effects
The tyrosine kinase inhibitors are also chemotherapeutic agents. In contrast to the classic chemotherapeutic agents, the tyrosine kinase inhibitors work in a targeted manner and thus cause fewer side effects. Read more about tyrosine kinase inhibitors and find out which cancers they can be used for at: Targeted chemotherapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Nausea and vomiting
The mucous membranes are also particularly frequently affected by the effects of chemotherapy, which is why one of the most common and unpleasant side effects of therapy is nausea and vomiting. Again, the occurrence of these side effects is not a must and varies greatly from person to person.
However, since nausea and / or vomiting significantly reduce the quality of life and the tolerability of the therapy, it is of particular importance to combat it with other drugs. In Germany, various active ingredients are offered here that can help on different levels. It is important to note that the therapy is given in good time before the administration of chemotherapy and is repeated often enough.
Hair loss
A common and very feared side effect of cancer therapy is hair loss of the scalp hair, but also of all other body hair. This does not happen in every patient on chemotherapy, and not to the same extent in everybody. Whether and how much the hair falls out depends on many different factors, such as the age of the patient, the active substance, the dose and the length of the chemotherapy.
Since the cytostatic agents used in chemotherapy damage rapidly growing tissue, the hair follicles are often attacked, which leads to the loss of existing hair. This can occur both immediately at the start of therapy and 4 weeks later. In many cases this condition is reversible upon completion of therapy. After a few months after the end of therapy, the hair grows back. It may take a few more months before they return to their original state. The loss rarely persists after therapy. Many means have been tried in the past for prevention.
The use of cold caps, which reduce the blood flow to the hair follicles and thus how far the chemotherapeutic agent reaches the hair follicle, is particularly common today.
to cough
If there is a cough while being given chemotherapy drugs, this can have various causes. On the one hand, the cough could be caused by an infection of the airways or lungs. On the other hand, certain chemotherapy agents can damage the lung tissue, which can lead to breathing difficulties and a dry cough. If a cough occurs during chemotherapy, those affected should consult their doctor.
fever
Fever is one of the body's natural defense mechanisms. The occurrence of fever should be taken seriously during chemotherapy in order to avoid possible complications and to treat them early. The administration of chemotherapeutic agents can impair the body's defense performance, which is why the patient's immune system is no longer as powerful in defending against infections as it was before. If a fever occurs, those who are currently undergoing chemotherapeutic treatment are called upon to present themselves to their doctor.
Side effects of adjuvant chemotherapy
An adjuvant (postoperative) Therapy for breast cancer means that this therapy is used after an operation. Often the tumors operated on were localized. It is recommended to have supportive chemotherapy after surgery to reduce the risk of relapse. Even after a successful operation, there is still the possibility that cancer cells can still be found somewhere in the body that can trigger a relapse, a so-called relapse. With a non-specific (i.e. widespread) chemotherapy one would like to destroy potentially remaining cancer cells.
Similar side effects occur with any chemotherapy, whether adjuvant or neoadjuvant, but they vary from person to person. During adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients, dry mucous membranes are less common.
Side effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy
In the neoadjuvant (preoperatively) Chemotherapy has basically the same side effects as with adjuvant chemotherapy. Neoadjuvant means that chemotherapy is given before an operation. In this way the tumor can be reduced in size or, in some patients, disappears completely. Here, too, the complaints are not limited to the tumor region, but affect the entire body.
Long-term effects of chemotherapy
While the acute side effects can usually be kept in check with highly effective drugs, it is not yet fully clear whether chemotherapy has long-term effects. Many cancer patients are not affected because they are of an advanced age during the illness. But this is particularly important for children and adolescents, since chemotherapy is mostly used due to its effectiveness and patients still have a long life expectancy after successful therapy.
It is believed that some cytotoxic drugs can cause secondary tumors, but only many years after the first tumor has been treated. It can also damage other organs. The organ tissue is destroyed and can severely restrict the function of the affected organ. Nerve cells are often attacked. In addition, the heart is also increasingly attacked in some patients. Premature menopause has been noted in some young women, and fertility loss has often been noted in young men.


















.jpg)