Side effects of antibiotics
introduction
Antibiotics are drugs that literally mean “against life”. As the name suggests, these are originally substances that arise in the metabolism of bacterial or fungal cultures and can kill other living things. Furthermore, growth can even be inhibited or even reproduction prevented.
Today antibiotics are mostly produced synthetically in the laboratory using various processes or obtained from genes. In a narrower sense, antibiotics are used medicinally to fight bacterial diseases caused by infections. Due to the origin of the name, one can immediately assume that this is not just about savior, but that there are also dangers and risks associated with taking an antibiotic.

This article will mainly focus on side effects of our largest organ, the skin, our joints, the psyche, the mouth and the intestines, as well as the body temperature through fever and toothache. The fact that antibiotics can spread side effects to any of these organs shows how diverse the side effects of an antibiotic and at the same time how risky such treatment can be.
However, if you always follow a few tips (e.g. always take the drug as prescribed by the doctor and do not stop taking the medication beforehand, do not exercise during the intake time and keep physical rest) then you can significantly reduce the risk of the antibiotic side effects to be.
Despite all these risks, it is important not to lump all antibiotics together, because there are more than ten different types that have different effects in the body because they have different chemical and biological effects. It is not possible to go into all the subgroups in detail here, as we are primarily concerned with the side effects.
Antibiotic side effects on the skin
The skin is the largest human organ. If you unfold it completely, it can be around 2 square meters, depending on your height and weight. In addition, symptoms of many diseases often first appear on the skin. Skin discomfort can also occur when taking antibiotics as a result of a bacterial infection.
Please also read our article on this Rash after taking antibiotics
Pimples
As mentioned above, the skin is our largest organ in terms of surface area. In addition, it serves the communication of our body with the environment and as a barrier to it. After stopping various antibiotics, some patients complain of an increased incidence of Pimples and in fact this can be a long-term consequence of antibiotic therapy.
Our skin is a very important one Excretory organ and tries to remove toxins through sweat. However, the pimples should go away after a week at the latest.
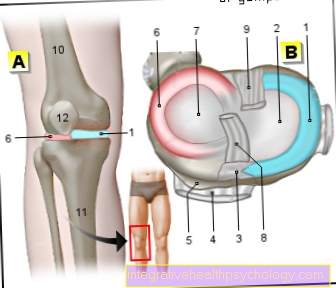
Joint pain
Another antibiotic side effect is joint pain. However, these are usually rather rare and depend on which antibiotic you are taking.
The so-called gyrase inhibitors inhibit the DNA multiplication of bacteria, which is important for their reproduction. Drugs that do this are for example Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin. These drugs cause it in tissues which not a good blood supply own, for example in Joints, changes and pain can occur. This happens through chemical changes in the connective tissue within the joint.
Adolescents and adolescents are most likely to be affected, as growing joints are particularly sensitive. In adult humans, prolonged use of antibiotics leads to one faster breakdown of the joint substance (Synovia) and can be in a arthrosis end up. The intake should therefore, if possible, only be temporary and a doctor should evaluate the risk-benefit ratio.
Antibiotic side effects on the psyche - depression
What causes and origins of depressions favored, can only be partially explained to this day. Probably an imbalance of neurotransmitters, i.e. biochemical ones, plays a role Messenger substances in the brain, a crucial role. Accompanying this are hereditary factors mostly conducive to the development of such a disease, but also difficult life situations or drastic experiences can be the cause of this illness.
The above-mentioned group of antibiotics Gyrase inhibitors, according to experience reports and package inserts, can also trigger depression. This usually subsides after stopping the antibiotic. Affected people sometimes over complain sadness and Fear of loss, up to schizophrenic and paranoid delusions. However, since it is not possible to make scientifically unambiguous statements about the exact causes of depression, it is largely unknown why such drugs can trigger depression. In some cases, suicide attempts have been reported after taking antibiotics.
Here, however, you should be familiar with the individual and their previous medical history before making a judgment about the risk of depression from antibiotics, as antibiotics alone usually do not lead to a mentally healthy person to serious depression with consequent suicidality. If you observe mood swings or other symptoms mentioned here in yourself, you should consult a doctor and report them about them.
- depression
- Test depression
Antibiotic side effects on the intestines
Antibiotics are used to fight bacteria. However, there are not only bacteria that can cause diseases, but also some that are very useful for our own body and take on important functions.
A good example of this is ours Gastrointestinal tract. There you can find so-called Lactobacteria and Bifidobacteriathat maintain the environment in our intestines and even lactose, enzymes that are important for our digestion and can produce various vitamins. In addition, they control the "harmful" bacteria as long as they have a very small ratio to the "good" lacto- or bifidobacteria.
Please also read our article on this Bacteria in the gut
In addition to the harmful bacteria, antibiotics can now also affect ours attack the body's own bacteria and thus bring our healthy inner milieu in the gastrointestinal tract into an imbalance. This is expressed quite often in stomach pain and soft stool or diarrhea.
A typical diarrheal illness in this context is the so-called Antibiotica-associated diarrhea or the pseudomembranous colitis. These clinical pictures are caused by a very stable bacterium (Clostridium difficile), which is not affected by most antibiotics. While other intestinal bacteria perish due to antibiotic therapy, Clostridium difficile gains the upper hand in the intestinal tract and can trigger that diarrheal disease.
After stopping the antibiotic, however, the normal environment should stabilize again in a relatively short time (1-3 days) so that the intestinal flora regains its old stability. Probiotic yoghurts can help here.
Antibiotic side effects on the stomach
When taking antibiotics, it is important to remember that you should take them with you a glass of water should take (not just one sip). Other liquids are less suitable here because tea or milk the absorption of the drug is hindered or even prevented by chemical interactions.
On Alcohol consumption should be used during the whole antibiotic therapy anyway waived as this can cause severe damage to the body. These chemical complexes can ultimately cause cramps or even nausea, and manifest as moderate to severe pain. However, these should go away after a few hours.
However, if that is not the cause of the symptoms, the reason is often - as in the intestine - an imbalance in the normal bacterial conditions. Here the body should always be viewed as a whole.
The stomach does not work in isolation, it receives its food through the esophagus, which is connected to the throat, and then releases the digested food to the intestines. Thus, side effects in the stomach can also affect the intestines and the flora in the entire gastrointestinal tract to bring out of balance.
Please also read our article on this Abdominal pain from antibiotics
Fungal infection in the mouth
Fungal infections of the mouth / throat associated with antibiotics usually occur when a weakened immune system is present and is therefore found either in older people or in children who have an already weakened immune system.
However, since antibiotics generally weaken the immune system, they can also occur in people with a generally good immune system as a result of prolonged antibiotic use. In technical jargon one speaks of one oral candidiasis or one Oral thrushwhich means nothing more than "fungal infection in the mouth". Characteristic are a white coating and red spotsthat have blood on them.
This results in a considerable reduction in quality of life, since eating, swallowing and drinking are all associated with pain.
The infection can even spread to the esophagus or the roof of your mouth and lips. Ultimately, a doctor can determine which fungus it is exactly and prescribe a drug against it. For this it is necessary to take swabs from the infected area and have it examined in a laboratory. Medication or Antifungal drugsUsed against this candidiasis can in turn cause damage to the eye.
Antibiotic side effects on the eye
Especially anti-infectives, i.e. drugs for the treatment of infectious diseases, including antibiotics and drugs against fungal infections (Antifungal drugs) can pose a risk to our eyes and eyesight in general. Especially with tuberculosis As a side effect, antibiotics used can damage the Optic nerve to have. These include the so-called optic neuropathy. This is one Circulatory disorder part of the optic nerve. Such a clinical picture is first of all noticeable in a disorder of color vision.
Special Antifungal drugsused against fungal infections have an increased risk of causing these symptoms. In most cases, however, after stopping the antibiotics / antifungals, an improvement is reported and the eye is able to regenerate completely.
A visit to an ophthalmologist is still recommended.
Toothache
Toothache is in most cases related to the infections in the mouth and throat. These can spread and one near a tooth annoy infested. For the sensation in the lower row of teeth the "Inferior alveolar nerve " with its branches responsible for the upper row of teeth branches of the Maxillary nerve.
If irritation occurs, see a dentist who can suggest further treatment, including an imaging test. The pain should go away relatively quickly after stopping the antibiotic (one week), but if it is too severe then pain relievers are recommended.
fever
Fever as a side effect when taking antibiotics is not uncommon. One speaks here of "drug fever" or "drug fever".
At allergic Reactions, a rise in temperature can occur relatively quickly, which can be accompanied by further symptoms. It is advisable to see a doctor as soon as possible. Fever, as a side effect of antibiotics, usually arises first after 5 to 6 days.
Especially antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins (broad spectrum antibiotics), Penicillin G, Ampicillin or Vancomycin and streptomycin are known as "feverish Drug". Certain antibiotics lead to the dissolution of the cell wall of the pathogen. A subsequent immune reaction to the released bacterial components causes the body temperature to rise.
It is often wrongly assumed that the infection is “getting worse”, which is why those affected often stop taking the antibiotic. It is advised to take the antibiotic continuously for the specified period in order to rule out other negative consequences.