External meniscus surgery
introduction
The type of surgery at a External meniscus lesion depends on both the extent of the tear and the age of the patient.
Depending on the type of tear, it can either be sewn (Meniscus suture), must be partially removed or completely removed and then replaced by a transplantation (artificial meniscus) to be replaced.
Regardless of the type of surgery, a A.rthroscopy (knee examination) carried out.

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Knee examination (arthroscopy)
The Knee examination (arthroscopy) gives the surgeon precise information about the extent of the actual damage, since even MRI images often cannot show the exact image of the lesion.
For arthroscopy, two accesses are usually made in the knee joint space. It serves an access to show the knee joint from the inside. Accordingly, the staff has one Camera and a lamp and the ability to Flushing of the knee joint to maintain the view.
The second access is used for intervention, i.e. the microsurgical operation.
The damage can now be viewed from all sides through the camera. The current stability of the knee joint is particularly important in order to decide on the surgical method.
Meniscus suture
The Meniscal refixation (meniscus suture) is the desired method for the operation of the external meniscus. The outer eniscus is fastened with high quality sutures or meniscus arrows made of absorbable materials. However, this surgical technique is only possible if the External meniscus is torn off the capsule and can be reattached there.
Especially in younger patients, refixation of the meniscus is carried out even if there are fewer tears close to the base.
In order to improve the chances of healing, the crack zone is additionally refreshed. This increases the blood flow in the area of the tear. Then the sewn meniscus heal. This requires a lot of patience and a long follow-up treatment.
Illustration of the inner meniscus / outer meniscus
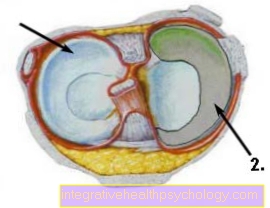
View from above of the lower leg (shin / tibia), part of the knee joint:
The menisci are crescent-shaped on the side of the knee and act as shock absorbers.
- External meniscus
- Medial meniscus
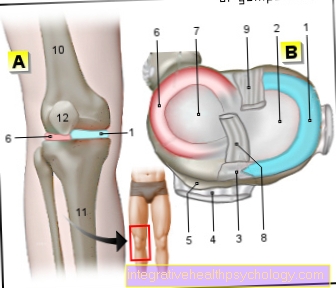
- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Inner articular knot
(Shinb.) -
Medial condyle - Transverse ligament of the knee joint -
Lig. Transversum genus - Kneecap ligament -
Ligamentum patellae - Bursa - Bursa
- Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Outer joint nodules
(Shinb.) -
Lateral condyle - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Lig. Cruciatum anterius - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligamentum cruciatum posterius - Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Kneecap - patella
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Partial meniscus removal (partial meniscus resection)
In the Outside mpartial eniskus resection the torn piece of meniscus is removed. However, since the meniscus can be removed, this surgical method (OP) is not always possible.
In addition, the sliding function of the outer meniscus in the Knee joint be lifted. this leads to Cartilage damage and one Osteoarthritis of the knee. For this reason, partial removal is only possible in the event of minor damage. After the partial removal, full weight bearing is possible on the day of the operation, depending on the pain.
Artificial external meniscus
A Meniscus replacement can either be artificial (artificial external meniscus) or directly from a human donor.
He will take the place of the distant meniscus set so that, in the best case, the body's own meniscus tissue can form anew at this point. The donor tissue is usually provided by internationally active tissue banks and was provided by deceased accident victims donated.
The exact size, side and shape of the meniscus must be determined for a successful transplant. Rejection reactions as with transplanted internal organs do not occur. Overall, a donor meniscus transplant has a good chance of success. However, the waiting times are often long, which is why in more acute cases an artificial transplant (artificial external meniscus) is selected.
The artificial meniscus tissue is made from an implant Polyurethane or Collagen.
There are no study results on synthetic meniscus implants (artificial external meniscus). The biological materials made from bovine (bovine) collagen, however, show good results.
It has been shown that within two years the bovine collagen in many patients was broken down and completely replaced by the body's own material.
In contrast to a partial removal of the meniscus, the follow-up treatment lasts for one artificial external meniscus very long. Athletes have to expect a break of several months to a year and then slow exercise.
Summary
Depends on the External meniscus lesion the surgical technique is selected.
In most cases an attempt is made to tear the external meniscus through a Meniscus suture put back together in the operating room.
This reduces the formation of a Osteoarthritis of the knee. However, in some cases meniscal suturing is not possible.
In these cases, the external meniscus is partially or completely removed in the operating room. Partial removal often leads to osteoarthritis of the knee, as the cartilage surface of the knee joint is destroyed.
For this reason, an implantation of one is popular artificial external meniscus or a donor meniscus. The results of an implantation with biological materials show good results, while no published data are yet available for the implantation of an artificial meniscus.