Colon cancer surgery - everything you need to know!
introduction
The diagnosis of colon cancer, like any other cancer, is a difficult diagnosis and demands a high level of adaptation from the person concerned. Colon cancer is the third most common cancer among men and the second most common among women. In general, when diagnosing colon cancer, surgery is seen as the treatment of choice. However, there are situations in which an operation cannot be performed. In this case, chemotherapy is attempted to reduce the extent of the disease. Irradiation is only used for the rectum, as this section has grown together with the environment, and only here is it possible to carry out the irradiation cycles with an exactly calculated alignment.

When should colon cancer be operated on?
In general, surgery is the method of choice for colon cancer if the tumor can be completely removed by surgery. This is the case if the tumor has not grown into the peritoneum over a large area. In addition, the tumor can be removed if it has not grown into large blood vessels in the abdomen. The distant metastases to other organs should also be removable, otherwise the cancer cells will spread further and the disease will not be stopped. Another requirement for colorectal cancer surgery is that the patient is generally able to operate. This means whether the patient can survive the rigors of the operation and required general anesthesia.
When should colon cancer not be operated on?
Factors that speak against colon cancer surgery are, on the one hand, the impossibility of completely removing the tumor. On the other hand, a patient should not undergo surgery if they most likely would not consider the operation. Another very important reason not to have an operation is the patient's will. If a patient who is capable of giving consent is unwilling to undergo an operation, he must not be forced to undergo the operation. This is also the case if the operation would very likely cure the patient and he certainly cannot survive without the operation.
Please also read our topic:
- Colon cancer therapy
- Stages of colon cancer and their prognosis
Procedure of the operation
Surgery for colon cancer can be performed using different approaches. The first option is open surgery, in which a large incision is made and the abdomen is held open with hooks during the operation. The second approach is laparoscopic. In this type of operation, working channels are made through several small incisions in the skin. A camera is inserted through one of these channels and the surgeon can operate with special tools through the other channels. The advantage of this method is the much smaller wounds, which have advantages in wound healing. The method chosen depends on the location and the feasibility of the laparoscopic operation.
The basic principle of the operation is the complete removal of the affected section of the intestine. Care must be taken that a certain distance from the tumor is maintained in order to ensure that no tumor tissue remains in the body. During the operation, the other abdominal organs, such as the liver, are also scanned for suspicious lumps. During the operation, lymph nodes are removed, which are then examined for cancer cells. If these are free of cancer cells, it can be assumed that they have not yet spread.
After removing the affected section of intestine, either a direct connection is made between the two ends, a so-called Anastomosis, made or an artificial anus (Anus praeter) can be created. This may have to be permanent. If the intestinal passage can be restored, this artificial exit can also be relocated back after a certain period of time.
Anus praeter - the artificial anus
An artificial anus, too stoma or Anus praeter called, may be necessary after an intestinal operation. For this purpose, the blind end of the intestine, which lies in the direction of the stomach, is connected to an opening in the abdominal skin. The other end of the intestine, which is towards the anus, is closed. In this way it is ensured that excretions reach the outside via a safe route.
The first choice for bowel surgery is a direct connection of the two bowel sections that surround the removed section. However, if this is not possible for various reasons, the artificial anus must be selected. If there are no wound healing problems and if the colon cancer can be completely removed, the artificial anus can be closed again after a certain time and the two sections of the intestine can be connected. The relocation requires a new operation in which the connection with the abdominal skin is separated again and the two blind ends of the intestine are connected to one another. However, if an intestinal passage cannot be restored after the operation, the stoma may have to remain in place forever.
Read more on this topic at: Anus prater - the artificial anus
Pain after the operation
Pain after major surgery is normal. The cuts and the normal inflammatory reaction that follows irritate nerve endings, causing pain. However, the pain should subside over time. Various methods can be used to reduce pain after surgery. These include pain pumps that deliver narcotics to the area around the spinal cord. This can be used to switch off the transmission of pain. If severe pain occurs during the healing process, this can be a sign of an infection of the intestinal suture. In this case, the operation must be repeated and the wound infection treated. However, pain can also occur due to flatulence or constipation, this also creates pressure on the intestinal suture, in order to prevent this, food intake is started very carefully after the operation.
For more information, see: Colon cancer pain
Complications of the operation
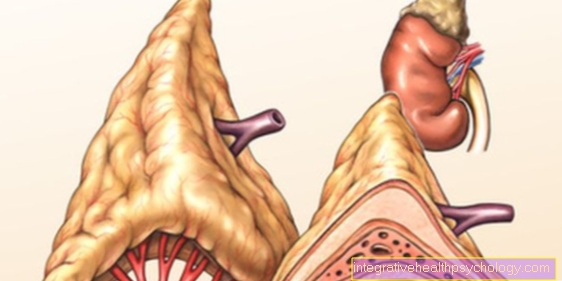
The most important complications during operations are injuries to the surrounding structures. Depending on the position of the bowel section to be operated on, different structures can be injured. These include the ureters, i.e. the connections between the kidneys and the urinary bladder, which can easily be overlooked and represent very fine structures. In addition, the spleen is at risk during operations, as it is a sensitive but very well perfused organ. If the capsule is injured, it will cause profuse bleeding. The spleen must be removed in this case. Another complication is blood vessel injury. If small blood vessels are injured, they can become obliterated. With larger blood vessels, the bleeding can reach dangerous levels.
The most important complication that only becomes noticeable after the operation is the anastomotic leak. This term means that the connection between the intestinal sections is not tight and germs can escape into the abdomen. The result is a dangerous infection. In this case, the operation must be repeated and the infected tissue removed and a new intestinal suture placed. In this case, a protective ileostomy is created to protect against further complications. This means that an artificial anus is created from the small intestine. The eliminations no longer have to pass through the problematic section.
For more information, see: Postoperative Complications - What Are There?
What scars can be expected?
The scars that remain after an intestinal operation depend on the surgical method chosen. If the operation was performed laparoscopically, usually only small scars remain. A larger incision is made in the pubic area, through which the intestine is removed from the abdomen. Accordingly, a slightly larger scar remains here. If the operation was carried out openly, a larger scar is created, which can be found in different parts of the abdominal wall depending on the area of operation.
Duration of the operation
The duration of the operation depends on the complexity of the procedure and the experience of the surgeon. The larger the tumor, the longer the procedure takes. Any complications, such as adhesions in the abdomen, also lead to the operation being extended. If problems arise during a laparoscopic procedure that require completion of the procedure, the abdomen must be opened and the operation continued using the open surgical method. This change also extends the duration of the operation. The duration of the procedure can be assumed to last a few hours. However, it is not possible to say in general how long the operation will take. It is not possible to foresee in advance all the problems that will prolong an operation.
Length of hospital stay
The operation is followed by a hospital stay, which lasts approximately 10 days to 2 weeks. The length of the stay, however, depends on how well the wounds heal and how quickly normal digestion can be restored. In the case of postoperative complications, the hospital stay can also be extended. After the operation, the food is slowly rebuilt. It starts with liquid food, such as soups, and gradually increases the firmness. It is important that food build-up takes place in the hospital, as this can also lead to complications.
You might also be interested in: Postoperative Complications - What Are There?
How long does the entire healing period take?
After removing a section of the intestine, attention must be paid to diet for a few weeks as the intestine has not yet completely healed. In the early days, diarrhea and pain after eating can often occur. It takes about a month or a little longer for the bowel to recover from the procedure. Always provided that there are no complications.
Read more about: Postoperative Complications - What Are There?
Do you need rehab afterwards?
Rehabilitation is generally recommended after major surgery. It is particularly important to regain strength when removing part of the intestine. In rehabilitation, the aim is to make those affected fit again for everyday life. After a major operation, the body is weakened and needs support in order to return to its normal performance. Rehabilitation is also particularly important for patients who have had an artificial anus.These patients need special training so that they can later take care of the anus on their own.
Also read: Anus prater - the artificial anus
OP costs
The question of the cost of colon cancer surgery cannot be answered across the board. In Germany, a coding system is used for operations in which the individual steps of an intervention are itemized. There are countless variations in colorectal cancer operations, which are assessed differently. The costs for colon cancer surgery start roughly in the four-digit range and can rise even further if there are complications or serious interventions. For those with statutory health insurance, the operation is covered by the health insurance.
How do I find a good clinic for colon cancer surgery?
When looking for a suitable clinic for colon cancer surgery, it is very important to pay attention to the expertise of the clinic. There are certified colon cancer centers in Germany that have to meet certain criteria in order to receive a certificate. One of these criteria is that a certain number of interventions must be performed. In addition, the clinics must consult interdisciplinary and with other clinics in order to find the correct treatment method for a certain type of tumor. In addition, the clinics must adhere to current guidelines for the treatment of colon cancer. In these, the current study situation is analyzed and evaluated by various bodies, which then make recommendations for correct treatment. In addition to certified colon cancer centers, university hospitals must also meet these requirements. When looking for a suitable clinic, you can also search the Internet, where you can also view the certified colon cancer centers.