Cataract surgery
introduction
The only successful treatment for cataracts at the moment is surgery. It is important to determine the underlying cause. As with all treatable sequelae of illness, an operation carried out can only bring improvement in the long term if the underlying illness is treated appropriately at the same time.
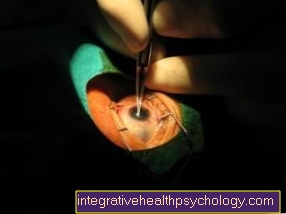
Cataract surgery is a common practice these days and is probably the most widely performed operation in the world. Years of experience have reduced serious complications to a minimal (approx. 1%) residual risk. Cataract surgery is usually performed within 20 minutes.

Various methods of treatment have been developed over time. First you can choose between so-called intracapsular and extracapsular operations distinguish.
- Both intracapsular methods becomes the whole lens with her capsule (Wrapping) away. This procedure was often used in the past. Nowadays, however, it is only carried out in rare cases when the lens capsule can no longer be obtained.
- Both extracapsular methods only the anterior lens capsule is removed. Then the contents of the lens are crushed and sucked off using ultrasound. The posterior capsule, however, is left to stand. In this way, the anterior and posterior segments of the eye (behind the lens) remain naturally separated and the complications are fewer than with the intracapsular methods.
After removing the lens, the human being is initially unable to perceive objects at close range sharply, since he lacks the refractive power of the lens.
This type of lenslessness is called Aphakia.
With the help of insertable artificial lenses it has become possible to deal with this problem. Artificial lenses have been developed that fit into eye can be used. The refractive power is previously with a Ultrasound machine calculated and compared with the other eye. Because the refractive power - differences between the two eyes must not be too big, because otherwise there will be different image sizes on the retina and that brain can no longer combine (merge) the two images.
There are three types of lenses:
- Posterior chamber lens:
This is the most popular type of lens. It is inserted into the capsular bag (in which the natural lens was previously located) and is attached there by elastic brackets. - Anterior chamber lens:
If the capsular bag is not preserved, this type of lens can be used. It is in front of the iris (iris) inserted and fixed in the chamber angle. Unfortunately, every now and then tissue changes can occur and the inside of the cornea (the corneal endothelium) can be damaged. - Iris-based lenses:
With this type of lens, the actual lens is also located in front of the iris, while the anchoring is behind the iris (iris claw lens).
Artificial lenses consist of either PMMA (Polymethylmetacrylate or also Plexiglass called) Silicone rubber or off Acrylic copolymers (mainly used for foldable lenses). The material properties have been developed in such a way that no toxic (toxic) Products are dispensed or the lenses dissolve in the aqueous humor.
At Children the cataract treatment is a little more difficult because the eyes are still in the growth and the size and refractive power are still changing. Therefore, correction with contact lenses is initially sought in children under 2 years of age.
After the age of 2, artificial lenses are usually used. But here, too, special calculations are made for refractive power and growth.
Cataract Surgery Risks
Risks during, immediately after and within the first 24 hours after surgery:
- Bleeding
- Bruise in the eye or black eye
- Gap in the cornea caused by the cut
- Infection or internal inflammation of the eyes
- Glaucoma (green star)
- Pronounced curvature of the cornea (astigmatism)
- Retinal detachment
- Rupture of the posterior capsule
A week to a month later:
- Movement of the inserted intraocular lens in the eye
Two to four months later:
- Swelling of the macular tissue (macula = place of sharpest vision on the retina)
- Secondary cataract
You might also be interested in this article: Macular edema
Operation time
The duration of a cataracts (Cataract) depends considerably on the practice of the surgeon and varies depending on the complexity of the individual case 10 and 60 minuteswith an average of 20 minutes.
First one eye is operated on and the other, if it is also affected by cataracts, is performed as a second operation some time later.
Anesthesia for a cataract
During cataract surgery, a local anesthetic is usually given as an eye drop or eye gel. An alternative is conduction anesthesia, through which the protective reflexes of the eye are switched off and the eye is completely motionless and also painless. For very nervous people, the possibility of general anesthesia should also be considered, but this puts a lot of strain on the body and is therefore Only to be chosen in extreme cases. Another method used for local anesthesia in ophthalmology is Retrobulbar anesthesia (RBA).
Here, an anesthetic injection is given to the side of the eyeball, so that freedom from pain is also achieved during the operation. A very similar variant is that Parabular anesthesia (PBA) but using a shorter needle.
Laser surgery
The infrared femtosecond laser has been used in laser correction for ametropia of the eye since 2004.
For cataract operations, the laser procedure today means that the operation can be carried out without a manual incision by a surgeon, which further lowers the complication rate.
The operation is now much easier to plan thanks to image-based computer control. This increases the accuracy and predictability of the outcome of the intervention.
At a glance:
- standardized, precise laser cuts
- Perfect opening of the lens capsule (capsulorhexis) and thus perfect fit of the new lens
- 40% less harmful energy in the eye
- more accurate results
- fewer human sources of error through computer control
- possible reduction / compensation of a corneal curvature (astigmatism)
- significantly fewer complications and side effects
Surgery costs
The standard operation is completely taken over in Germany as a checkout service, with one foldable intraOkulare L.ins (IOL) is inserted into the eye.
In addition, additional options or alternative surgical methods are available, which are associated with additional costs for the patient.
For example, the Femto cataract Laser treatment for barely € 1,000 per eye to choose from, in which the operation is performed using laser beams.
There are also various additional options that can be purchased to optimize the lens. This ranges from improved color vision to replacing glasses and costs between € 1,000 and € 2,000.
Follow-up treatment for cataract surgery includes several follow-up examinations over the next three months. These are carried out on an outpatient basis by established ophthalmologists and billed through their practices. In total, costs between € 150 and € 200 can be expected.
Surgery on both eyes at the same time
are both eyes of cataracts affected, the operation of the worse affected eye is always started.
Follow-up care then takes several weeks and approx six to eight weeks one can speak of a healing of the treated eye. The procedure on the second eye can generally take place a few days after the first operation. However, there is a recommendation to schedule the operations at least a week to a month apart. This makes it possible to observe any complications that may arise after the first operation in order to take this into account for the second operation and, if necessary, to counteract them prophylactically.
However, if the decision for a procedure is also made Multifocal lenses, the second surgery should take place in less than a week. This is to avoid that the difference between the two eyes becomes too big and the adaptation to the new visual conditions can take place with less complications.
Follow-up treatment and duration of healing
After the procedure, the treated eye is given a slightly thicker one Ointment bandage covered and the patient remains in the monitoring room for a certain time to make sure that his circulation is stable and that no other side effects occur.
If that is the case, he can already follow a few hours be released back home, but should of course come back for regular check-ups.
It is not possible to drive a car immediately after the cataract operation, but the patient can still eat and drink as usual on the day of the operation and medication can also be taken as usual (however, the doctor should be informed of the medication and its dosage.) In diabetics and patients with High blood pressure medication the topic of medication should be discussed before the operation.
As long as the ointment bandage is on the eye and the eye has not yet completely healed, care should be taken when washing and showering and that the area does not come into contact with soap. Also sports, such as. Swimming, should be paused and physical exertion, which make you sweat more, should be avoided. In front dust one should also protect the eye.
Reading and watching TV is usually possible again after just over a week. Since the eyesight has changed, it is necessary to have new glasses fitted. This can be done about four to six weeks after the operation, when the eye has healed completely and is used to the new lens.
Complications and side effects
Cataract surgery is one of the safest and -with 7,000 interventions per year in Germany alone- the most frequently performed routine operations worldwide and the side effects and complications are extremely low.
97 to 99 percent of all cataract operations carried out are completely uncomplicated. However, like any surgical intervention, the procedure generally involves some risks.
For example, the posterior wall of the capsule may tear during surgery.
Behind the lens is the glass body in the human eye, which consists of a gel-like, transparent liquid and fills almost the entire eye.
It presses with its mass on the retina at the back of the eye and keeps it pressed tightly to its base. If some of the vitreous fluid escapes when the capsule ruptures, the vitreous body loses volume and can no longer press the retina properly. The retina may become detached from the ground, which is called retinal detachment.
The risk of a capsule rupture with an intracapsular cataract extraction is around six to eight percent, while the capsule almost never occurs with extracapsular cataract extractions.
Also very rare, but theoretically possible, is the penetration of bacteria into the interior of the eye, where they can lead to inflammation (Endophthalmitis). In the worst case, if the inflammation is not treated, the affected eye can even go blind.
During the procedure, there may also be an increase in pressure inside the eye, which leads to small blood vessels in the back of the eye bursting.
The escaping blood can be in the eye (intraocular) as well as in the lens capsule (intracapsular) accumulate. However, with a probability of less than 1%, this complication is extremely rare.
For this reason, it is extremely rare that macular edema develops. This creates an accumulation of fluid in the area of sharpest vision, the "yellow spot", which can lead to considerable visual problems.
As a result of the incision in the cornea and its subsequent healing, the cornea may be more curved for some time after the operation than before.
However, this usually grows together again within a few weeks.
However, if there is a severe deterioration in vision, unusually severe redness, or even severe pain after the operation, it is imperative to see an ophthalmologist as it is an ophthalmological emergency.
A widespread consequence of the cataract surgery is the so-called "after cataract" (also known as Secondary cataract designated).
Depending on the surgical method, it occurs in around 20 to 30 percent of patients.
Younger people are usually more affected than older people.
Here, the rear parts of the lens capsule still remaining in the eye become cloudy and, like the actual cataract before, worsen vision.
However, the removal of this clouding is very simple: with the help of a laser or another surgical procedure, the lens capsule parts are removed quickly and without risk and vision is restored immediately.
Related topics
More information on cataracts:
- Main subject of cataracts
- Lens Opacity, Cataracts - You Should Know That!
- Cataracts: symptoms
- Cataracts: causes
- Cataracts: treatment
Further information that may be of interest to you:
- Green Star
- Ophthalmology
- eye
- diopter
A list of all the topics related to ophthalmology that we have already published can be found at:
- Ophthalmology A-Z













.jpg)