Operation of knock knees
introduction
Knock knees are called genu valgum in medical terminology. This is an abnormal leg axis. The knees stand too tight together while the feet due to foot misalignments too far be apart. In addition to the foot malpositions, there are also frequent Vitamin deficiencies and especially Calcium deficiency responsible for the knock knees. Untreated knock knees can lead to consequential damage to the hip and knee joint. Due to the failure, it comes to faster wear of the cartilage surfaces, which can result in considerable discomfort in the joints. That is why it is usually from a young age Axis deviation of more than 20 degrees Corrective surgery is recommended by an orthopedic surgeon in order to avoid subsequent damage.

Surgery for knock knees
Surgery is particularly indicated if the Misalignment of the legs already in childhood pronounced and as a result there is severe impairment in everyday life and in sports. The Leg axis correction The goal of the knock-knees is to straighten the legs and thus also possible subsequent complications such as increasing wear and tear early arthrosis to prevent. Symptoms may not appear at first and appear at a very late stage. A complete replacement of the knee joint only takes place at a very advanced stage. Nevertheless, the patient should be made aware before an operation that the follow-up treatment requires a lot of patience and that the subsequent stress must first be significantly reduced.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Corrective osteotomy
The surgery is often in general anesthetic carried out. In some cases, a Local anesthesia be enough. In addition, the operation induces an emptying of blood. To do this, a cuff that can be inflated is attached high up on the thigh, which stops the blood supply for a certain period of time. This makes the operation easier for the doctors because they have a better view of the surgical area. In the case of knock knees, the correction is made on the thigh bone near the knee.
Since with knock knees the outer joint surfaces are stressed too much, one tries to straighten this overload and rather towards it If one to steer. This process is also known by doctors as a varus osteotomy.
There are two ways to correct the leg axis. Either a wedge is removed from the affected bone or machined in to achieve the desired degree of angle. Most of the time, the decision is made to remove a bone wedge. In order to gain access to the thigh bone, an incision must be made on the outside. The size of the cut is about 5-8 cm. First, a Arthroscopy carried out. This is a reflection of the knee joint. In particular, the joint surfaces are examined. Since the outer joint surfaces of knock knees are more heavily loaded, the cartilage is already very frayed there.
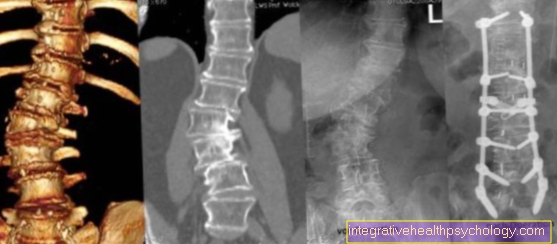
During arthroscopy, special devices can be used to remove excess and frayed cartilage and the first signs of wear and tear. This is followed by the so-called "unfolding" of the thigh bone. For this purpose, a wedge-shaped piece of bone is removed so that the tip of the wedge points to the inside of the thigh is removed, can be filled, in this case one speaks of a closed-wedge osteotomy. If, on the other hand, the gap remains open, one speaks of one open-wedge osteotomy. With the latter, the gap is gradually filled with newly formed bone material. This method is particularly suitable for younger patients in whom bone growth has not yet stopped. With both options, the leg is finally fixed in an exactly straight position using plates and screws. The individual surgical steps are carried out X-rays controlled and precisely documented.
Complications
Like most operations, the Corrective osteotomy some risks with knock knees. Typical complications that can arise include Secondary bleeding, Bruising and Infections. Furthermore, nerves on the thigh can be injured Signs of paralysis or Sensory disturbances may result. Similar damage can result from the Blood congestion arise. Furthermore, the success of the operation is not guaranteed. The bone healing may not meet the desired requirements. In addition, it is possible that inflammation occurs due to the attached plates and screws, or that the patient with a allergic reaction reacts to the material used. In a preliminary talk, the patient or the parents of a child should be informed about possible risks.
Aftercare
Follow-up treatment in the hospital takes about 4-5 days. The patient can then be discharged if there are no complications. In the first 2-3 weeks, the patient should take good care of the operated leg and maximum load with a weight of 20kg. Therefore he is given forearm crutches to walk. The material used today to fix the bones is a very angularly stable plate system. Therefore, depending on the healing process, full exposure may be possible after 3 weeks.
To that Knee joint and being able to put weight on the leg at an early stage, the patient receives a targeted one at an early stage physiotherapy. This also speeds up the healing process. Subsequent to the healing, slightly stressful sports such as cycling or swimming can be performed.
forecast
How well a correction of the deformity heals depends on many factors. The age and size of the knock knees play an important role. In general, people with a corrected deformity have an increased risk of a arthrosis to develop. Nevertheless, studies have shown that most patients are symptom-free for more than 10 years after an operation and do not need a knee joint prosthesis.
Epiphysodesis in Children
The term "Odese" means one stiffening in the knee reclining streak. This surgical technique offers another way of correcting the knock knees. Since it is a variant that aims to straighten the leg axis through the body's own bone structure, this technique is used only in children possible, whose long tubular bones still have a distinct growth plate.
To correct knock knees, a small incision is made on the inside of the Knee joint carried out. Then a small plate (eight-plate) is attached to the inner area of the growth plate with two screws. It prevents the bones from growing further on this side, while the outer side of the growth plate can continue to grow normally.This straightens the angular deviation of the leg.
Aftercare
In-patient treatment in the hospital does not last longer than 3-4 days in most cases. Subsequently, the operated leg should not be fully loaded. For 14 days receives the child Forearm crutches. The course of growth is checked at regular intervals.
Means X-rays the correction of the deformity can be assessed. This is also to help ensure the timing is right to remove the plate and screws. In many children, the leg axis has straightened out enough after about a year that the plate can be removed and the bones are in the correct angular position.