Pigment disorder in the face
Synonyms in a broader senseHyper- / hypo- / depigmentation, white spot disease, vitiligo
English: pigment disorder

Symptoms
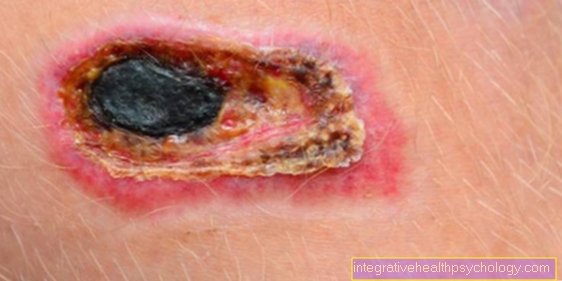
The leading symptom of Pigment disorders and Pigmentation disorders in the face consists in the too strong or too weak or completely missing color of the skinthat can affect individual areas or the entire body. Depending on the type of Pigment disorder is present, the symptoms differ significantly in terms of size, symmetry, color and / or expression.
Freckles are usually at least partially hereditary. They are small, round, sharply defined, frequently occurring brownish spots that only appear on areas of the skin that are exposed to direct sunlight. The brown color increases with increased exposure to the sun. Freckles are usually more likely to be found in younger people, and they are more likely to be found on the face, upper body and arms. Blondes or redheads with light skin are most commonly affected.
The so-called age spots (Lentigines seniles, lens spots) are also caused by an increased formation of melanin as a result of long-term exposure to light on the skin, but this does not occur until the age of 40 at the earliest. They are slightly larger and darker than freckles and are most commonly found on the back of Hand, Forearms or im face. Also Pigment disorders on the neck are widespread.

Another form of Hyperpigmentation is the melasma (Choasma). This pigment disorder is particularly common in younger women, often during pregnancy or after taking hormonal contraceptives, concerned. The appearance is brownish pigmentation, especially on the forehead, temples and cheeks, which are often symmetrically distributed over the face. The spots are also rarely found on the forearms. In contrast to the lens spots or the freckles, these are Skin changes irregularly shaped and can also flow together to form larger areas. When exposed to sunlight, the corresponding areas of the skin can become even darker.
Under Vitiligo (White spot disease) one understands a spot-shaped, complete discoloration of the skin on various parts of the body, whereby these mostly on Hands, arms, legs, face and in Genital area occurs. Now and then it happens that in this area the hair are white. As a rule, this disease begins in childhood or adolescence and often occurs in connection with other diseases (for example thyroid disease or Diabetes mellitus) on. In diagnostics, it is particularly important to differentiate white spot disease from yeast disease, as this also causes white spots on the skin, but requires a different therapy.
At the Albinism the production of melanin is either shut down or completely stopped, but the melanocytes are present. In contrast to white spot disease, the symptoms appear evenly over the whole body. Depending on the severity, those affected have lighter skin, hair and also eyes or, if the melanin is completely absent, skin that looks pink, white-blonde hair and pink eyes. Because the skin is poorly protected against UV rays due to the lack of melanin, there is an increased risk for sunburn and Skin cancer. Since the iris of the eye is also practically colorless, these patients have an increased sensitivity to light and, under certain circumstances, as a result, reduced eyesight.









.jpg)