Polymyalgia rheumatica
definition
In the Polymyalgia rheumatica it is inflammatory and, as the name suggests, rheumatic disease. It is shown by inflammation of the blood vessels, the arteries, that pump blood from the heart to the body. It occurs with a frequency of 50 affected per 100,000 inhabitants, so not that rare.
It mainly comes to Muscular pain In the area of the shoulder and pelvic girdle, as in most cases the main artery and arteries of the upper extremities are affected by the inflammation. Those affected are usually over 60 years old. It is accordingly a Disease of old age. Women are two to three times more likely to be affected than men.
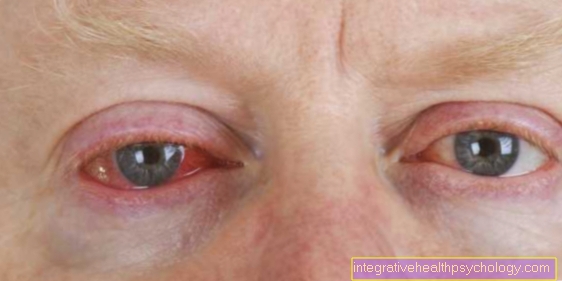
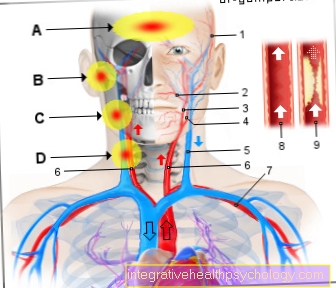
In about 50% of the cases, the polymyalgia rheumatica goes with a so-called Giant cell arteritis hand in hand. The two diseases overlap and cannot be strictly separated from one another. In the case of giant cell arteritis, so-called giant cells can be detected in the tissue examination. It usually occurs in the area supplied by the carotid artery. In around 20% of those affected by polymyalgia rheumatica, a giant cell arteritis occurs Temporal arteritis (Inflammation of the temporal artery).
Guideline
The Guideline for diagnosis and therapy of Polymyalgia rheumatica is based on scientific studies. The aim is to use guidelines to achieve the best possible treatment outcome for the patient and to standardize therapies worldwide. Unfortunately, the guideline on polymyalgia rheumatica is still being drawn up and will probably only be published in 2017. According to statements made so far, the therapeutic method commonly used in Germany will be confirmed by the guideline.
causes
A real cause some people participate in the Polymyalgia rheumatica sick and others not, has not yet been found. It is believed that predispositions to the disease are genetically inherited. It is very likely that the disease is triggered by an autoimmune process. At a Autoimmune disease cells of the immune system mistakenly attack the body's own cells.
Laboratory values
Polymyalgia is a disease that affects the people Vasculitis (Diseases associated with vascular inflammation) counts. The disease can lead to a Increase in inflammation levels come. These include, for example CRP value, the White blood cell count in the blood and the Sedimentation rate. The polymyalgia rheumatica is however no disease which is diagnosed based on the laboratory values. Only the rate of sedimentation plays a role in the diagnosis. However, a normal sedimentation rate will rule out the presence of the disease not from.
Read more about the topic here: Vasculitis - When blood vessels become inflamed
Symptoms
The leading symptom is relative severe pain in the area of the muscles of the upper half of the body, i.e. especially areas such as the shoulder, neck and also the hips are affected. The symptoms appear relatively quickly when the disease begins. It is typical of a rheumatic disease that the pain is usually at night occur. The pain is present both at rest and during exercise.
Then there is often one in the morning Stiffness of the affected parts. This makes the morning routine in the bathroom difficult for many patients. As the day progresses, the symptoms get better. Some patients also occur general disease symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, fatigue, lack of drive, weight loss and night sweats. Sometimes the disease can also be severe depressions accompanied.
If a headache in the area of the temples and visual disturbances occur at the same time, this indicates a parallel temporal arteritis. The artery can often be felt and also seen thickened.
diagnosis
Polymyalgia rheumatica is diagnosed primarily by taking blood. In the blood you can then determine that certain inflammatory parameters (CRP and ESR values) are increased. Sometimes the number of white blood cells (leukocytes) is also increased. Even if the muscles are painfully affected in polymyalgia rheumatica, it is typical for the disease that the laboratory value of creatine kinase (CK), the increase of which suggests damage to the muscles, is not increased.
A so-called rheumatoid factor can still be detected in many rheumatic diseases, but this is not the case with polymyalgia rheumatica. In addition to the laboratory results, the patient's symptoms are also groundbreaking. A confirmed diagnosis of polymyalgia rheumatica is given if at least four points are achieved from the list with the following criteria:
- Morning stiffness longer than 45 minutes (2 points)
- Rheumatoid factor and / or anti-CCP antibodies are negative (2 points)
- Pain in the pelvic girdle or limited mobility in the hip joint (1 point)
- otherwise no other joint painfully affected (1 point)
- Ultrasound detected inflammatory changes in both shoulders (1 point)
- and at least one shoulder and hip joint is affected by inflammation (1 point)
Read about this: How do you recognize rheumatism?
Furthermore, if there is a justified suspicion of illness, a therapy attempt can be started. Therapy is usually with so-called glucocorticoids, which also includes cortisone. If the pain is improved by the administration of cortisone, the diagnosis is also confirmed.
Course of polymyalgia rheumatica
The course of polymyalgia rheumatica depends on how quickly one Therapy with cortisone is initiated. If left untreated, the disease can cause discomfort for years. The symptoms can appear in episodes. Phases of illness with few or no symptoms and phases of illness with severe symptoms can alternate. If it occurs together with temporal arteritis, it remains untreated Risk of blindness. Symptoms usually appear after the start of drug treatment after a few days clearly in the background. Not to be forgotten, however, are the side effects that can occur as part of cortisone therapy. Even if this therapy is very effective, cortisone therapy can lead to numerous undesirable effects such as osteoporosis, Development of stretch marks, Developing a gray or green stars, one Diabetes mellitus, Fat distribution disorders with formation of a Full moon face or Bull's neck and immune deficiency come.
treatment
As already mentioned, therapy takes place with the administration of Glucocorticoids (cortisone). Their effect is based primarily on an anti-inflammatory effect, which reduces pain. Cortisone works very quickly, so that the pain usually improves within hours to a maximum of days. If the symptoms improve in the course of therapy, the dose of the cortisone preparation can be reduced step by step so that a dose is achieved at which there should be hardly any side effects. Under no circumstances should the dose be lowered too quickly, as the Signs of inflammation and the pain then increases again immediately.
However, if the therapy does not work immediately or if its effect diminishes, the dose must be increased again. The therapy with cortisone should be carried out over a period of two years. The long therapy is intended to reduce the risk of the disease regressing. In the past, the disease was treated with much higher doses of cortisone, so that although the disease was successfully treated, those affected then suffered from the consequences of the cortisone therapy. The side effects often led to the development of one osteoporosis. Today this usually no longer occurs due to the reduced dose.
As a preventive measure, all patients are typically given a standard prophylaxis Calcium and / or vitamin D supplements prescribed in parallel with cortisone therapy. If the therapy does not work sufficiently, it can be supportive Methotrexate should be used so that the dose of cortisone does not have to be increased excessively. Methotrexate suppresses the immune system, which is due to the presumably autoimmune component of the disease Improvement of the symptoms leads.
Dosage of cortisone
Depending on whether it is a pure polymyalgia rheumatica or a combination of polymyalgia and Temporal arteritis (also as Giant cell arteritis or Horton's disease the dose of cortisone therapy differs. If there is also temporal arteritis, it is usually a high dose of 100 mg Cortisone recommended per day. This is because in temporal arteritis the Risk of blindness consists. Such high dose cortisone shock therapy is intended to avoid this.
Read more about the topic here: Giant cell arteritis
For pure polymyalgia rheumatica, an initial dose of is usually sufficient 20-30 mg Cortisone per day. she will In the morning taken as this is the body's cortisol level the highest and the intake is therefore most physiological. Cortisone therapy usually has to be continued over a longer period of time. The goal, however, is the Reduce dose slowly over time. In polymyalgia with arteritis, the dose is reduced to 20-30 mg per day after two months at the earliest. If there is pure polymyalgia rheumatica, the dose can usually also be reduced after about two months, for example to 10-15 mg per day. The further step-by-step dose reduction then takes place. After about 6-9 months the dose can be reduced reduced to less than 7.5 mg per day become. this is the Threshold dose under which long-term cortisone therapy should lead to less serious side effects. A complete tapering (i.e. a further dose reduction until therapy is completely discontinued) is usually required tried after two years at the earliest.
Treatment - Without cortisone
Cortisone therapy is definitely the best therapy out there for that Polymyalgia rheumatica gives. Even so, many patients cannot cope with a long period of time because of the side effects Cortisone therapy befriend. Unfortunately, there is no reasonable or even remotely comparable alternative to therapy with cortisone, so that therapy with cortisone is actually unavoidable.
An alternative, although not cortisone-free, is additionally using immunosuppressants such as Methotrexate to be treated so that a lower corticosteroid therapy can be used right from the start. Unfortunately, cortisone therapy cannot be avoided, especially in the initial phase.
Homeopathic treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica
There are many homeopathic remedies that can be used to treat polymyalgia rheumatica. First and foremost is Traumeel®, a substance that is said to have an anti-inflammatory effect. Aesculus-Heel drops, Hamamelis-Homaccord drops or Arteria-Heel drops can also be used. However, the effect of homeopathic substances has not been scientifically proven. Especially when it is a question of polymyalgia with additional temporal arteritis, if left untreated, dangerous processes can occur, since the eyesight can be acutely endangered here. In any case, a doctor of conventional medicine should be consulted as soon as possible. The only proven effective therapy for polymyalgia so far is cortisone therapy.
Diet in polymyalgia rheumatica
Polymyalgia rheumatica is one Vasculitis, so one inflammatory disease of the vessels. Diet does not play an important role in the disease. Because of the treatment with Cortisone supplements however, it can make sense to take certain additional preparations. Cortisone has numerous possible side effects as part of long-term therapy. One of them is the Weakening of the bone structure with the resulting development of a osteoporosis. In order to be able to counteract this as effectively as possible, it can be useful regularly Vitamin D and Calcium supplements to take. These counteract the weakening of the bone structure, as they are actively involved in bone formation.
Read more about the topics here: osteoporosis, Vitamin D, Calcium carbonicum
Duration of polymyalgia rheumatica
As mentioned above, the duration of the episode depends on how quickly a drug therapy with cortisone is started. If left untreated, it can drag on for years. After starting cortisone therapy, the symptoms usually disappear within a few days.
forecast
The forecast the polymyalgia rheumatica is relatively good. In most cases, a low dose is sufficient Cortisone therapy over at least a year to get the inflammation under control. The therapy is then continued for another year in order to avoid a relapse.
However, even after the disease has subsided, it can come back, this can never be ruled out, because the underlying therapy disappears inflammation not entirely, just suppressed. After two years at the earliest, one should try to stop the medication and observe whether the symptoms reappear and the therapy has to be continued accordingly.
Curability of polymyalgia rheumatica
Polymyalgia can be treated very well with cortisone shock therapy. This means that the symptoms can be suppressed through longer-term drug therapy. In many patients, the symptoms no longer occur afterwards. However, there are also recurrences, i.e. a recurrence of the disease after successful treatment.
Likelihood of relapse
After successful treatment of the disease, in some cases there may be a relapse, i.e. a recurrence of the symptoms. One then speaks of a relapse. It is not clear exactly how high the recurrence rate is. In general, many patients respond very well to cortisone therapy and do not suffer a relapse.
Alcohol and polymyalgia rheumatica - are they compatible?
In general, there is no scientific evidence that alcohol increases the symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica. However, there are those affected who report that after drinking alcohol the Pain increase. It should also be remembered that cortisone therapy is necessary to treat the disease. When combining Cortisone and alcohol should be used with caution. This does not mean that it is necessary to refrain from alcohol completely, but that consumption should be significantly restricted.
Read more about the topic here: Cortisone and alcohol - are they compatible?








.jpg)