Back training
introduction
The back muscles should not be missing in a good training program for muscle building. In addition to a supporting effect on arm and leg movements, a healthy back is particularly important for good posture and an upright gait.
Back problems are the number one widespread disease in Germany and should therefore not be underestimated. With targeted muscle building training for the back, you reduce the risk of injury to the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, protect yourself from bad posture and alleviate any discomfort. Any problems should always be discussed with a doctor before starting back training.

The Back training includes training the back muscles with different objectives.
So prevents the deep Long Back extensor (M. erector spinae) when bending the upper body the "tilting forward"in the state. This muscle has the greatest expression in the field of Lumbar spine and as it progresses upwards along the spine it becomes increasingly narrow and weaker. Especially with complaints in the area of Lumbar spine Targeted back training for this muscle group is recommended.
Another big muscle in your back is that broad back muscles (M. latissimus dorsi). During back training, this muscle is responsible for pulling the body from the "top front" (lat pulldowns / pull-ups).
Of the Rhomboid muscle (M. rhomboideus) and transverse trapezius (M. trapezius) take on the function of pulling the weight towards the body from the front (rowing). These muscles are in the range of Thoracic spine.
In back training, a muscle is almost never trained in isolation. Other muscles always take on a supporting function. In back training, one always differentiates between a target muscle and the supporting muscles.
For health reasons, back training should always be combined with a Abs workout to be viewed as. Build a straight abdominal muscle and a deep, long back extensor Trunk flexors and Trunk extensor. Like biceps and triceps, they are agonists and antagonists. Imbalances in the trunk muscles are often resolved Back pain out.
Areas of application
The motives for back training are very diverse. Rehabilitation and the treatment of existing back pain are among the largest areas of application. Since a well / adequately trained muscle corset has a positive influence on the passive structures (bones and ligaments) in the trunk muscles, back training is useful for everyone.
The second spectrum of back training includes compensatory back training. In many sports there is a one-sided strain on the muscles (kickback sports, football, etc.). This favors the development of a muscular imbalance between the stomach and back muscles, but also within the muscles. Adequate back training helps to balance out this one-sided burden.
Another field is back training for aesthetic reasons. If the training takes place in an appropriate framework and scope, the same prophylactic functions are fulfilled, only the motivation for the training is different.
The back muscles
The back muscles are one of them Support and holding muscles. It is for walking upright and for lifting objects, i.e. for Everyday movements responsible.
Training this muscle group is therefore particularly important for general wellbeing.
Since the Back muscles If it is not about a single muscle, but about muscle groups, the back training should be accordingly complex. The training of the back muscles should also be therapeutic for chronic ones Back pain be performed.
Figure back muscles
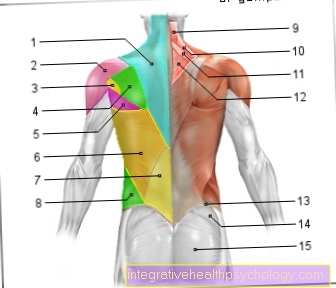
Back muscles
- Trapezius -
Trapezius muscle - Deltoid -
Deltoid muscle - Small round muscle -
Teres minor muscle - Subbone Muscle -
Infraspinatus muscle - Large round muscle -
Teres major muscle - Broad back muscle -
Latissimus dorsi muscle - Back extensor (lower lying) -
Erector spinae muscle - Outer weird
Abdominal muscles -
M. obliquus externus abdominis - Belt muscle
(second layer) -
Muscle splenius - Scapula lifter
(second layer) -
Muscle levator scapulae - Small rhomboid muscle
(second layer) -
Rhomboideus minor muscle - Large rhomboid muscle
(second layer) -
Rhomboideus major muscle - Iliac crest -
Iliac crest - Gluteus Middle -
Gluteus medius muscle - Gluteus Muscle -
Gluteus maximus muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Description of the back training
The back muscles are divided into several sections, depending on the respective function. When training the back muscles, a distinction is made between two areas of the back, the lower back muscles and the upper back muscles. Both areas should be trained equally hard.
One of the most popular back exercises for the lower back is the deadlift. In addition, the entire body is strengthened and the neck also benefits from this exercise. This exercise can mostly be done in the gym, unless you have a barbell at home. Correct execution is the alpha and omega of this exercise.
The pull-ups are ideal for building muscles in the upper back. A sturdy bar is required for this exercise. There are many possible variations of this exercise to train different areas of the upper back. Different grip types and grip widths enable varied muscle building training. Since you train with your full body weight directly with this exercise, this exercise is only possible for beginners with the help of a knee rest on the machine. A good beginner exercise, on the other hand, is pulling lat to the chest, as the back can be specifically trained in isolation and the weight can be flexibly adjusted. Another effective form of exercise for building muscle in the back is rowing. This exercise mainly trains the deeper muscles of the back and is also ideal for beginners.
As already mentioned at the beginning, back training together with abdominal muscle training has a number of health effects. In order to be able to achieve these effects, however, some basic rules must be observed when performing the procedure.
The movements during training should always be carried out functionally. This means that the execution of the movement is similar to that of a conventional, everyday movement. This can be, for example, lifting a water tank. The deadlift exercise is aimed at learning the correct, healthy lifting of objects.
Furthermore, it should be ensured that all muscle groups of the back muscles are integrated into the back training.
To avoid mistakes, some knowledge of back training is necessary. If you lack this knowledge, you should definitely seek professional advice.
Below are some exercises (only a small selection) shown. The exercises always result from the direction of movement of the respective muscles.
Read more on the topic Build back muscles
Back exercises
As already mentioned, the exercise always results from the respective movement (contraction) of the muscles.
For back training, this results in forms of movement with pulling towards the body in all possible forms and variations. This also puts strain on the arm flexor muscles (biceps).
Note:
By changing the position (e.g. Stand upright with the upper body bent forward) the stressed muscles change.
Of the Butterfly reverse leaning forward trains the upper back muscles. In the upright position, however, the becomes much stronger Shoulder muscles claimed.
The best exercises for the upper back
There are a variety of exercises for the upper back.
One is the shoulder press, standing with the dumbbells. Depending on the level of ability, the dumbbells are equipped with appropriate weight plates. The dumbbells are held in the starting position close to the body (in front of the collarbones) and held up.
The elbows point down and the forearms forward. Now both dumbbells are raised at the same time or alternately until the elbow is almost straight. At this point the movement is reversed and the dumbbell is returned to the starting position.
Seated rowing on the machine is good exercise for the broad back muscles and the back extensor. It can be trained with weight plates or arbitrarily adjustable levels of difficulty.
Rowing can also be done bent forward with a barbell or dumbbells.
The pull-up is the ultimate exercise for the upper back and the goal of many sports enthusiasts.
The body is hanging by the arms (elbows stretched) and pulled up as far as possible (elbows bent as far as possible).
Depending on how wide the grip of the hands is chosen, the biceps and back muscles are more or less involved.
Half Superman is performed on his stomach.The legs are closed and lie on the floor, the arms are stretched forward and the head rests on the floor with the forehead.
Now the upper body and arms are lifted off the floor as far as possible and held in this position for as long as possible. The head is held in line with the spine.
Then the upper body is lowered slowly and in a controlled manner to the floor, where a short break is taken before the exercise begins again.
The butterfly reverse is a training machine that trains the upper back. You sit in the machine with your chest leaning against a cushion. The arms grip two handles and are stretched forward.
Now the two training arms of the device are guided outwards by the handles with almost straight arms up to the level of the shoulder axis. The shoulders must not be pulled up.
At this point the exercise can be held briefly before slowly returning the arms to the starting position.
The diagonal stretching with dumbbells takes place in a quadruped position. The dumbbells are held in the hands and used as support handles at the beginning. Now the arms can be lifted forwards or to the side.
Depending on your preference, the legs can be stretched diagonally to increase the level of difficulty. Knees and elbows can touch each other under the body when moving back.
If this exercise is to be done with just extending the arms, a pezi ball can be added under the abdomen to increase the difficulty. The deep back muscles are increasingly involved.
The best exercises for the lower back
Bridging or the pelvic lift are particularly suitable for the lower back. Above all, the back extensor is strengthened.
The starting position is the supine position, with the legs hip-width apart. Depending on your level of ability, your arms are either placed on the floor or crossed on your chest. Now the pelvis is lifted off the floor as high as possible. At the highest point it is held briefly before it is slowly lowered again.
One leg can be lifted off the floor to increase the difficulty. In addition, the feet can be placed on a wobbly surface, such as a bosu ball (half rubber ball with a hard plate). Now the torso and especially the lower back have to do more stabilization work, which makes the training more intense. Here, too, the experienced can proceed with one leg.
The back can be stretched in a machine against weight plates or in a device with your own body weight. In both cases, the back extensor is strengthened, especially in the lumbar spine area.
For this purpose, the upper body is moved upwards with a straight spine against a weight or against gravity. The freer variant “clamped” in the device can still be modified.
To do this, the spine is rolled up vertebra by vertebra from top to bottom and then rolled out vertebra by vertebra. However, this requires previous experience, as the control of the individual muscles must first be learned.
You can also work with an additional weight when stretching your back "free". However, this is only recommended for advanced athletes, as a certain amount of strength is a basic requirement.
The deadlift is one of the supreme disciplines among the exercises for the lower back. This very complex exercise with the barbell is a very effective exercise, but can lead to injury if done incorrectly.
When standing hip-width apart, the barbell is lying on the floor. It is grasped with the spine straight and the legs bent. The entire back is straight and under tension. The shoulders are actively pulled back and down and the barbell is gripped with arms extended.
The legs and hips are now brought into extension at the same time, which lifts the barbell up close to the thigh. Only after the hips have been fully extended, the barbell is slowly brought back down to the starting position.
The tension in the shoulders (pulled back and down) is only relieved when the number of repetitions for this training set is reached or a proper execution is no longer possible. During the entire exercise, the head is always held in line with the spine.
When bending the legs, it is particularly important that the buttocks are pulled back and down so that the knees can ideally remain fixed over the ankles. Otherwise, overuse of the knee joint can occur.
1. Back training by lat pulling
The lat pull is the conventional and safe way to train the broad back muscles and shouldn't be missing in any training plan. It is used both in health sports and in professional weight training. The use of the upper arm muscle can be controlled by varying the grip width. To avoid tension in the neck muscles, the weight should be pulled to the chest. A similar back exercise would be the pull-ups.
For more detailed information on this exercise, visit our topic Lat pull
2. Back training through back isolator
The back isolator works in a manner comparable to the latissimus pull with a pulling movement towards the body. With the back insulator, however, the athlete sits upright and does not pull the weight down, but from the front to the chest. Since the athlete trains on a device with a fixed movement, the coordination requirements are low. Target muscles are the rhombus and the transverse trapezius.
For more detailed information on this exercise, visit our topic Back insulator
3. Back training through hyperextension
With the hyperextensions (overstretching) in back training, the deep, long back muscles are trained. Sedentary work and little movement make these muscles atrophy and lead to complaints in the lumbar spine. Targeted training of these muscles through hyperextension is therefore particularly important. Hyperextension should be avoided in patients with back pain in the lumbar spine. This is not possible when performing movements on the floor. Targeted equipment in the gym makes more sense.
For more detailed information on this exercise, visit our topic Hyperextension
4. Deadlift back training
In addition to hyperextension, the deadlift is another exercise for training the long, deep back muscles. This exercise is a useful exercise from health sports, as it is a good way to learn how to lift objects. However, the weight should be kept very low at the beginning and in order to learn the correct movement.
For more detailed information on this exercise, visit our topic Deadlift
5. Back training for dumbbells
For back training, in addition to exercises on a barbell or machine, there is also the option of training with a dumbbell. This type of training is very popular, as these training devices are very space-saving and can still be used very intensively and effectively. These exercises are only suitable for beginners to a limited extent, as prior experience with free weights should be available.
Free exercises are more effective than guided exercises on the machine, but the risk of injury is also slightly higher.
Dumbbell rowing is an exercise that is good for training the back. This basic exercise supports the muscle building of the back in width as well as in depth. In this exercise, the knee and lower leg of the left leg rest on a bench. The other leg is on the floor and the upper body is bent forward. The left hand supports the upper body on the bench. The right hand grabs the dumbbell and holds it on the outstretched arm. The back should be straight and in a slightly hollow back. Now the arm is pulled up slowly and in a controlled manner while exhaling. If the upper arm is parallel to the body, the dumbbell is then lowered again. Again, this is done slowly and in a controlled manner. Eight to 20 repetitions can be performed depending on the training goal. The execution of the exercise can be varied in speed and explosiveness.
When rowing with both arms bent forward, the starting position is shoulder width with the knees slightly bent. The upper body is leaning forward with the spine straight and the dumbbells are in the hands. Here, too, the shoulders are actively pulled back and down and the stomach is tensed to increase stability. Now both arms are bent as far as possible and the dumbbells are lifted upwards. The elbows and upper arms remain close to the torso and upper body. The head is in a physiological position, in extension of the spine. The tension in the shoulders is only released after the final repetition.
The dumbbell shoulder raise is another back exercise that is performed while standing. Both arms are holding a dumbbell and the body is upright with a straight back and shoulder width apart. With an extended arm, the shoulders are lifted and rotated backwards, while exhaling. Then the shoulders are lowered while inhaling.
The deadlift can be done with a barbell but also with a dumbbell. This exercise is primarily aimed at strengthening the back extensor. But the upper back and neck are also trained. This exercise is relatively complex and in the beginning this exercise should only be performed under supervision until you have a feel for how to do it correctly. Mistakes can lead to serious back problems in the long run.
Good mornings with the dumbbell are another exercise for back training. In an upright stand shoulder-width apart, with knees slightly bent, the dumbbells are held in front of the upper body. The upper body is bent to about 90 ° with the back straight. Keep your knees slightly bent. Then the upper body is straightened up again.
Another exercise is the superman / superwoman. You lie with your stomach on a mat and lift your upper body and legs. This means that the back extensor and upper back have to hold the body parts up and work. With dumbbells, the arms can now be bent and stretched alternately, which involves the shoulder muscles even more in the movement. Biceps and triceps are also innervated to a greater extent.
In addition to countless other exercises for the back, the "bent reverse flys" and "thoraric rotation" are known and often built-in exercises.
6. Back training with barbells
The deadlifts and good mornings that almost everyone knows about the back. Both exercises train the lower back muscles.
- The good mornings are an exercise that is more suitable for beginners. You stand shoulder width apart with your feet slightly rotated outwards. The legs are very slightly bent and the barbell rests on the neck muscles with or without additional weights. The hands grip the bar a little wider than shoulder width to stabilize it on the neck. Now you start to lean your upper body forward. The back must remain straight. The chest is pushed forward and the head remains in line with the spine. The upper body is lowered forward as long as the back is straight. A trainer or training partner can control this. Then the upper body is brought back to the starting position, the upright position, and the hips are slightly hyperextended.
The deadlift is considered a heavy exercise, but also a very effective one. However, if done incorrectly there is a risk of injury.
One exercise for the upper back is the bent-over row with a barbell. The starting position is the same as with the Good Mornings. However, the barbell is now lying on the floor for the time being. The upper body is leaned forward while the back remains straight. To do this, the shoulder blades are pulled together. The barbell is grasped with straight arms and brought to the stomach by bending the arms. Keep your upper body still when performing the movement.
Back training at home
If you want to save the money on expensive equipment and the gym, you can use some exercises for training the back muscles at home.
An exercise for the large back muscle (M. latissimus dorsi) is the lying lat press. The starting position is lying on your back. The upper arms lie next to the body on the floor, the forearms point straight up. The legs are bent with feet on the floor or in the air at a 90 ° angle in the knee joint. To do this, the upper arms are firmly pressed off the floor and the upper body is guided upwards. The view goes upwards so that the head is in line with the spine. The buttocks remain on the floor. The movement must come from the arms, not from the stomach. This position is held briefly and then returned to the starting position. Variations are possible in the position of the thighs in relation to the stomach. The closer the thighs are to the stomach, the more challenging the exercise becomes.
An exercise for the back extensor that can also be performed without aids is called Superman. You lie down on your stomach on the floor and stretch your arms and legs forwards or backwards. At the beginning you slowly raise your arms and legs at the same time. The range of motion is not particularly large, so the highest position is held for a few seconds. Alternatively, arms and legs can be alternately raised and lowered.
The reclining camel is an exercise that also trains the back extensor. This exercise can only be carried out with your own body weight, but also with an additional weight. The starting position is kneeling on the floor. The body is directed upright with the knees up and the gaze goes forward so that the head is in line with the spine. The knees are hip-width apart and the hands can be placed on the hips or on the chest. Now you slowly lean your upper body back so far that you can reverse the movement on your own. The movement takes place exclusively in the knee joints, the back remains straight and does not form a hollow back. This exercise should always be done slowly and in a controlled manner.
If you want to learn more about this topic or about other exercises, read: Strengthening the back muscles
Back training without equipment
Back training without equipment
For back training without equipment, all you need is a soft pad and some space around.
In the prone position, the closed legs are in an extended position and the arms are extended over the head. The view is directed down into the ground. Now the arms are raised individually or together.
Somewhat more experienced athletes can lift their upper body as far as possible. This position can be held for a few seconds and then lowered again.
The same can be done with one or both legs. In order to increase the coordination requirements, arms and legs can be raised in opposite directions, i.e. diagonally.
Other movements such as arm circles, chopping knife movements or flexion-extension changes can be incorporated. A further increase could be achieved by adding additional weights, a Theraband or gymnastic balls.
The forearm support is an exercise that is largely attributed to training the abdominal muscles. However, this exercise can also make a major contribution to a strong, healthy back. The back extensor is also heavily used in the static holding exercise and makes up a large part of the stability.
Back training for women
When it comes to back training for women, exercises that are performed with your own body weight are often chosen.
One of these exercises is hyperextension, or hyperextension of the lower back. For this exercise, there is a device in every studio in which you can stand or lie down. The feet are fixed by a bracket and the upper body is free from the hip joint. The upper body is lowered and the angle between the upper body and legs is 90 °. Now the upper body is lifted up against gravity.The hip angle of 180 ° is exceeded and a slight hyperextension is taken. The head remains in line with the spine. Then, by releasing the tension, the upper body is brought back to the starting position, hanging, and the exercise begins again.
For beginners, it is advisable to keep your arms on your upper body. Advanced athletes can put their arms forward over their heads to make the exercise more difficult.
Another exercise is the pull-ups. Women like to use "superbands" to support this back exercise. You need a bar or a horizontal bar. In the comb grip you hang from the bar and from this position you begin to pull your body upwards until you come over the bar with your chin. The core muscles are tensed to give the body stability. Then the tension is slowly given in and the body is allowed to sink back into a stretched position. Other exercises that women like to do are deadlifts and barbell rows.